The moon changes shape in the sky over time. These changes are called phases, and they happen as the moon orbits around Earth.
Each phase shows us a different part of the moon lit by the sun. People have watched these patterns for centuries to keep track of time and plan their days.
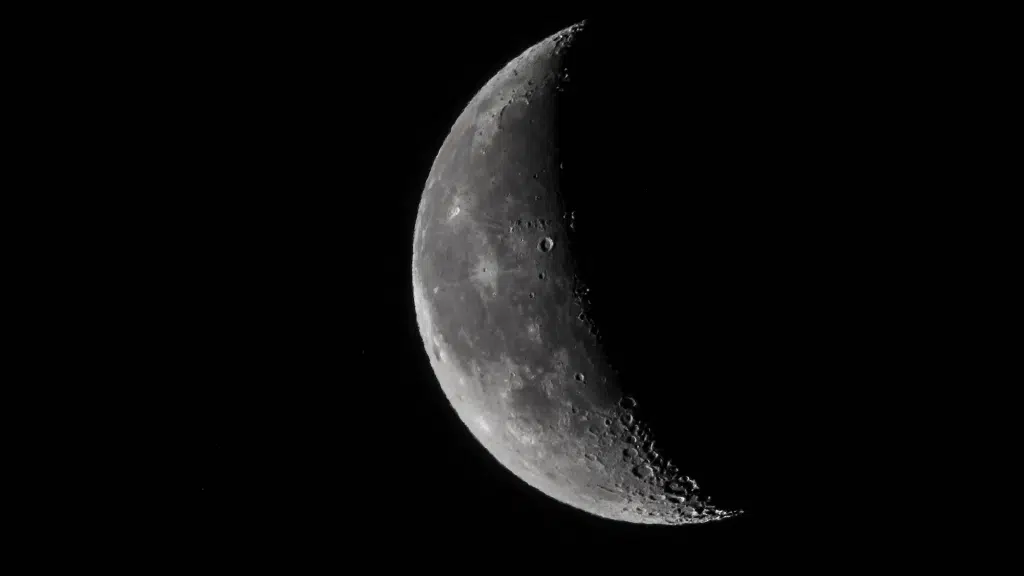
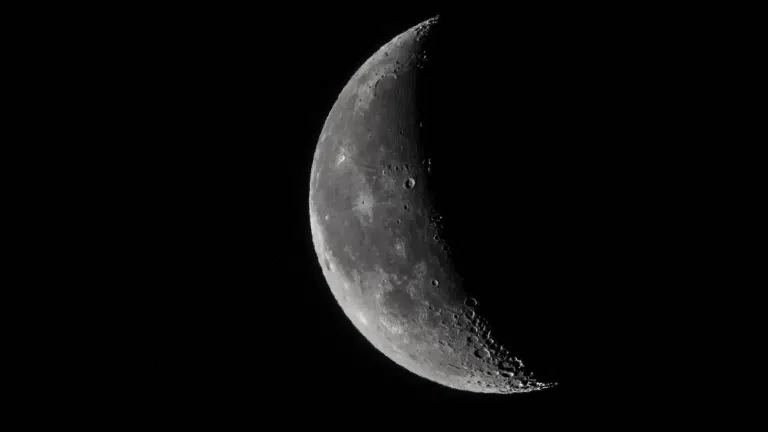
One of these phases is the first quarter moon, a stage that happens early in the moon’s cycle. It is an important point in how the moon moves and shines.
Learning about this helps us understand how the moon moves and changes as it orbits Earth.
What is the First Quarter Moon?
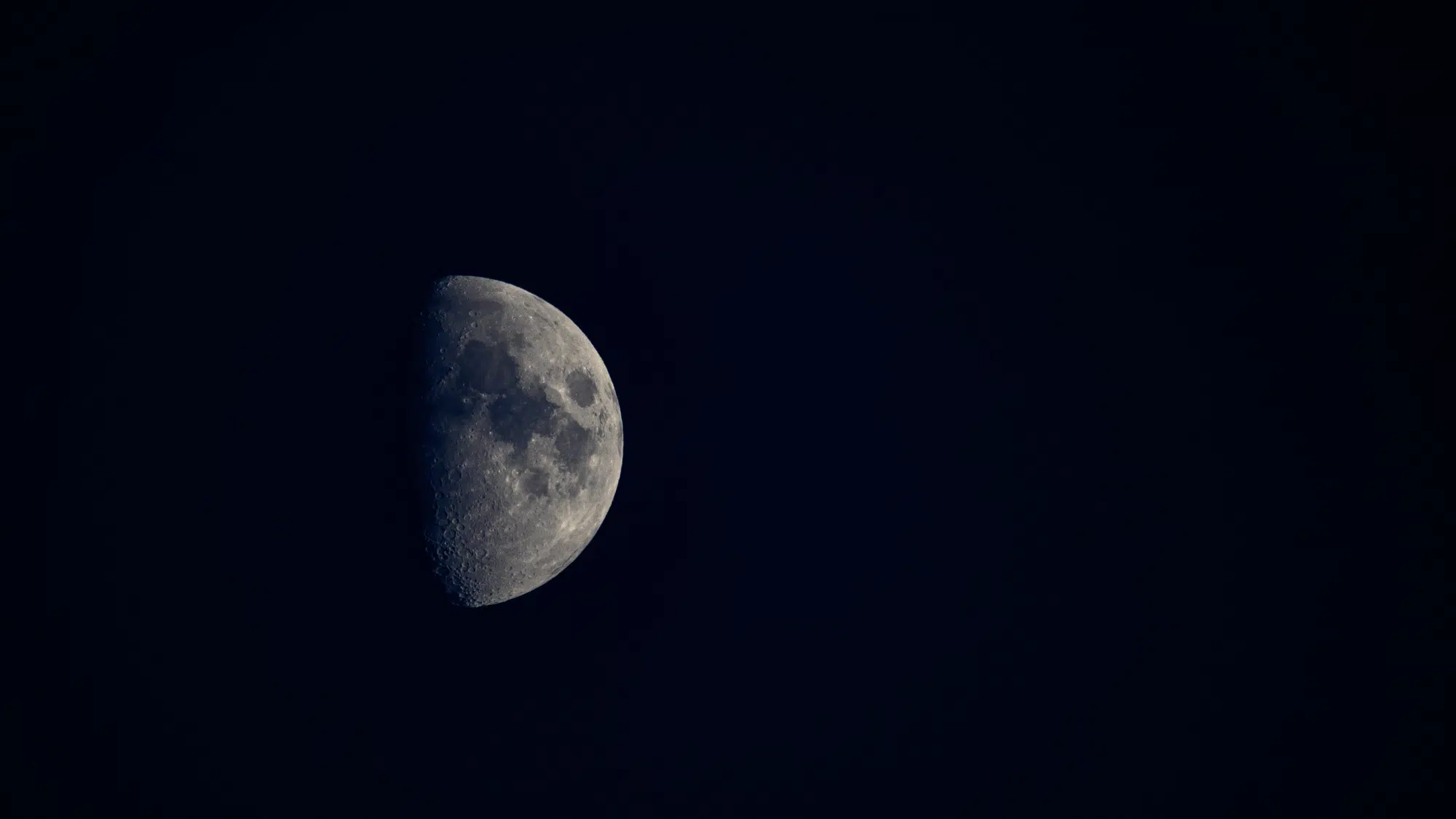
The first quarter phase of the moon occurs about seven days after the new moon, when the moon is half-bright and half-dark from Earth.
The right side lights up for Northern Hemisphere observers, while the left side glows for those in the Southern Hemisphere.
Despite appearing as a half-circle, it’s called “first quarter” because the moon has completed one-quarter of its orbital journey around Earth.
The term describes its position in space, not its visual appearance. This phase is easy to spot in the evening sky and reveals the moon’s craters and mountains clearly.
The next first-quarter moons are expected on November 27, 2025, at 11:59 PM (UTC) and December 27, 2025, at 12:10 PM (UTC).
Characteristics of the First Quarter Moon

The first quarter phase of the moon marks an important point in the moon’s monthly cycle when light, position, and gravitational forces all work together to create noticeable changes on Earth and in the sky.
Appearance
During this phase of the moon, the sky looks darker and clearer, making the moon’s bright glow stand out. Its light is strong enough to cast faint shadows on the ground in areas with little artificial light.
Sunlight hitting from the side creates sharp contrasts that reveal craters and ridges not seen in other phases.
While the moon seems smooth from a distance, binoculars or a telescope show its rough surface in clear detail.
Position and Timing
This phase appears when the moon has completed about one-quarter of its orbit around Earth.
At this point, it forms a 90-degree angle with the sun and Earth. This phase happens roughly one week after the new moon and one week before the full moon.
It rises around midday and sets around midnight, making it visible in the afternoon and early evening sky. Its high position at sunset makes it easy to see without needing special equipment.
Effect on Tides
In this stage, the sun and moon pull on Earth’s oceans from different directions.
These forces partly cancel each other out, leading to smaller differences between high and low tides. This pattern is known as a neap tide.
During neap tides, high tides are not as high as usual, and low tides are not as low.
These gentler tides happen twice each month, once during the waxing half and again during the last quarter moon.
The Moon’s Orbit and Why We See Phases
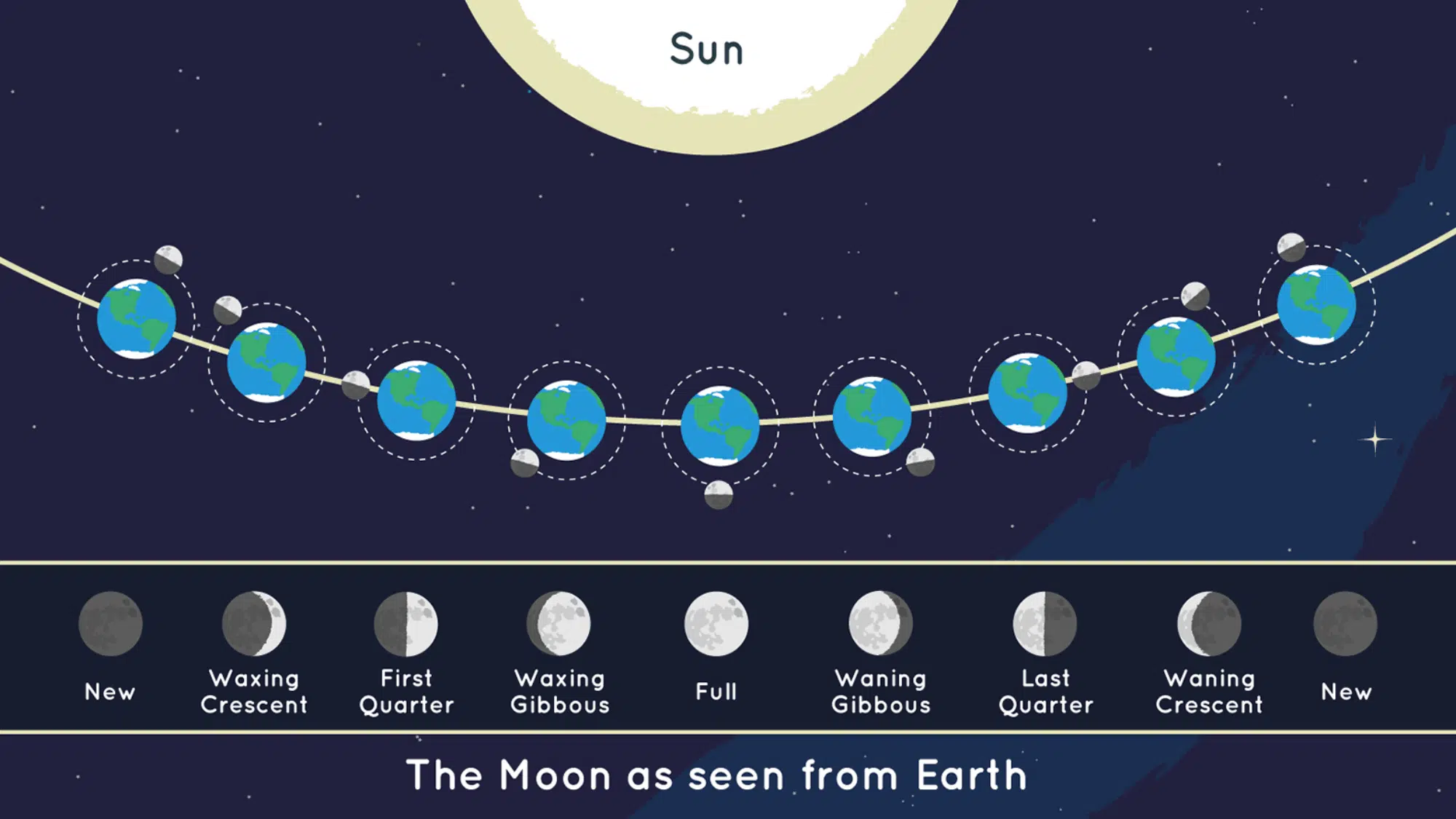
Image Source: NASA Science
The Moon orbits Earth once every 29.5 days, following a slightly tilted and oval-shaped path. Each phase marks how much of the Moon’s lit side is visible from Earth.
We see these phases because the Moon doesn’t make its own light; it reflects the Sun’s light. As the Moon’s position changes in its orbit, the angle between the Sun, Moon, and Earth shifts, letting us see more or less of the bright half.
This constant change creates the lunar cycle we notice every month. These are the phases of the moon:
| Phase of the Moon | Description |
|---|---|
| New Moon | The Moon is between Earth and the Sun, and its lit side faces away from us. |
| Waxing Crescent | A thin crescent of light appears on the right side as the Moon starts to grow. |
| First Quarter | Half of the Moon’s surface is lit, showing a perfect half-circle. |
| Waxing Gibbous | More than half is lit, as the Moon moves toward being full. |
| Full Moon | The entire face of the Moon is illuminated by the Sun. |
| Waning Gibbous | The light starts to shrink, with most of the Moon still visible. |
| Last Quarter | Half of the Moon is lit again, but on the opposite side from the first quarter. |
| Waning Crescent | Only a small sliver of light remains before the new moon begins again. |
The Spiritual Meaning of the First Quarter Moon
The first quarter is often seen as a time to take action and build confidence. It represents the moment when ideas and goals begin to take shape after being set during the new moon.
Spiritually, it encourages people to overcome obstacles and stay focused even when challenges appear. This phase reminds us that progress takes effort and patience.
Many believe it symbolizes balance: between planning and doing, thinking and acting.
It can be a meaningful time to start new routines, make important decisions, or strengthen commitments.
The growing light of the moon is often linked with personal growth, courage, and motivation, showing that steady effort leads to results.
Cultural Influence of the First Quarter Moon
In many ancient cultures, the first quarter has helped shape calendars, stories, and religious practices. The moon’s predictable cycle provided structure for societies worldwide.
1. Babylonian Timekeeping: The Babylonians used it to divide their months into equal parts, making it easier to predict important events.
2. Chinese Astronomical Traditions: In China, early astronomers used this phase of the moon to track the passage of time and plan celebrations tied to lunar changes.
3. Native American Seasonal Markers: Among Native American tribes, this phase often marked a time to begin hunting or gathering.
4. Modern Cultural Impact: Today, the moon still plays a role in modern culture. It influences art, music, and festivals, and many people follow lunar calendars for gardening or spiritual reflection.
Fun Facts About the First Quarter Moon
This stage has many surprising and lesser-known details that make it special.
- Astronauts train using first-quarter lighting because the side shadows help them practice spotting surface features like craters and ridges.
- Animals and insects like sea turtles and fireflies respond to moonlight levels, and this phase of the moon affects their nighttime activity.
- Photographers prefer this phase because side lighting highlights craters and mountains, creating crisp and detailed lunar images.
- Sometimes appears near bright planets like Jupiter or Saturn, giving skywatchers striking nighttime pairings to enjoy.
- No matter the phase, we always see the same side of the moon because it rotates once per orbit, a motion called synchronous rotation.
First Quarter Moon in Lunar Calendar 2026
The following dates for sighting are based on Mountain Standard Time (MST, UTC−07). If you live in the Western United States (UTC−08), the times occur one hour earlier, while in the Eastern United States (UTC−05), they occur two hours later.
| Date | Time (UTC) | Approximate Distance (miles) |
|---|---|---|
| January 25, 2026 | 09:48:23 PM | 227,100 |
| February 24, 2026 | 05:28:59 AM | 225,750 |
| March 25, 2026 | 12:19:22 PM | 226,760 |
| April 23, 2026 | 07:33:22 PM | 229,920 |
| May 23, 2026 | 04:12:05 AM | 234,750 |
| June 21, 2026 | 02:55:57 PM | 240,450 |
| July 21, 2026 | 04:05:48 AM | 245,950 |
| August 19, 2026 | 07:46:34 PM | 250,100 |
| September 18, 2026 | 01:44:25 PM | 251,930 |
| October 18, 2026 | 09:13:37 AM | 250,920 |
| November 17, 2026 | 04:48:31 AM | 247,150 |
| December 16, 2026 | 10:43:09 PM | 241,500 |
There is a possibility that the moon phases can occur at slightly different times depending on the time zone and exact observation. Please confirm the dates and time whilst moon sighting.
Conclusion
The first quarter moon phase is a key part of the lunar cycle and an exciting time for learning and observation.
It shows how the moon’s position, light, and movement connect with life on Earth. Watching it can help people understand patterns in the sky and the rhythm of nature.
This phase also reminds us how ancient cultures used the moon to guide their days and decisions.
If you are studying science, observing the sky, or enjoying a quiet evening outside, this phase of the moon offers a clear view of how space and Earth work together.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is It Called First Quarter if It Looks Half?
Because the Moon has traveled one-quarter of its orbit, even though half of its illuminated surface is visible.
Can You See the First Quarter Moon During the Day?
Yes. It often rises around midday and can be seen clearly in the afternoon before sunset arrives.
How is It Different from The Third Quarter Moon?
First quarter is waxing and growing brighter, while the third quarter is waning and gradually fading toward the new moon.