Looking up at the night sky, the moon catches attention with its changing faces. Sometimes it glows bright and full. Other times, it appears as a slim crescent.
But there’s one phase that often gets overlooked, even though it holds its own special beauty and significance. It shows up after the moon has passed its full glory but before it disappears completely from view.
This particular phase marks an important turning point in the lunar cycle, and understanding it can deepen anyone’s connection to the rhythms of the night sky.
So what exactly is this mysterious phase, and why does it matter? Let’s find out.
Understanding the 8 Moon Phases of the Lunar Cycle
The moon travels through eight distinct phases each month, creating a predictable pattern that has guided humans for centuries and continues to influence our understanding of time.
- New Moon: The moon sits between Earth and the sun, making it invisible from our view. This marks the beginning of a fresh lunar cycle.
- Waxing Crescent: A thin sliver of light appears on the right side. The moon starts becoming visible again in the evening sky.
- First Quarter: Half of the moon’s face lights up. Despite its name, this phase occurs a quarter of the way through the cycle.
- Waxing Gibbous: More than half of the moon shines brightly. The illuminated portion continues growing each night until it reaches fullness.
- Full Moon: The entire face of the moon glows brilliantly. Earth sits between the sun and the moon, allowing complete illumination.
- Waning Gibbous: The light starts decreasing after the full moon. More than half remains visible, but it shrinks nightly.
- Third Quarter: Half of the moon’s face shows light again, but on the opposite side from the first quarter. This phase appears in the early morning sky
- Waning Crescent: A thin crescent appears on the left side. The moon prepares to complete its cycle and return to the new moon phase.
Third Quarter Moon in the Lunar Cycle Explained
The third quarter moon represents a specific geometric alignment in the Earth-moon-sun system.
At this point, the moon has completed roughly three-quarters of its orbit around Earth since the new moon phase began. The positioning creates a 90-degree angle, with Earth at the vertex, the moon on one side, and the sun on the other.
This configuration means sunlight strikes the moon from a particular direction, illuminating exactly half of the lunar surface visible from Earth.
The moon rises around midnight and sets near noon, making it most observable during morning hours.
The gravitational interplay between these three celestial bodies remains constant, but their changing positions create the visual effect of different phases.
This orbital dance takes approximately 29.5 days to complete, moving the moon systematically through its eight recognized phases before the cycle repeats itself.
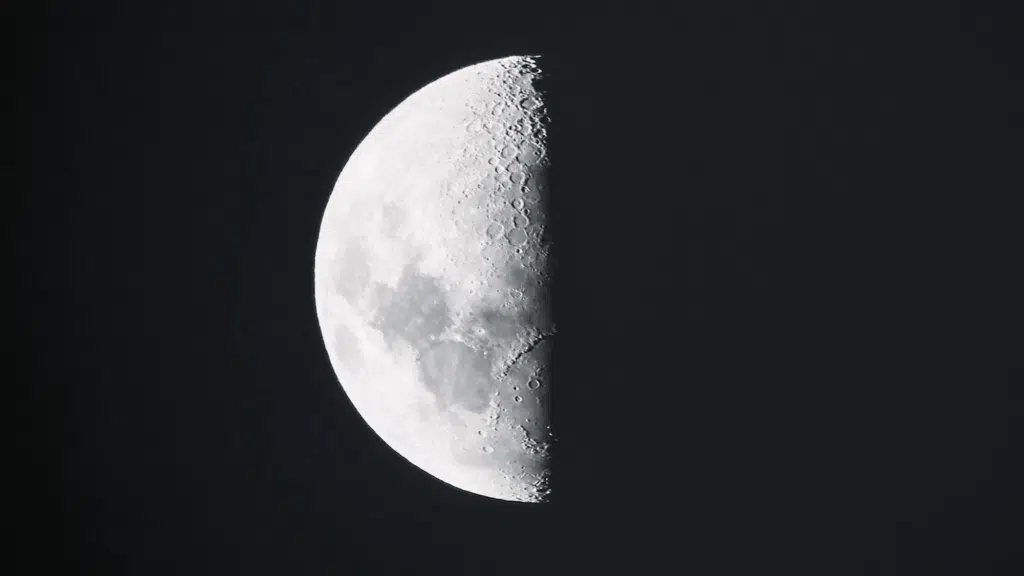
What Does the Third Quarter Moon Look Like?
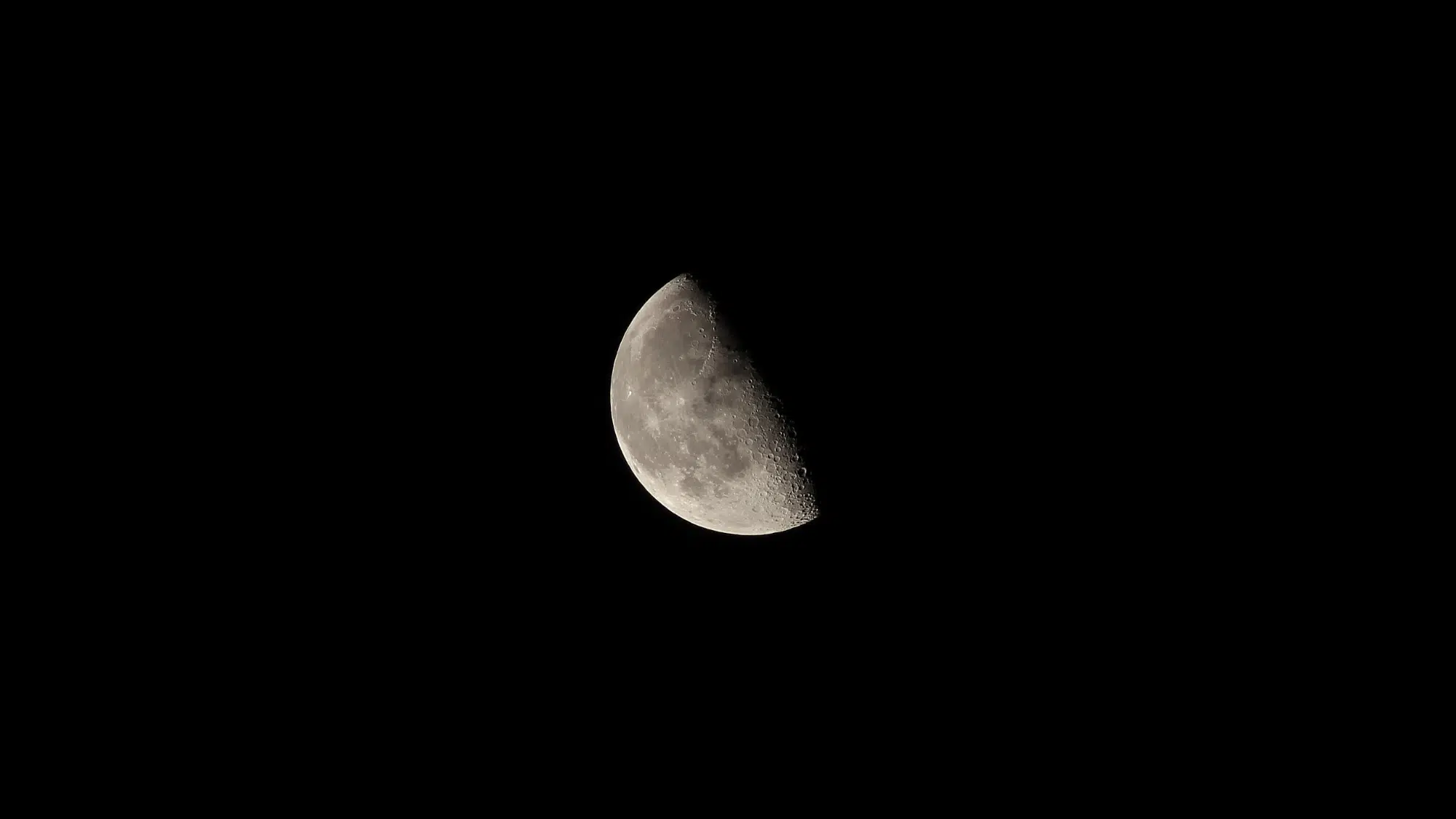

The third-quarter moon presents a striking, half-illuminated appearance in the sky.
The left side of the moon glows with reflected sunlight, while the right side remains cloaked in darkness. This creates a perfect semicircle that looks like someone sliced the moon straight down the middle.
Unlike the first quarter moon, which shows its right half lit up, the third quarter displays the opposite side. The illuminated portion resembles a backward letter D or the left half of a circle.
The contrast between light and shadow appears sharp and defined, making the moon’s cratered surface particularly visible along the terminator line where darkness meets light.
Observers can spot this phase hanging in the western sky during morning hours.
It stands out prominently against the brightening dawn, offering a beautiful sight before the sun takes over the sky completely
Third Quarter Moon vs First Quarter Moon
The third quarter and first quarter moons mirror each other in appearance but differ significantly in timing, position, and illuminated sides.
| Aspect | Third Quarter Moon | First Quarter Moon |
|---|---|---|
| Illuminated Side | The left half is lit up | The right half lit up |
| Best Viewing Time | Early morning hours | Evening after sunset |
| Sky Position | Western sky at dawn | Western sky at dusk |
| Rising Time | Around midnight | Around noon |
| Setting Time | Near noon | Around midnight |
| Cycle Position | Three-quarters through | One-quarter through |
| Waxing or Waning | Waning (decreasing light) | Waxing (increasing light) |
| Next Phase | Waning crescent | Waxing gibbous |
Effects of a Third Quarter Moon on The Earth
The third quarter moon creates measurable effects on Earth, particularly through gravitational forces that influence water bodies and natural rhythms.
1. Neap Tides: The moon and sun form a right angle, creating weaker tidal ranges with smaller differences between high and low tides.
2. Gravitational Pull: The combined gravitational forces of the moon and sun partially cancel each other out during this phase.
3. Ocean Currents: Reduced tidal movements lead to calmer coastal waters and less dramatic shifts in ocean current patterns.
4. Marine Life Behavior: Certain fish and marine creatures adjust their feeding and spawning activities based on the reduced tidal activity.
5. Animal Activity: Some nocturnal animals show altered behavior patterns due to the decreased moonlight available during evening hours.
6. Plant Growth: Studies suggest minor influences on plant sap flow and growth rates, though research remains ongoing in this area.
7. Sleep Patterns: Reduced nighttime illumination may affect human and animal circadian rhythms differently than during brighter moon phases.
Cultural and Symbolic Meaning of the Third Quarter Moon
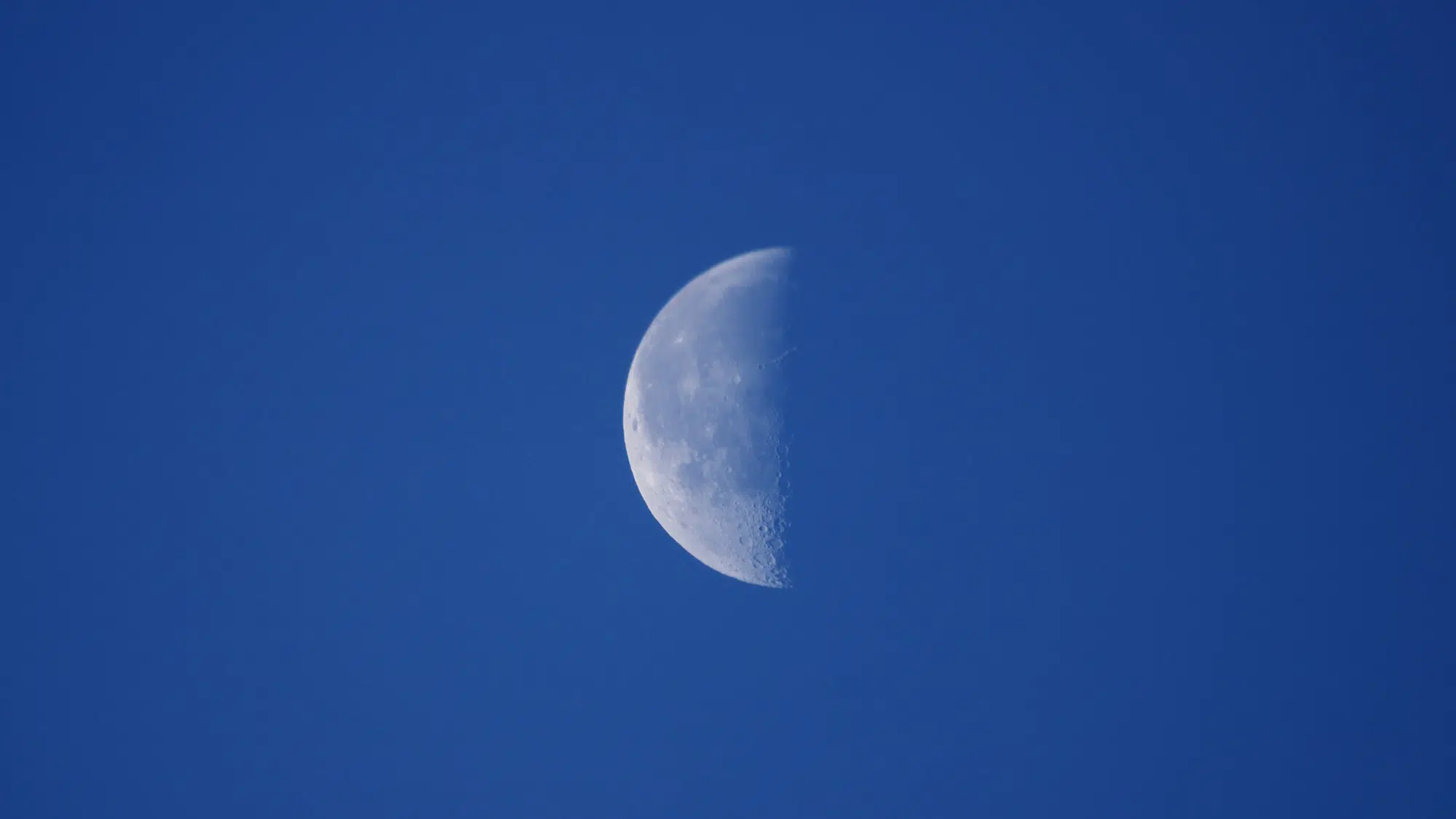

Throughout history, cultures worldwide have assigned deep symbolic meaning to the third quarter moon.
Many traditions view this phase as a time of release, reflection, and letting go of what no longer serves a purpose. Ancient civilizations saw it as a period for cleansing and making space for new beginnings.
The waning light symbolizes the natural cycle of decline before renewal.
Spiritual practitioners often use this phase for meditation, forgiveness, and breaking old habits. Some cultures associate it with wisdom gained through experience, as the moon has journeyed far in its cycle.
Farmers historically used this phase for specific agricultural tasks, believing the decreasing light affected crop growth. The third quarter moon continues to hold significance in modern spiritual practices and folklore traditions.
Moon Phases Calendar 2026: Track Third Quarter Dates
| Lunation | Date | UTC Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1274 | Jan 10, 2026 | 15:48 |
| 1275 | Feb 9, 2026 | 12:43 |
| 1276 | Mar 11, 2026 | 09:38 |
| 1277 | Apr 10, 2026 | 04:51 |
| 1278 | May 9, 2026 | 21:10 |
| 1279 | Jun 8, 2026 | 10:00 |
| 1280 | Jul 7, 2026 | 19:29 |
| 1281 | Aug 6, 2026 | 02:21 |
| 1282 | Sep 4, 2026 | 07:51 |
| 1283 | Oct 3, 2026 | 13:25 |
| 1284 | Nov 1, 2026 | 20:28 |
| 1285 | Dec 1, 2026 | 06:08 |
| 1286 | Dec 30, 2026 | 18:59 |
Note: Times account for refraction; verify locally for visibility around evening/midnight rises.
Best Astrophotography Tips for Third Quarter Moon
Capturing the third quarter moon requires specific techniques to showcase its unique half-lit appearance and dramatic shadow details effectively.
- Timing Matters: Photograph during early morning hours when the moon sits high in the sky and atmospheric distortion remains minimal.
- Use a Telephoto Lens: A lens with at least 200mm focal length captures the moon’s details and craters along the terminator line clearly.
- Manual Focus is Key: Set your camera to manual focus and zoom in on the moon’s edge to achieve the sharpest possible image.
- Lower ISO Settings: Keep ISO between 100-400 to reduce noise and maintain image quality while capturing the moon’s subtle surface details.
- Fast Shutter Speed: Use shutter speeds between 1/125 and 1/250 seconds to freeze the moon’s apparent motion and prevent blurring.
- Bracket Your Exposures: Take multiple shots at different exposure settings to ensure you capture both the bright and shadowed areas properly.
- Shoot in RAW Format: RAW files preserve maximum detail and flexibility for post-processing adjustments to highlights and shadows.
To Conclude
The third quarter moon offers more than just a beautiful sight in the morning sky.
From its scientific positioning in the lunar cycle to its cultural significance across civilizations, this phase connects us to ancient rhythms that continue shaping life on Earth.
The gravitational effects create neap tides, while photographers find unique opportunities to capture its dramatic half-lit face.
Next time the third quarter moon appears, take a moment to observe its distinct features. The knowledge gained changes a simple glance upward into a deeper connection with the cosmos surrounding us.