Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered what amazing things are hiding out there? Let me introduce you to the California Nebula, one of space’s most interesting sights!
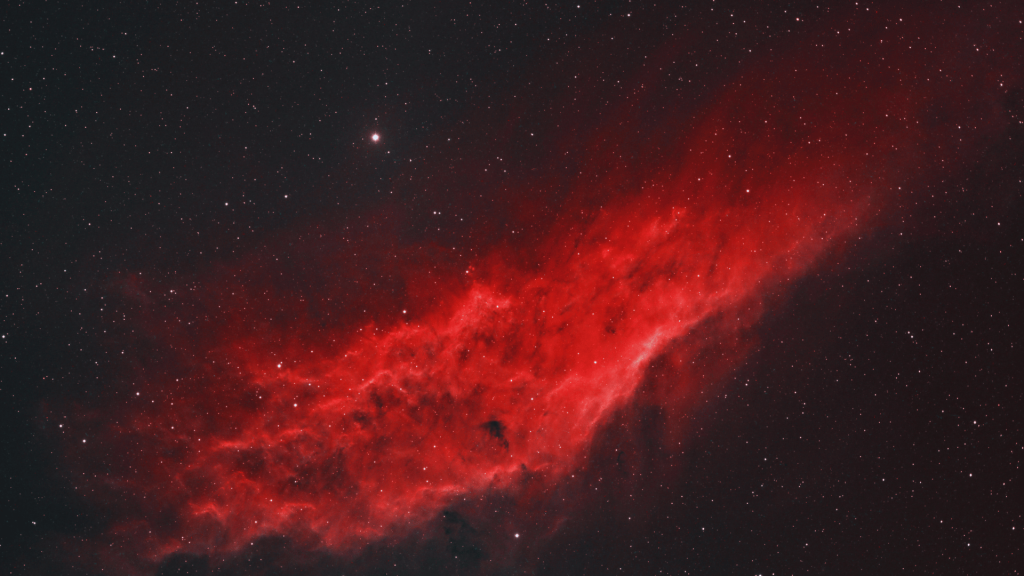
The California Nebula, also called NGC 1499, is a huge cloud of glowing gas floating in space. It got its name because it looks like the shape of California when we see it through telescopes.
What makes it special? A nearby star lights it up like a cosmic lamp, making the gas glow bright red. Astronomers love studying it to learn how stars affect the space around them.
Ready to see more cosmic wonders? Keep reading to know what makes the Nebula truly spectacular!
What is the California Nebula?
Discovered by E.E. Barnard in 1884, the Nebula is notoriously difficult to observe visually due to its low surface brightness.
The nebula is illuminated by the hot blue star Xi Persei, whose intense ultraviolet radiation ionizes the surrounding hydrogen, causing it to glow.
Astrophotographers typically use H-alpha filters and long exposures to capture its beauty. It’s best viewed during the autumn and winter months in the Northern Hemisphere.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | California Nebula (NGC 1499) |
| Type | Emission nebula |
| Constellation | Perseus |
| Distance | ~1,000 light-years |
| Size | ~100 light-years wide |
| Color | Red H-alpha emission |
| Best Viewing | Autumn–winter (Northern Hemisphere) |
A Closer Look at the California Nebula’s Physical Features
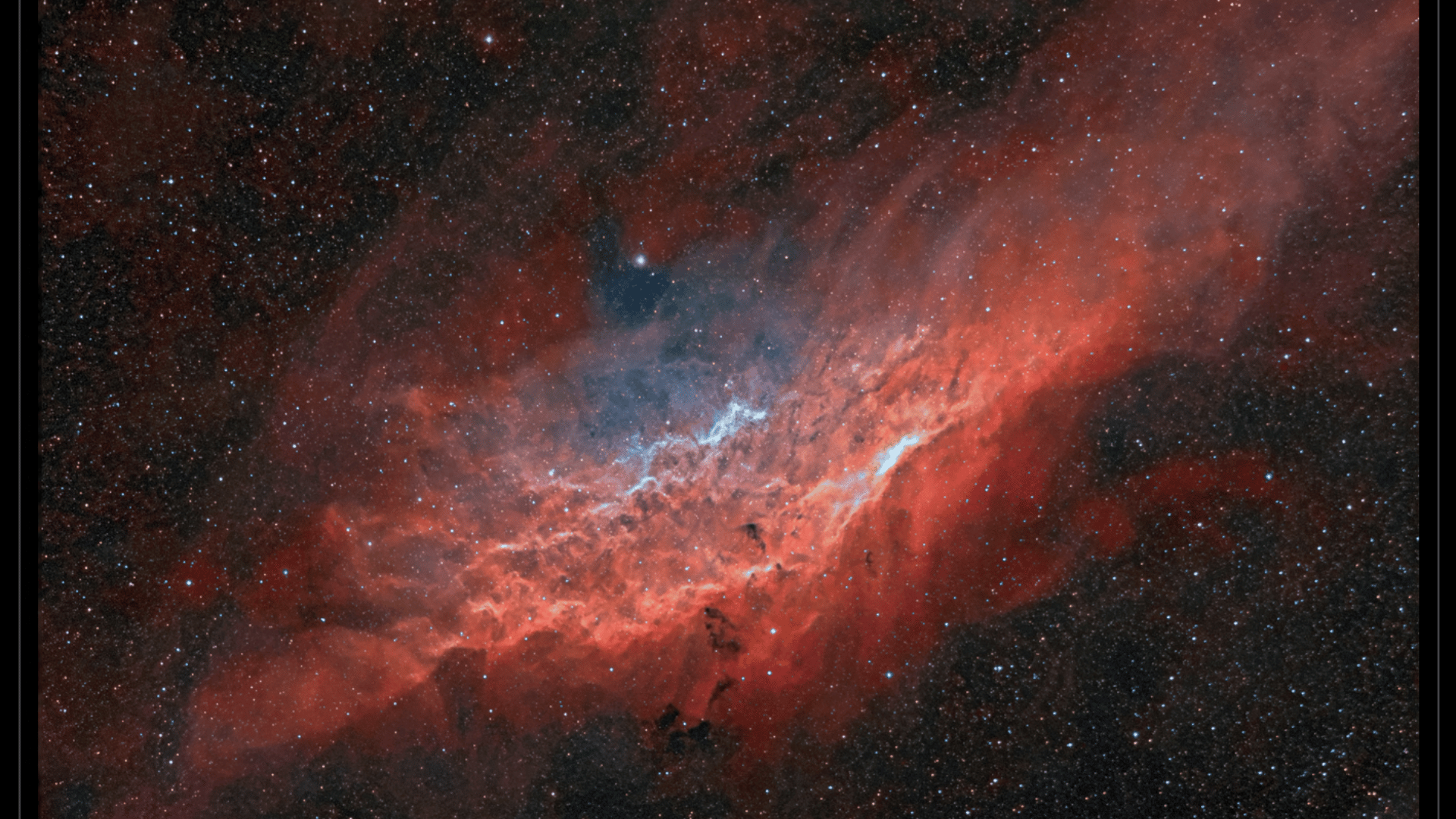
Image Source: Astro Anarchy
Understanding the nebula’s physical characteristics helps explain its formation, color, and evolution. From gas clouds to glowing dust, the nebula’s physical makeup defines its beauty and cosmic role
1. Size and Scale
The California Nebula spans approximately 100 light-years across, making it one of the largest emission nebulae visible from Earth.
To understand this scale, imagine light traveling at 186,000 miles per second, taking an entire century to cross from one end to the other.
Despite its enormous size, the nebula appears relatively faint in our sky because its light spreads over such a vast area.
Its distinctive elongated shape resembles the outline of California, which is how it earned its popular name.
2. Illuminating Star
Xi Persei, a massive O-type star, powers the California Nebula’s spectacular glow. This stellar giant is approximately 300,000 times more luminous than our Sun and burns at high temperatures.
Located at the nebula’s edge, Xi Persei emits intense ultraviolet radiation that ionizes the surrounding hydrogen gas.
The star’s powerful stellar winds and radiation pressure continually shape and energize the nebula.
Without Xi Persei’s energy, the California Nebula would remain a dark, invisible cloud of gas floating silently through space.
3. Visibility
Despite its impressive size, the Nebula is notoriously difficult to observe visually, even with large telescopes.
Its low surface brightness means the light spreads thinly across the sky, making it nearly invisible to the naked eye.
The nebula mainly emits H-alpha red light, which is hard for our eyes to detect. Astrophotographers use H-alpha filters and long exposures for the best images.
Light pollution from cities makes observation even more challenging, requiring dark-sky locations for any chance of detection.
Why the California Nebula Glows?
The California Nebula’s beautiful red glow comes from a powerful nearby star called Xi Persei. This hot, bright star acts like a giant cosmic lamp, shooting out invisible ultraviolet light into space.
When this ultraviolet light hits the hydrogen gas in the nebula, something amazing happens—a process called ionization.
The light gives energy to hydrogen atoms, exciting them like charging a battery. When these energized atoms release their energy, they produce a specific red light called H-alpha emission.
Despite this glow, the nebula is extremely difficult to see with our eyes. It spreads its light over such a huge area that it appears very dim. Our eyes also don’t detect this particular shade of red.
Photographers use special H-alpha filters and long camera exposures to capture the nebula’s beauty, revealing colors our eyes cannot see.
Scientific Significance of the California Nebula
The Nebula serves as a valuable laboratory for astronomers studying several key cosmic processes:
1. Stellar Radiation and Ionization
The nebula demonstrates how massive stars affect their surroundings. Xi Persei’s ultraviolet radiation ionizes the hydrogen gas, creating a natural experiment in stellar wind dynamics and radiation pressure. This helps scientists understand how hot stars shape the interstellar medium.
2. Interstellar Medium Structure
The nebula’s filamentary structure reveals information about magnetic fields, turbulence, and density variations in space. These patterns help astronomers understand how matter distributes itself across vast cosmic distances.
3. Star Formation Research
Emission nebulae like NGC 1499 are often associated with stellar nurseries. By studying the nebula’s composition, temperature, and density, researchers gain insights into conditions that may trigger or inhibit new star formation in molecular clouds.
4. Chemical Composition Analysis
Spectroscopic studies of the nebula reveal elemental abundances in the local interstellar medium, helping astronomers understand galactic chemical evolution and the distribution of elements created in previous generations of stars.
5. Distance Measurement Techniques
The nebula serves as a testing ground for calibrating distance measurement methods, essential for mapping our galaxy’s three-dimensional structure.
How to Observe the California Nebula?
The Nebula (NGC 1499) is a breathtaking object in the night sky, but it can be a challenge for amateur astronomers to view directly.
Its vast size and faint glow mean it requires specific conditions and techniques to appreciate.
| Equipment | Purpose/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Large Binoculars | May reveal faint haze under dark skies. |
| Wide-Field Telescope | Best for capturing the nebula’s large size. |
| Hydrogen-Alpha (Hα) Filter | Enhances contrast and reveals the nebula’s red glow. |
| Narrowband Filter | Blocks light pollution and highlights emission details. |
| Astrophotography Setup | Long exposures with DSLR/astro-camera capture vivid detail. |
Tips for Photographing the California Nebula
Capture the stunning red glow of the California Nebula with these essential tips for clear, detailed, and beautifully composed astrophotography shots.
- Use a Narrowband Filter: Capture rich detail by using H-alpha or dual-band filters to isolate the nebula’s red hydrogen glow.
- Choose Dark Skies: The California Nebula (NGC 1499) is a faint shoot from a dark-sky site with minimal light pollution.
- Long Exposures Matter: Stack multiple long exposures (3–5 minutes each) to reveal fine nebular structure and texture.
- Use a Modified DSLR or Astro Camera: Cameras sensitive to H-alpha light will pick up the nebula’s deep crimson color more effectively.
- Frame with Context: Include nearby star clusters or background Milky Way fields for dramatic composition.
- Track Accurately: Use an equatorial mount for precise tracking to prevent star trails during long exposures.
- Process Carefully: Enhance contrast and color balance in post-processing to bring out the nebula’s signature red hue.
Conclusion
The California Nebula reminds us of the amazing universe we inhabit. This glowing red cloud teaches scientists important lessons about how stars work and how they change the space.
What’s really cool is that amateur astronomers with cameras can capture pictures of this nebula from their own backyards.
The Nebula proves that beautiful and important discoveries are waiting everywhere in the night sky. Each observation helps us understand our place in this vast universe a little bit better.
Want to see the California Nebula yourself? Grab some binoculars, find a dark spot away from city lights, and start your own stargazing adventure tonight!