Has someone ever thought about what the biggest star in the universe is?
To most people, the Sun feels unimaginably large, dominating our sky and powering life on Earth.
But in the grand scale of the cosmos, it’s actually an average-sized star. Some stars grow so massive that they stretch across distances so vast, the Sun would seem tiny beside them.
Astronomers have found giant stars that could swallow much of our solar system if placed at its center.
This blog takes a closer look at which star currently holds the title of the largest known, and how it compares to our familiar Sun, offering a glimpse into the awe-inspiring diversity of the stars above.
What Do Astronomers Mean by the ‘Biggest Star’
When people ask about the biggest star, they’re usually talking about size, specifically diameter, not brightness or mass.
Astronomers make clear distinctions; the star with the greatest volume isn’t always the most massive or the brightest.
Some stars are extremely dense, while others expand outward into vast, thin layers of gas called supergiants.
At the small end are white dwarfs, about the size of Earth. At the other extreme are red supergiants, which can stretch far beyond the orbit of Jupiter.
Understanding these differences helps explain why “biggest” doesn’t always mean “heaviest” or “brightest.
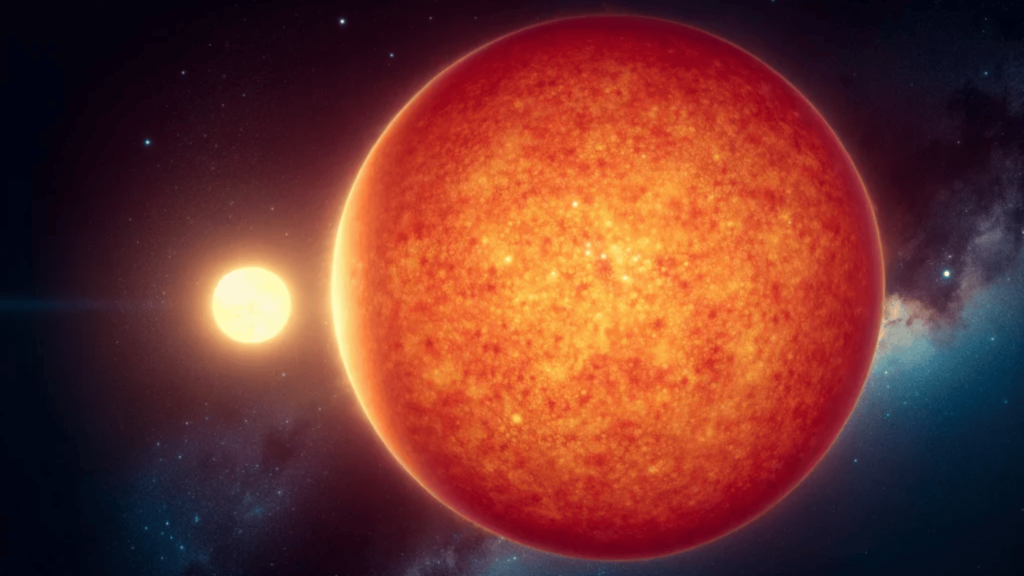
UY Scuti: Universe’s Biggest Known Star
Image Source: Space
The title of the largest known star currently belongs to UY Scuti, a red supergiant roughly 9,500 light-years away in the constellation Scutum.
This cosmic giant has a radius about 1,700 times that of the Sun. If UY Scuti sat where the Sun is, its outer edge would reach far beyond Jupiter’s orbit, engulfing Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and the asteroid belt.
UY Scuti is nearing the end of its life. Like all red supergiants, it will one day explode as a supernova, leaving behind a neutron star or black hole.
Because its outer layers constantly shift, scientists can only estimate its true size; new measurements could adjust its record in the future.
Some studies also suggest that other stars, such as Stephenson 2-18 or Westerlund 1-26, may rival or even exceed it, showing how much we still have to learn.
Comparison of the Biggest Star and the Sun
| Feature | The Sun | UY Scuti |
|---|---|---|
| Radius | ≈ 696,000 km | ≈ 1,700 × the Sun’s radius |
| Volume | 1 Sun | ≈ 5 billion Suns could fit inside |
| Visual Analogy | Basketball | Stadium-sized balloon |
| Role | Powers and sustains life on Earth; the central star of our solar system | Red supergiant, one of the largest stars ever observed |
How Massive Stars Grow and Change
Image Source: ThoughtCo
To understand why stars like UY Scuti grow so large, we need to look at how massive stars live and die.
- The biggest stars become enormous due to their evolution.
- Massive stars burn fuel extremely quickly, much faster than smaller stars.
- As they near the end of their lives, their outer layers expand, forming red supergiants.
- Their enormous size makes them unstable compared to average stars.
- They live short lives, collapsing in dramatic supernova explosions.
Biggest, Brightest, or Most Massive: What’s the Difference?
Not all stars are alike. The biggest, brightest, and most massive each hold different records, showing how size, light, and weight don’t always match in the universe.
| Category | Definition | Example Star |
|---|---|---|
| Biggest Star | Largest by radius or volume | UY Scuti |
| Brightest Star | Shines with the most luminosity (light) | Eta Carinae |
| Most Massive Star | Contains the greatest amount of matter | R136a1 |
Conclusion
Studying enormous stars like UY Scuti gives us more than numbers; it reveals how the universe builds, changes, and renews itself.
These giants shape galaxies by creating and spreading the elements that form new stars and planets.
They remind us that even short-lived stars leave lasting effects long after they fade.
Learning about them helps us see our Sun and our place in space with greater perspective.
In every massive star’s life and death, we find clues about where we came from and how the cosmos continues to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is UY Scuti the Most Massive Star as Well?
No, UY Scuti is only the largest by radius. Stars such as R136a1 are far more massive, holding records for stellar mass rather than sheer size.
How Do Astronomers Measure the Size of Stars?
They use methods such as interferometry, light analysis, and spectroscopy to estimate radius and brightness.
Are There Stars Bigger than UY Scuti that We Haven’t Found Yet?
Possibly. With advancing telescope technology and deeper space exploration, astronomers may eventually uncover even larger stars that remain hidden in distant, unexplored regions of the universe.
Why Do Some Stars Become Red Supergiants?
Massive stars expand into supergiants when they run out of hydrogen fuel and start fusing heavier elements.