Looking at Mars through a telescope opens up a whole new world of details that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Many people are curious about what features they can actually spot when viewing Mars through a telescope from their backyard.
The red planet shows different details depending on the size and quality of the telescope being used.
Simple telescopes can reveal basic surface features, while larger ones show polar ice caps, dust storms, and seasonal changes.
Understanding what to expect when viewing Mars through a telescope helps stargazers prepare for this exciting experience and know what equipment works best for their needs.
What Mars Looks Like to The Naked Eye vs. A Telescope
To the naked eye, Mars appears as a small reddish-orange dot in the night sky that looks similar to a bright star.
The planet’s color comes from iron oxide on its surface, which gives it the rusty red appearance that people notice easily.
However, viewing Mars through a telescope reveals much more detail and changes the simple dot into a fascinating world.
Through even a small telescope, Mars becomes a round disk with visible surface markings that change based on the planet’s rotation.
Larger telescopes show polar ice caps, dark regions, and bright areas that represent different types of terrain.
How Mars Looks Through Different Telescopes
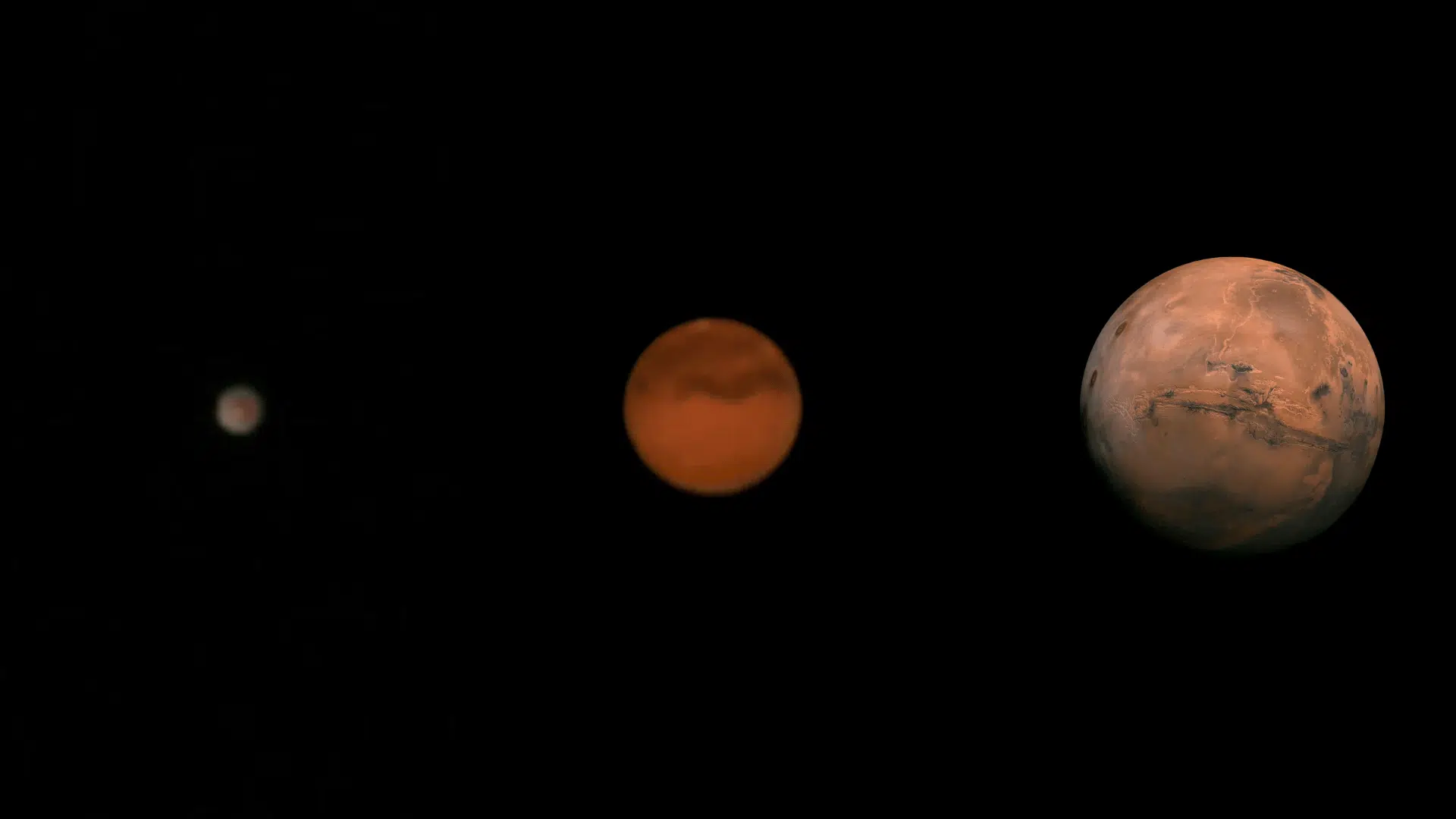

Different telescope sizes reveal varying levels of detail when viewing Mars, from basic features for beginners to advanced surface details for professionals.
| Telescope Size | What You Can See | Surface Features | Polar Caps | Dust Storms | Best Magnification | Experience Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (4-6 inch) | Basic disk shape with hints of surface markings | Faint dark and light areas | Visible during the Martian winter | Large storms only | 100-150x | Beginner |
| Medium (8-10 inch) | Clear surface features and seasonal changes | Distinct dark regions and bright deserts | Clear ice caps and seasonal changes | Most major dust storms | 200-250x | Intermediate |
| Large (12+ inch) | Fine surface details and atmospheric features | Small surface features and color variations | Detailed polar regions and melting patterns | Small local dust storms | 300-400x | Advanced |
Advanced Tools for Observing Mars
Observing Mars can become far more detailed and exciting with specialized astronomical tools. These devices help reveal colors, surface features, and movements that ordinary telescopes can’t show. Below are some key tools that make a big difference for Mars watchers:
- Red Filters: Improve contrast between light and dark regions on Mars’ surface, making features like plains and polar caps easier to see.
- Blue Filters: Highlight dust storms, clouds, and haze in Mars’ thin atmosphere.
- CCD Cameras: Capture high-quality digital images that show details invisible to the human eye.
- Computerized Telescope Mounts: Automatically track Mars as it moves across the sky, keeping it centered for longer observations or photography.
- Spectroscopy Equipment: Analyzes the composition of Mars’ surface and atmosphere, helping scientists understand its materials and weather patterns.
How Equipment Affects What You See
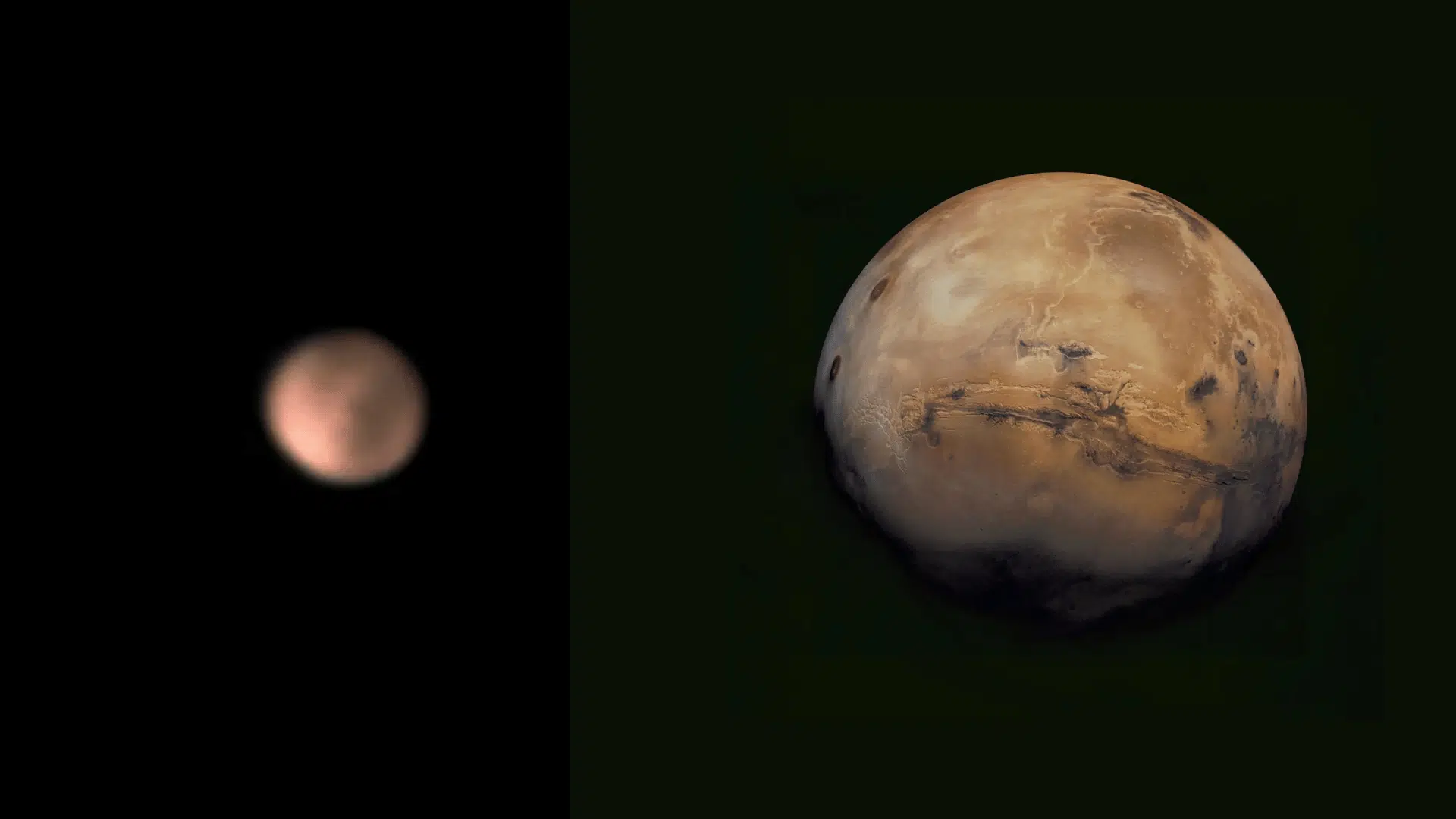

The quality and size of telescope equipment dramatically change what observers can see when viewing Mars through a telescope during observation sessions.
Larger mirrors or lenses collect more light, making faint surface features visible that smaller telescopes cannot show.
High-quality optics reduce atmospheric turbulence effects that blur planetary details, especially important for Mars observation.
Magnification must be balanced carefully – too little shows Mars as a small disk, while too much magnification makes the image dim and shaky.
Atmospheric conditions on Earth affect Mars viewing more than telescope size, with steady air producing sharp images even through modest equipment.
Mars at Opposition: The Best Time for Photos
Mars reaches opposition approximately every 26 months, providing the best opportunities for telescope observation and photography:
- July 2035: Closest approach in 15 years, excellent for small telescopes
- September 2037: High in the sky during evening hours, perfect for photography
- November 2039: Good viewing conditions for Northern Hemisphere observers
- December 2041: Mars appears largest in telescope eyepieces
- February 2044: Extended observation window with stable atmospheric conditions
- March 2046: Favorable positioning for detailed surface feature photography
- May 2048: Optimal timing for capturing polar ice cap seasonal changes
These opposition periods offer the best chances to see Mars through a telescope with maximum detail and minimum atmospheric interference affecting image quality.
Tips for Photographing Mars Through a Telescope

Image Source: NBC News
Photographing Mars through telescopes requires special techniques and equipment to capture clear images of the red planet’s surface features successfully.
- Use planetary cameras: Designed for small, bright objects rather than deep-space imaging equipment for best results.
- Take multiple short exposures: Stack them together to reduce atmospheric turbulence effects on the final images.
- Wait for steady atmospheric conditions: When stars appear sharp and twinkling is minimal, for the clearest Mars photos.
- Start with lower magnifications: frame Mars properly before switching to higher power for detailed surface shots.
- Use color filters: Enhance different surface features and bring out contrast in Martian terrain details.
- Practice focusing techniques: Before Mars viewing sessions, to quickly achieve sharp focus during optimal seeing conditions.
Conclusion
Viewing Mars through a telescope reveals a fascinating world of surface features, polar ice caps, and atmospheric changes that are not visible to the naked eye.
The size and quality of telescope equipment determine how much detail observers can see on the red planet’s surface.
From basic telescopes showing simple disk shapes to large instruments revealing fine surface features, each upgrade in equipment opens new possibilities for Mars observation.
The best viewing opportunities occur during opposition periods when Mars appears largest and brightest in Earth’s sky.
Grab your telescope tonight and start your Martian observation path.