Famous astrophysicists have spent their lives studying stars, planets, galaxies, and everything else in space to help humans understand the universe better.
These brilliant scientists use math, physics, and powerful telescopes to answer big questions about how space works and where everything came from.
From finding black holes to proving the Big Bang theory, astrophysicists have changed the way people think about their place in the cosmos.
Learning about these great minds helps people appreciate the hard work and dedication required to open space’s mysteries.
Their discoveries continue to shape modern science and inspire new generations to look up at the stars with wonder and curiosity.
What is an Astrophysicist?
An astrophysicist is a scientist who studies space, stars, planets, and everything in the universe using physics and mathematics to understand how things work.
These scientists spend years learning about gravity, light, energy, and matter to explain what happens billions of miles away from Earth.
Famous astrophysicists work with telescopes, computers, and complex equations to test their ideas about space and make new discoveries about the cosmos.
Some astrophysicists study black holes, while others focus on how stars are born and die, or how galaxies form and move through space.
Their work requires patience, creativity, and strong problem-solving skills to answer questions that have puzzled humans for thousands of years about the nature of reality.
Top Famous Astrophysicists and Their Discoveries
From black holes to galaxies, these top astrophysicists expanded cosmic knowledge and left lasting legacies in science.
1. Claudius Ptolemy

Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
Claudius Ptolemy was one of the earliest figures to shape our cosmic understanding. His geocentric model placed Earth at the center of the universe, influencing astronomy for over a thousand years.
Despite being outdated, his ideas were crucial in laying the groundwork for future scientific debates. His theories helped scholars through the Middle Ages.
Even today, his work remains a milestone in the history of astronomy.
- Lifespan: 100–170 AD
- Achievement: Proposed the geocentric model of the universe
2. Nicolaus Copernicus

Image Source: Britannica
Copernicus was a Renaissance-era astronomer and mathematician who revolutionized astronomy by placing the Sun at the center of the solar system.
His heliocentric theory challenged centuries of accepted belief and reshaped scientific thinking forever. Today, he is celebrated as one of the most famous astrophysicists who changed how we view our place in the cosmos.
His work ignited the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus’s courage redefined humanity’s understanding of the universe.
- Lifespan: 1473–1543
- Achievement: Developed the heliocentric theory
3. Galileo Galilei

Image Source: Britannica
Known as the “Father of Modern Observational Astronomy,” Galileo made groundbreaking telescopic observations.
He discovered Jupiter’s moons, observed the phases of Venus, and challenged traditional views. His defiance against dogma paved the way for scientific freedom and revolutionized the study of space.
Galileo’s courage helped establish evidence-based science as the standard. His contributions continue to inspire curiosity about the cosmos.
- Lifespan: 1564–1642
- Achievement: Discovered Jupiter’s moons and supported heliocentrism
4. Johannes Kepler
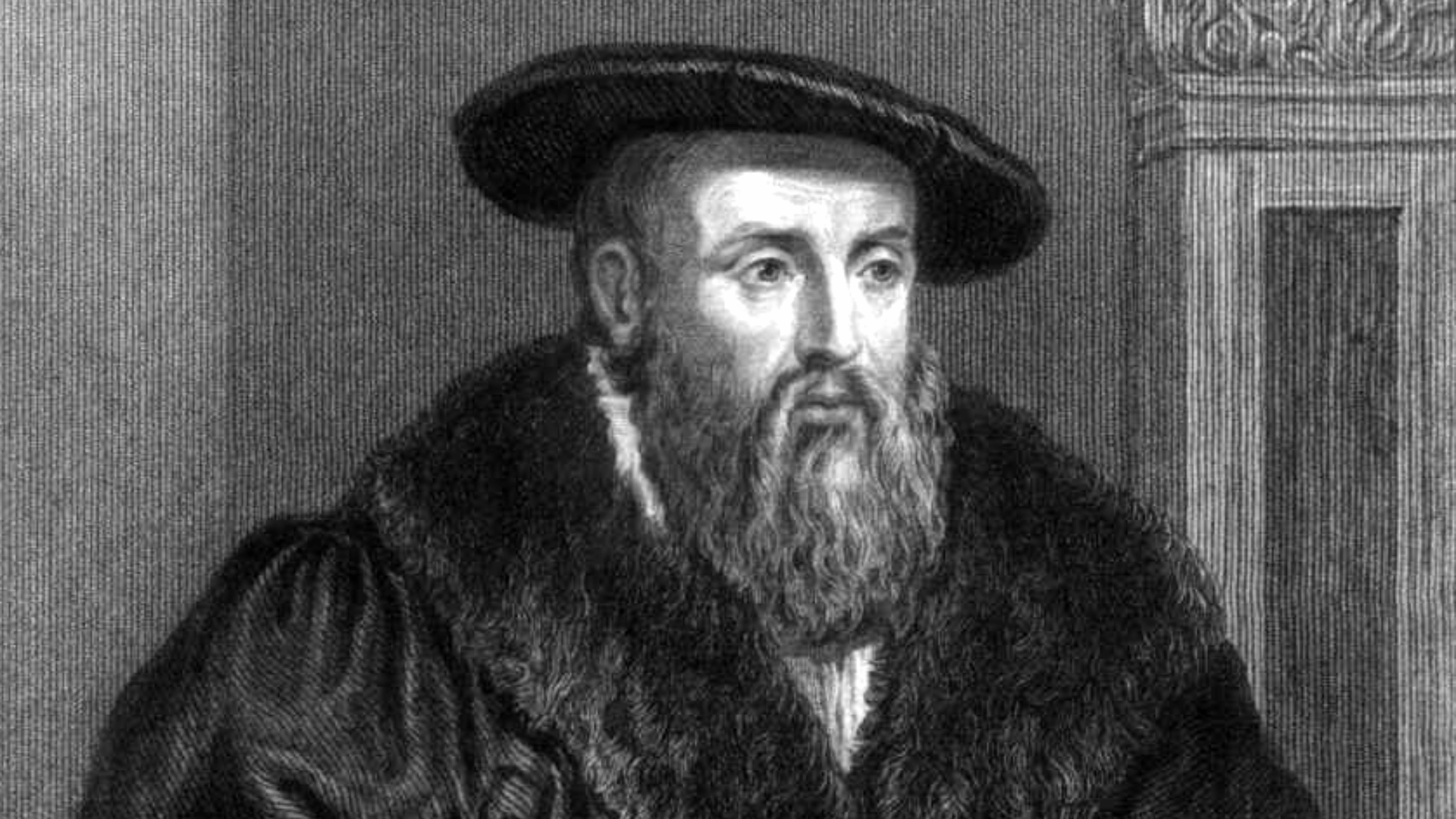

Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
Kepler changed astronomy by formulating his three laws of planetary motion. His insights proved planets orbit the Sun in ellipses, not circles, strengthening Copernican ideas.
His work bridged mathematics and astronomy, laying the foundation for Newton’s theories.
Kepler’s dedication reshaped orbital mechanics and inspired future generations of scientists. His discoveries also improved timekeeping.
- Lifespan: 1571–1630
- Achievement: Established three laws of planetary motion
5. Isaac Newton
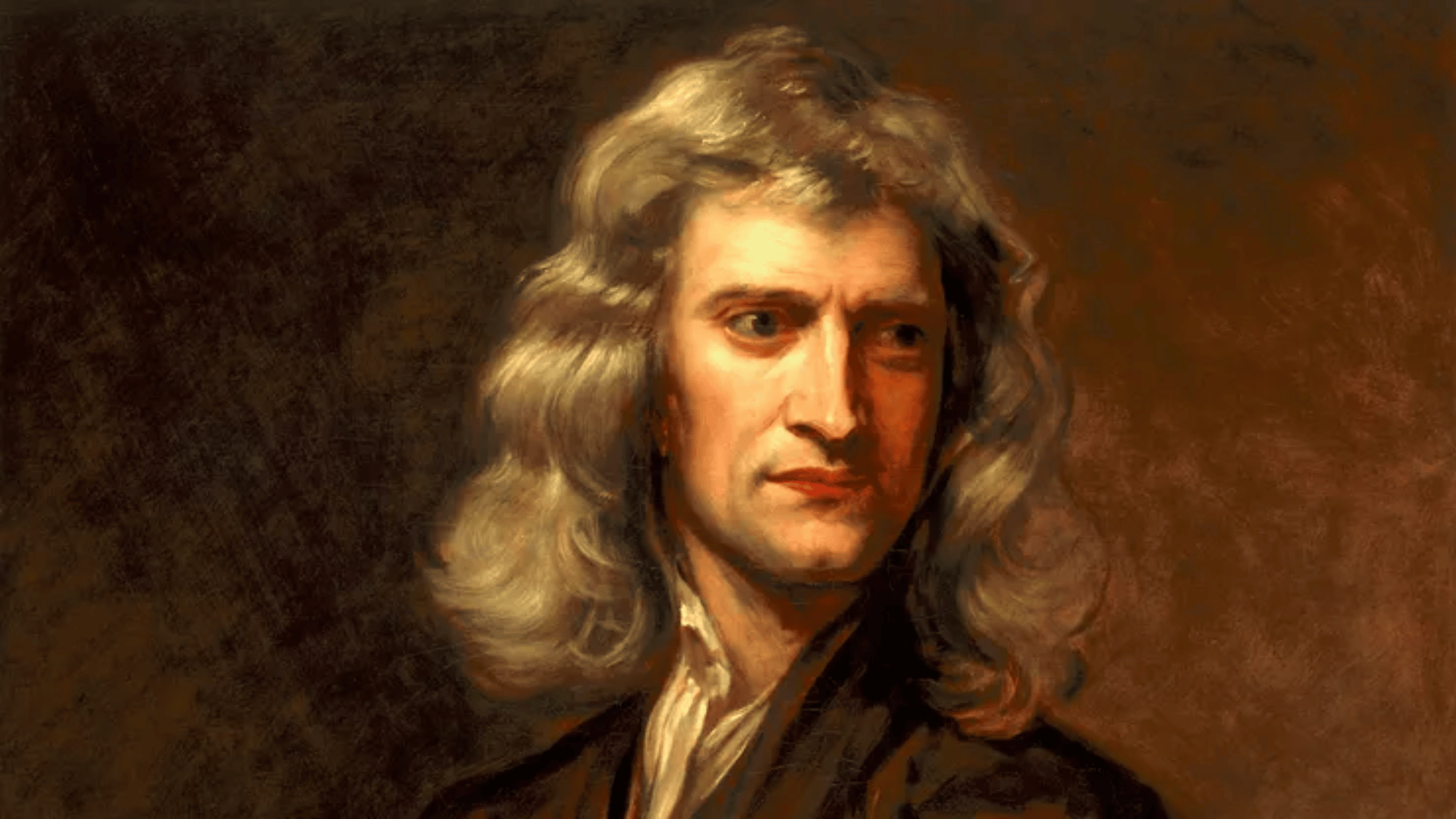

Image Source: Britannica
Newton’s contributions extended far beyond physics. His universal law of gravitation explained planetary motion with unmatched precision.
He united heaven and Earth under the same set of laws, proving that celestial and terrestrial phenomena follow the same principles.
His “Principia” remains a cornerstone in astrophysics and physics alike. Newton’s brilliance influenced nearly every branch of science.
- Lifespan: 1643–1727
- Achievement: Formulated universal gravitation
6. Edmond Halley
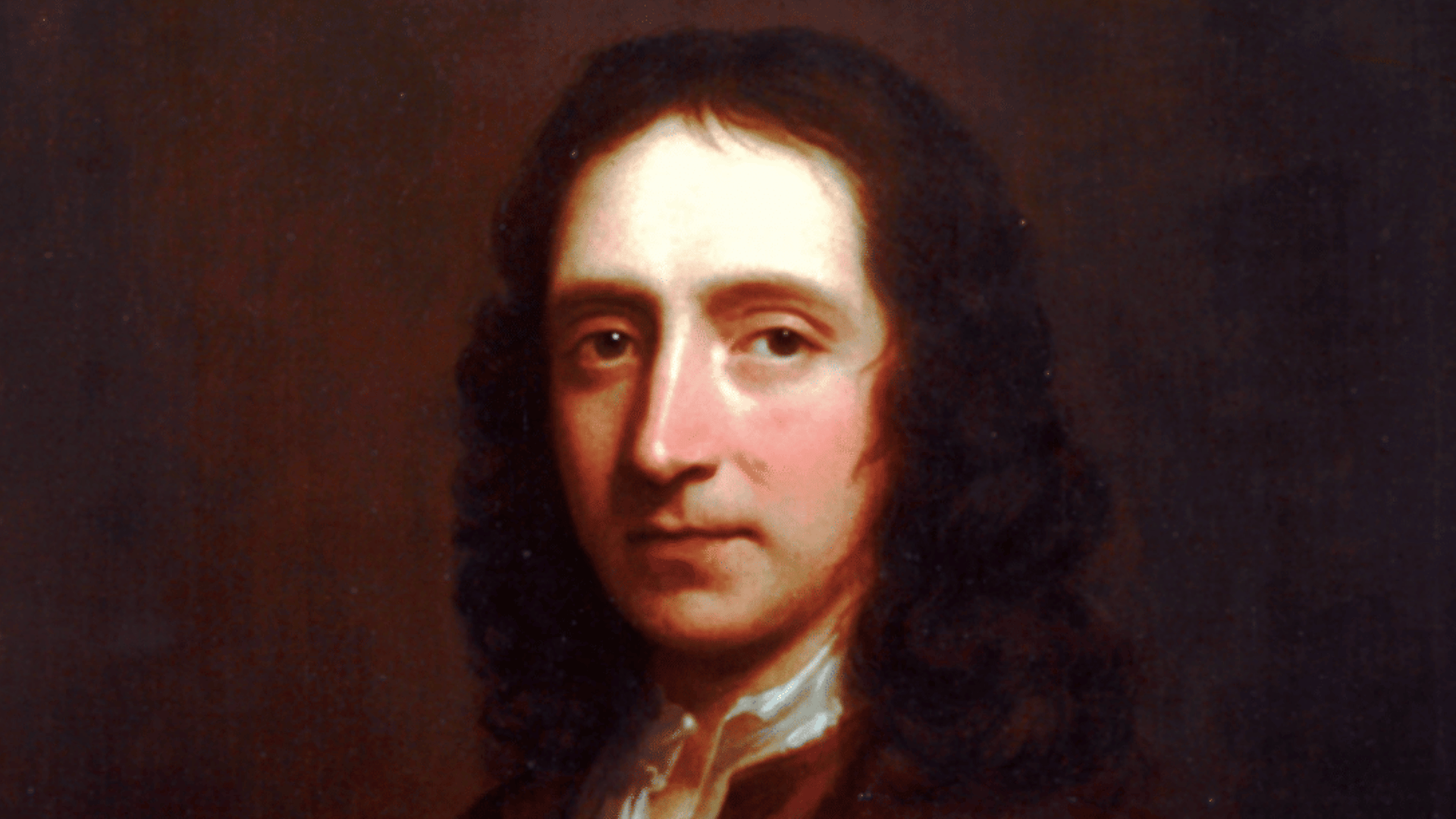

Image Source: World History Encyclopedia
Halley is best remembered for calculating the orbit of the comet that now bears his name, Halley’s Comet.
His prediction confirmed Newton’s theories of motion. As one of the most famous astrophysicists of his era, Halley also made advances in mapping stars and understanding Earth’s magnetic field.
His efforts bridged theory and observation. Halley’s work remains essential in linking science with public awareness.
- Lifespan: 1656–1742
- Achievement: Predicted return of Halley’s Comet
7. Christiaan Huygens
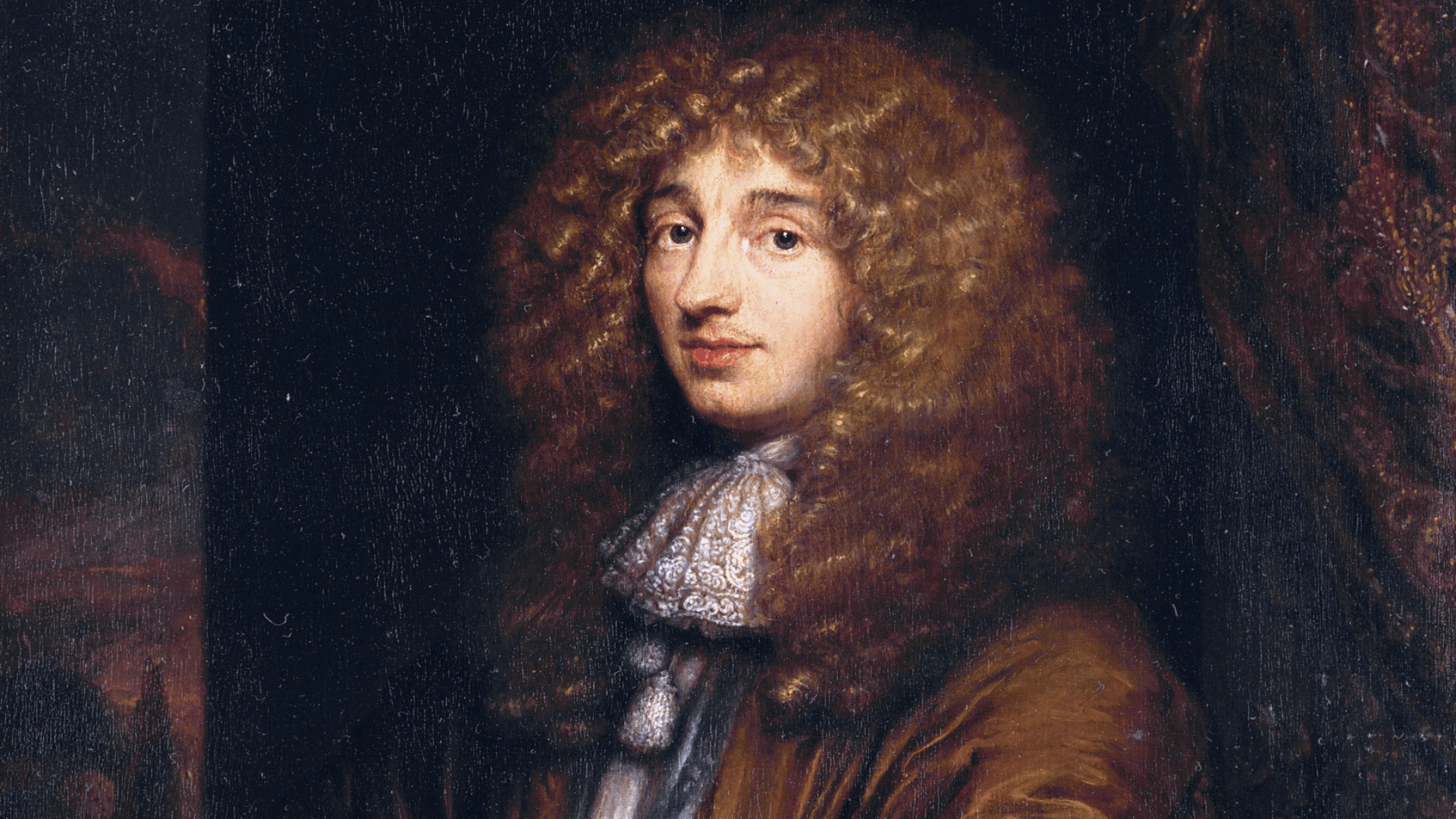

Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Christiaan Huygens made key contributions to astronomy and physics during the 17th century.
He is best known for finding Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, and for proposing the wave theory of light. Huygens also designed improved telescopes, which allowed him to make sharper observations.
His discoveries helped broaden our view of planetary systems. He remains one of the great scientific minds of the Scientific Revolution.
- Lifespan: 1629–1695
- Achievement: found Titan and advanced the wave theory of light
8. William Herschel

Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
William Herschel, a German-born British astronomer, is renowned for his discovery of Uranus in 1781, the first new planet found in modern history.
He also catalogued thousands of stars and nebulae, expanding the known universe.
Herschel, with the help of his sister Caroline, built some of the most powerful telescopes of his era. His passion reshaped the way humanity understood deep space.
- Lifespan: 1738–1822
- Achievement: Finding Uranus and cataloguing deep-sky objects
9. Pierre-Simon Laplace
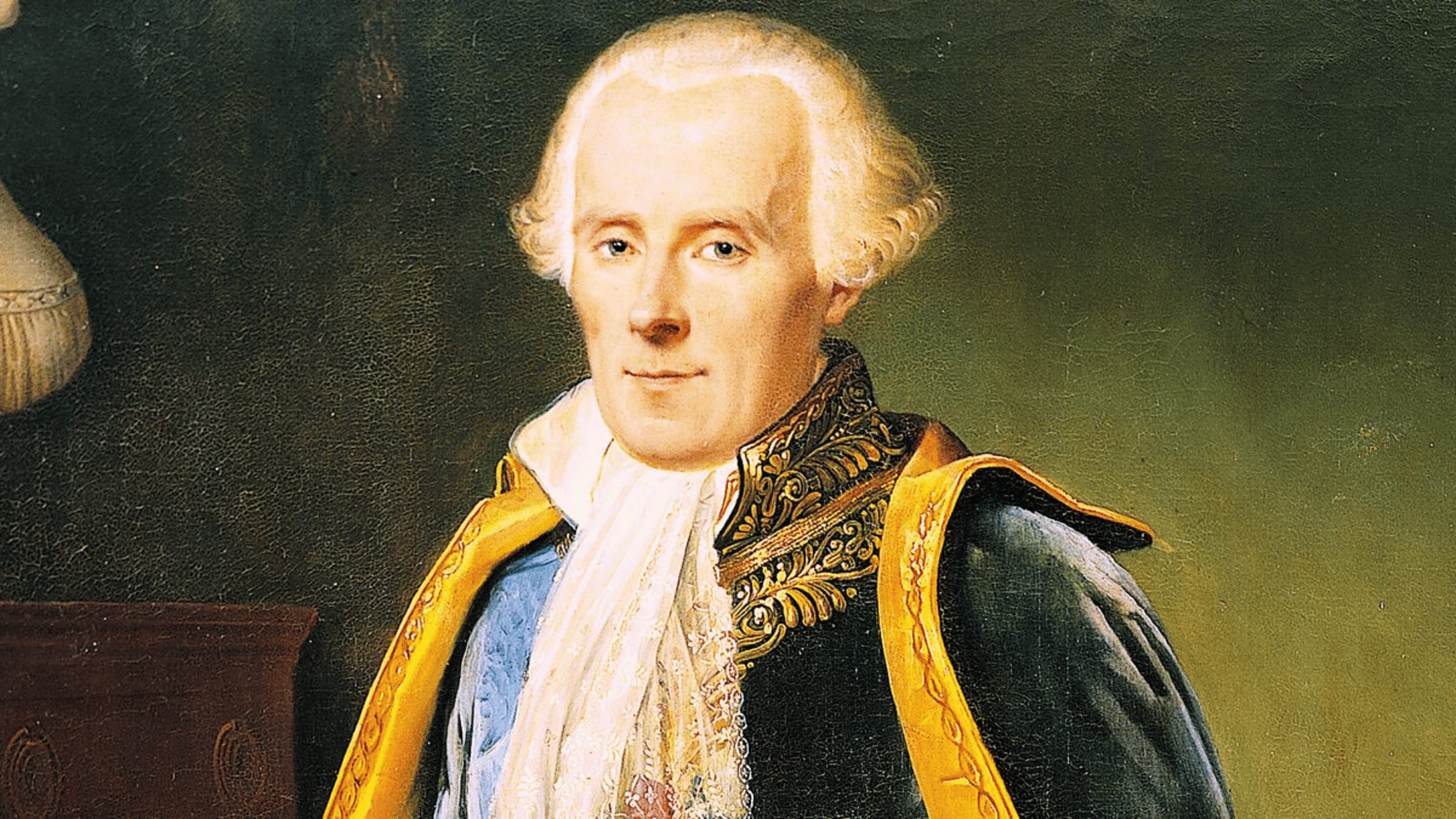

Image Source: BBC
Laplace was a brilliant French mathematician and astrophysicist whose work laid the foundation for celestial mechanics.
He expanded Newton’s theories by applying advanced mathematics to explain planetary motions. Laplace also proposed the nebular hypothesis for the formation of the solar system.
His rigorous approach helped change astronomy into a more exact science. Today, he is remembered as the “Newton of France.”
- Lifespan: 1749–1827
- Achievement: Developed celestial mechanics and the nebular hypothesis
10. Henrietta Swan Leavitt
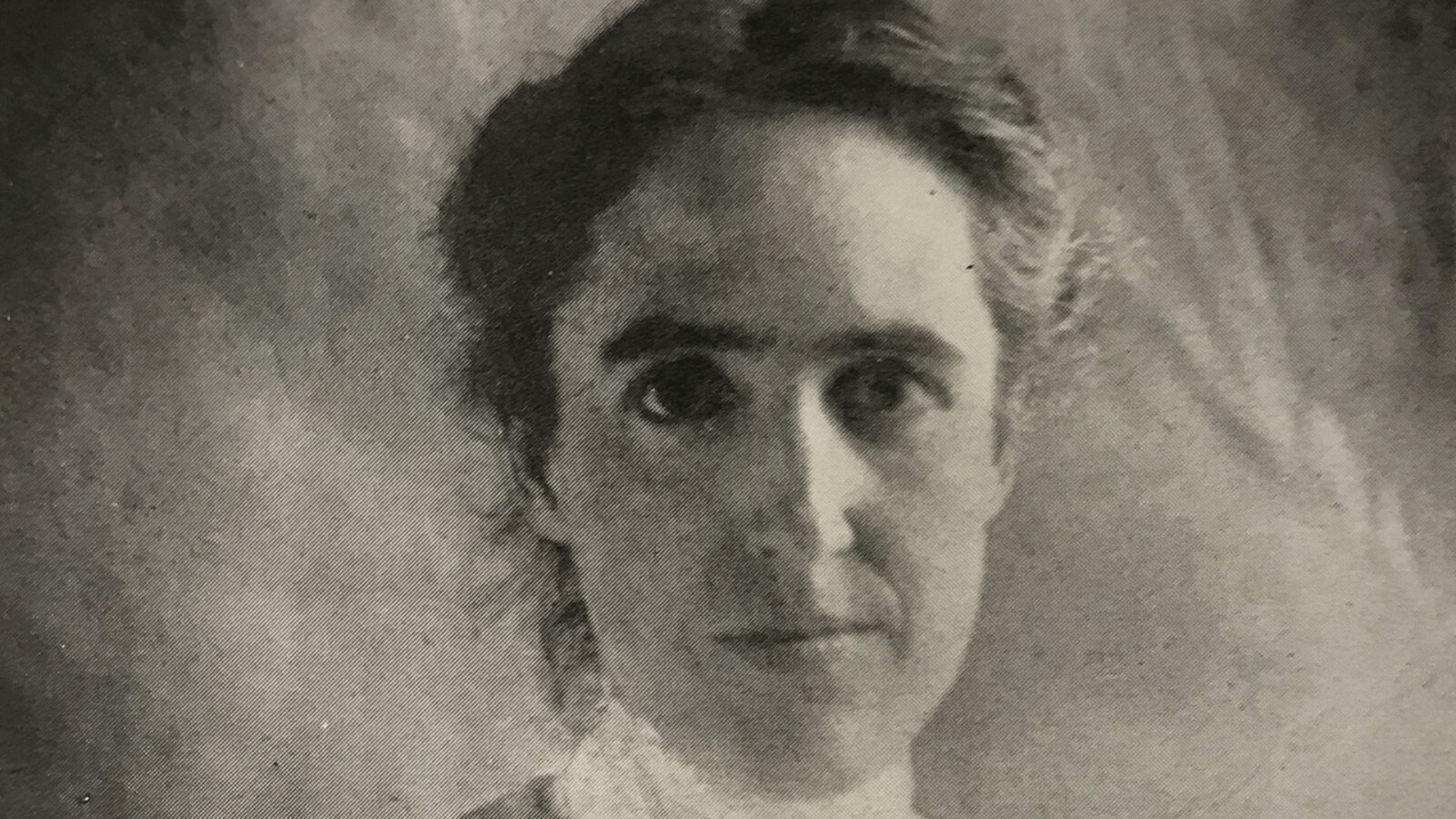
Image Source: The New York Times
Henrietta Leavitt, one of the most influential women in astrophysics, revolutionized how we measure cosmic distances.
While studying variable stars at Harvard, she found the period-luminosity relationship of Cepheid stars. This breakthrough became the foundation for calculating distances to faraway galaxies.
Despite limited recognition during her lifetime, her contributions opened doors to modern cosmology. She changed astronomy forever.
- Lifespan: 1868–1921
- Achievement: Discovered Cepheid variable stars’ period-luminosity law
11. Edwin Hubble
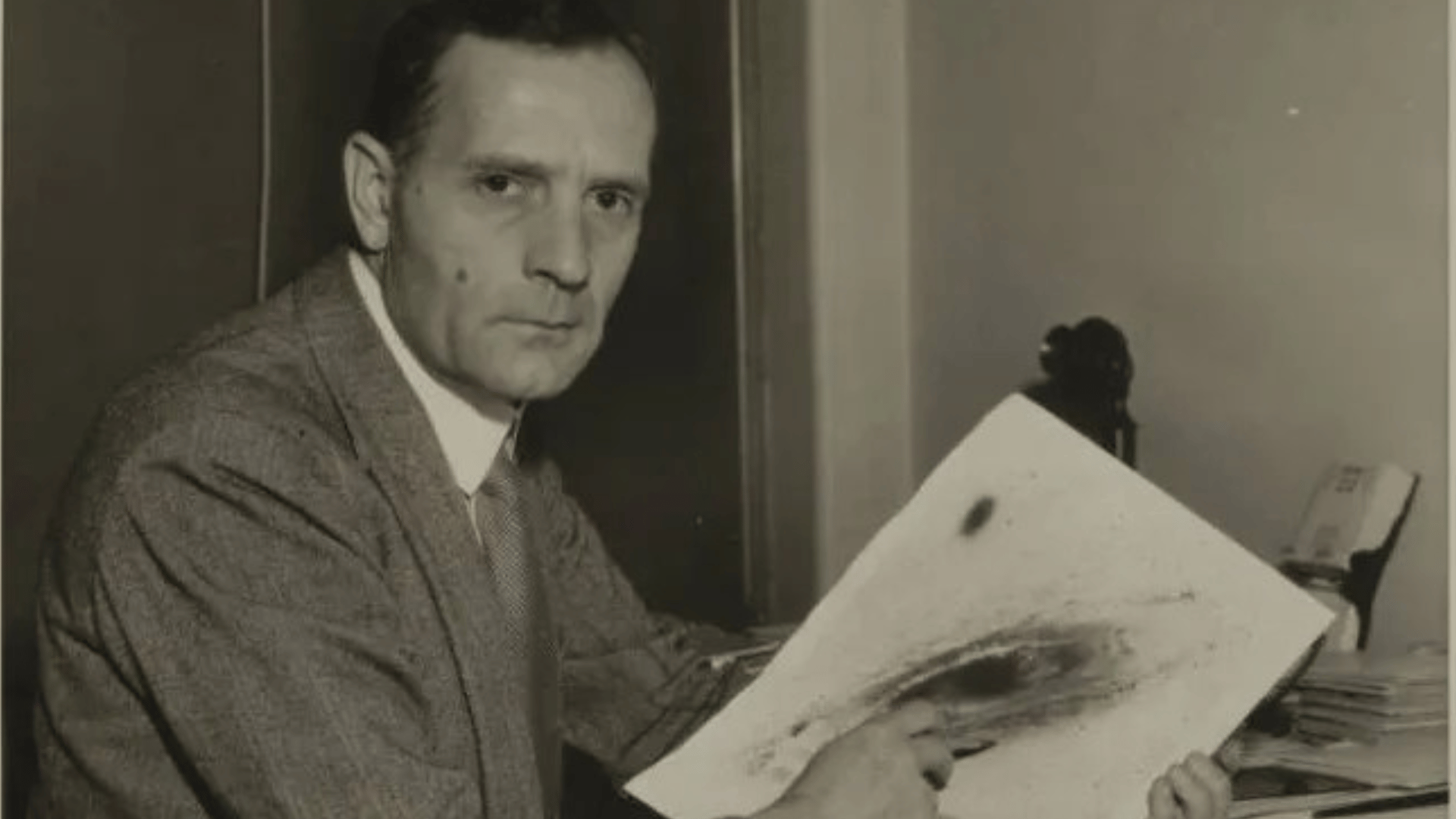

Image Source: NASA Science
Edwin Hubble changed astronomy by proving that galaxies extend far beyond the Milky Way.
His observations of redshift led to the finding of the expanding universe, which became the basis of the Big Bang theory.
The Hubble Space Telescope, named in his honor, has continued his legacy of cosmic findings. Hubble’s vision turned astronomy into a modern science of galaxies and the cosmos.
- Lifespan: 1889–1953
- Achievement: Discovered the expanding universe
12. Albert Einstein
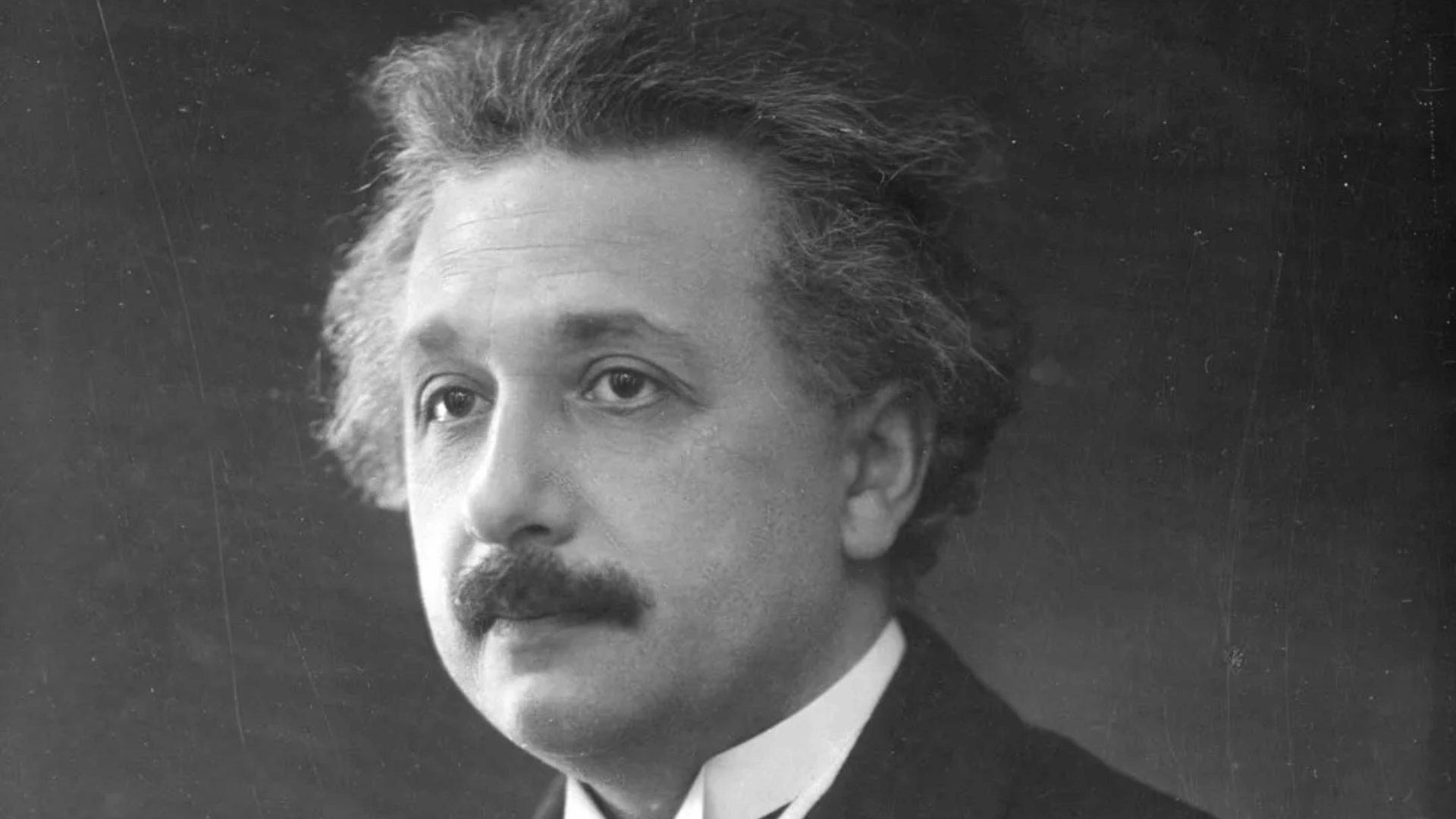
Image Source: Britannica
Though primarily a physicist, Albert Einstein’s theories profoundly impacted astrophysics. His general theory of relativity redefined gravity and explained phenomena such as black holes and gravitational lensing.
Einstein’s insights gave scientists a new framework to study space-time itself.
His genius extended far beyond equations, inspiring generations of researchers. Even today, relativity remains central to astrophysical research.
- Lifespan: 1879–1955
- Achievement: Developed the theory of relativity
13. Arthur Eddington
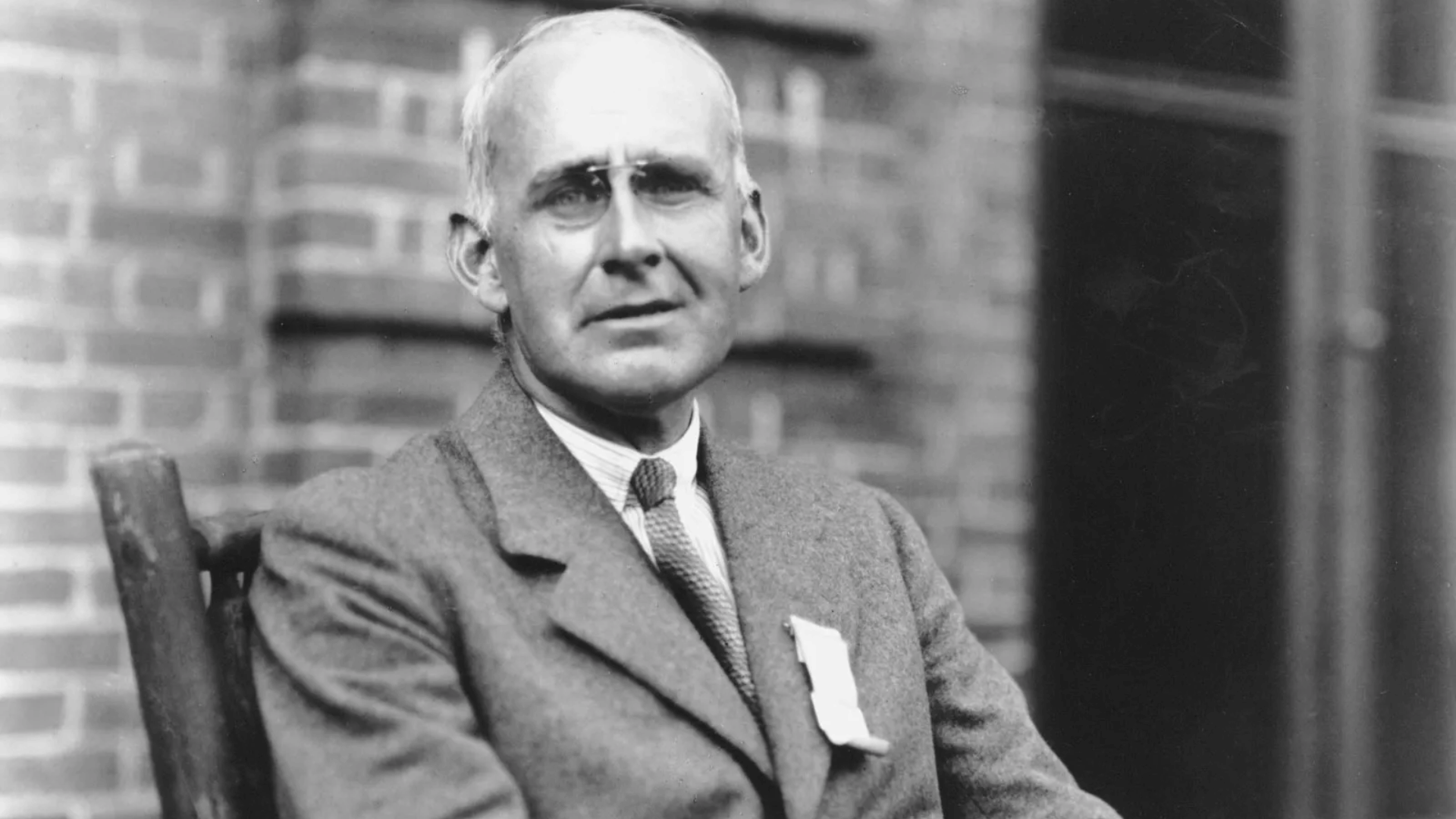

Image Source: Britannica
Arthur Eddington was a British astrophysicist best known for providing the first observational proof of Einstein’s general relativity.
During the 1919 solar eclipse, he observed the bending of starlight around the Sun, confirming Einstein’s predictions.
Eddington also contributed to understanding stellar structure and energy. His work brought relativity into the mainstream. He became a bridge between theoretical physics and observational astronomy.
- Lifespan: 1882–1944
- Achievement: Proved Einstein’s relativity through eclipse observations
14. Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar
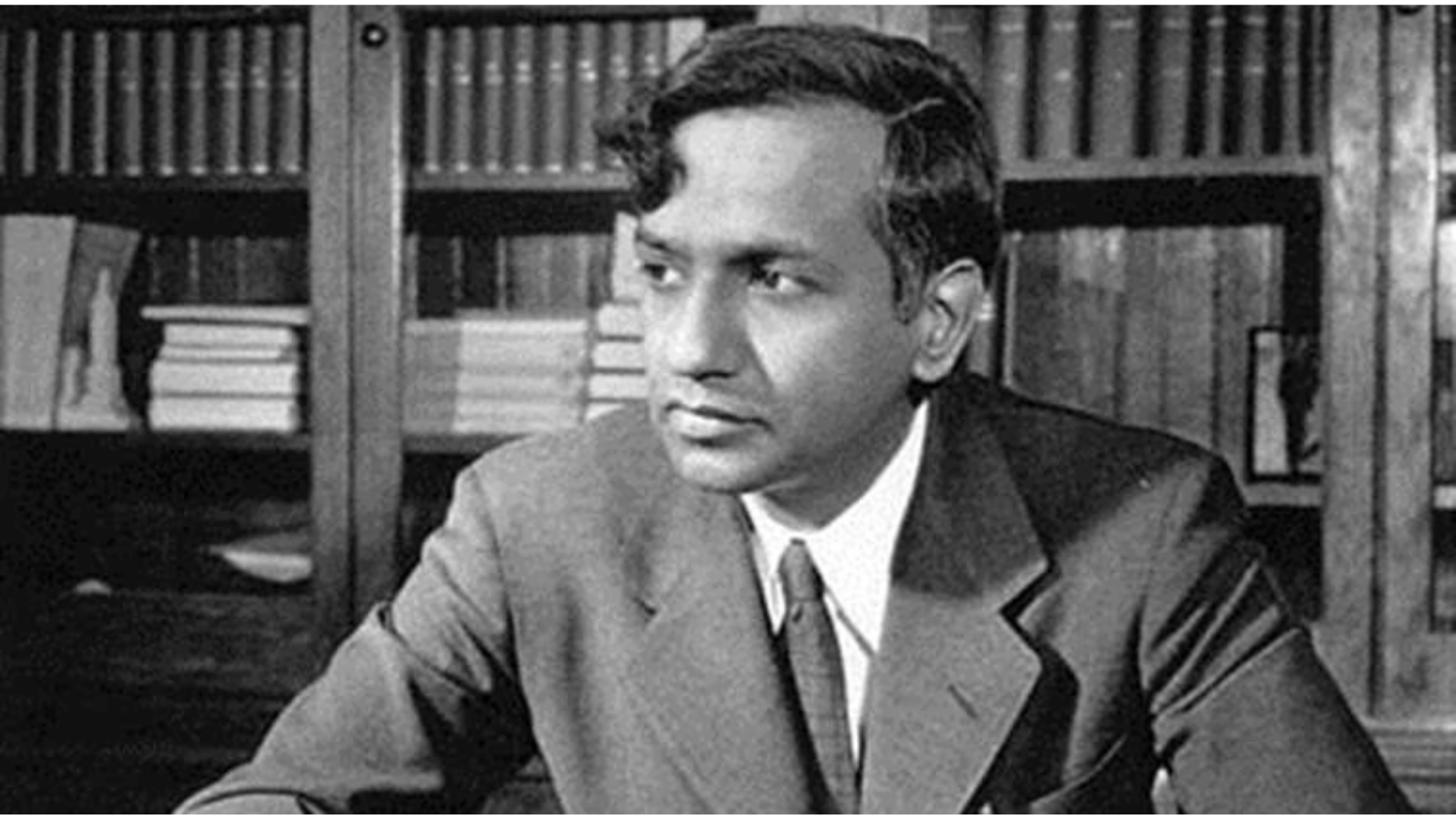

Image Source: The Indian Express
Chandrasekhar, an Indian-American astrophysicist, made groundbreaking contributions to stellar evolution.
He calculated the maximum mass of a white dwarf star, known as the Chandrasekhar limit, beyond which a star collapses into a neutron star or black hole. His insights changed astrophysics and earned him a Nobel Prize.
His precise work showed the life cycles of stars. Chandrasekhar’s brilliance continues to help astrophysical theory.
- Lifespan: 1910–1995
- Achievement: Discovered the Chandrasekhar limit for stars
15. Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin

Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin was a pioneering female astrophysicist who revealed that stars are primarily composed of hydrogen and helium.
Her doctoral thesis was revolutionary, yet initially dismissed by the scientific community. Over time, her findings became accepted as foundational astrophysics.
She went on to study stellar spectra and variable stars. Payne’s groundbreaking research changed our understanding of stellar composition. She paved the way for women in astronomy.
- Lifespan: 1900–1979
- Achievement: Proved stars are mainly hydrogen and helium
16. George Gamow
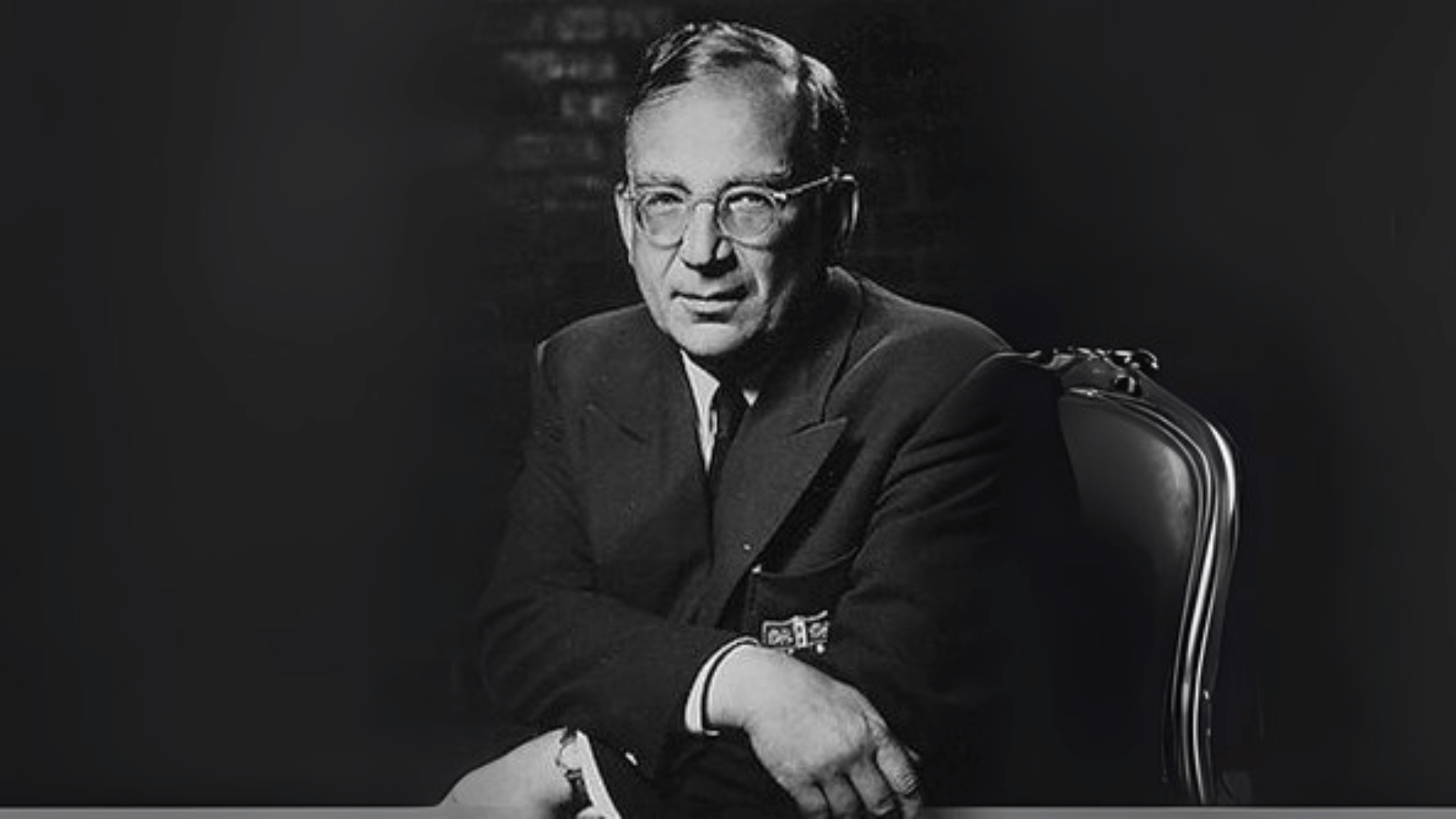

Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
George Gamow was a Russian-American theoretical physicist who contributed to the Big Bang theory of the universe.
He, along with colleagues, proposed that the early universe was hot and dense, predicting cosmic microwave background radiation.
Gamow also contributed to nuclear physics and DNA structure. His imaginative theories reshaped cosmology. Gamow’s boldness made him one of the most influential thinkers in astrophysics.
- Lifespan: 1904–1968
- Achievement: Pioneered the Big Bang theory and cosmic radiation prediction
17. Fred Hoyle
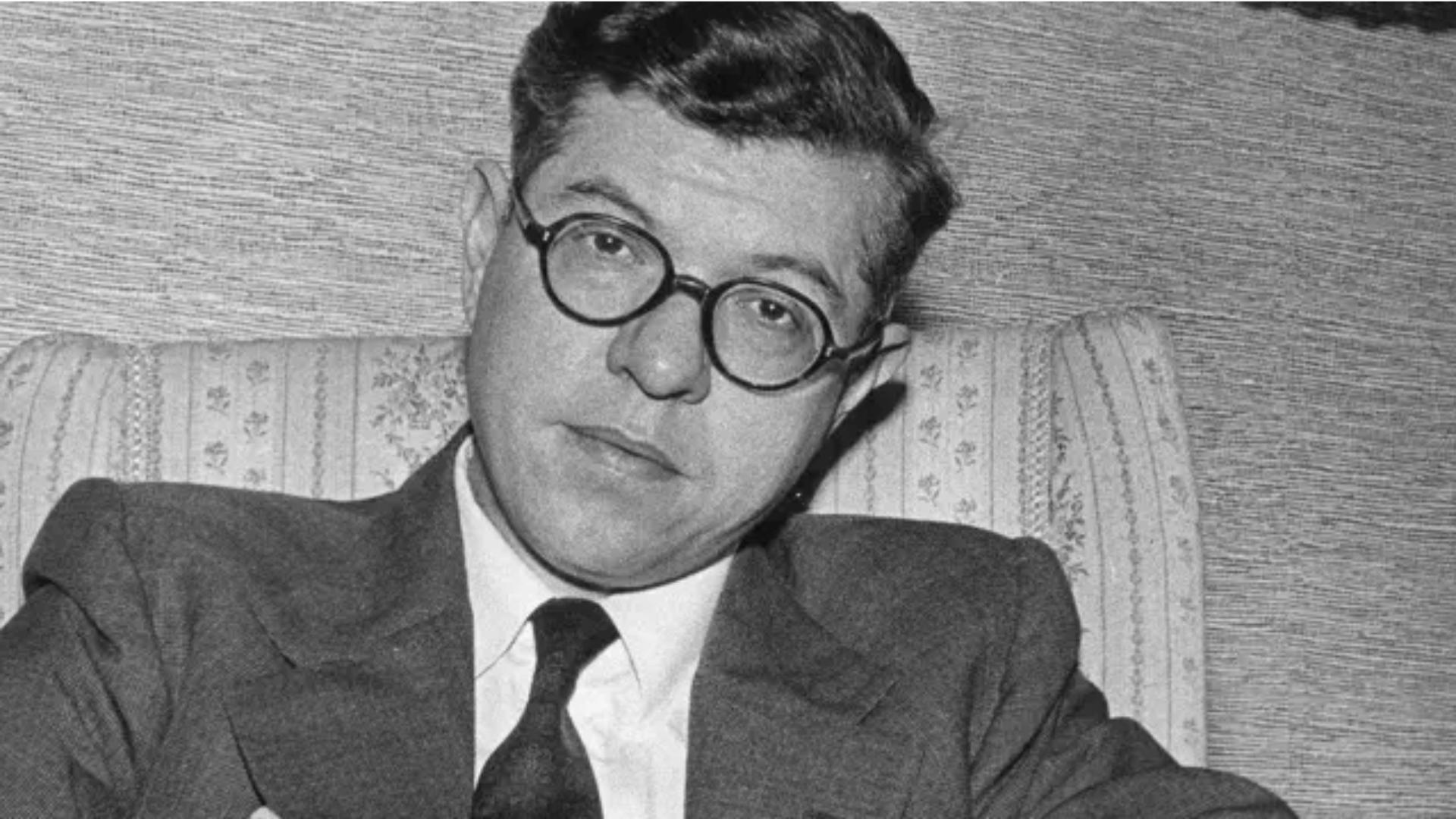

Image Source: BBC
Fred Hoyle, a British astrophysicist, is remembered for his controversial yet impactful ideas. He opposed the Big Bang theory, coining the term as a critique, while supporting a steady-state universe model.
Hoyle made vital contributions, particularly in nucleosynthesis, the creation of elements in stars.
His theories advanced our knowledge of stellar processes. Hoyle’s legacy highlights the value of debate in science.
- Lifespan: 1915–2001
- Achievement: Explained nucleosynthesis in stars
18. Stephen Hawking
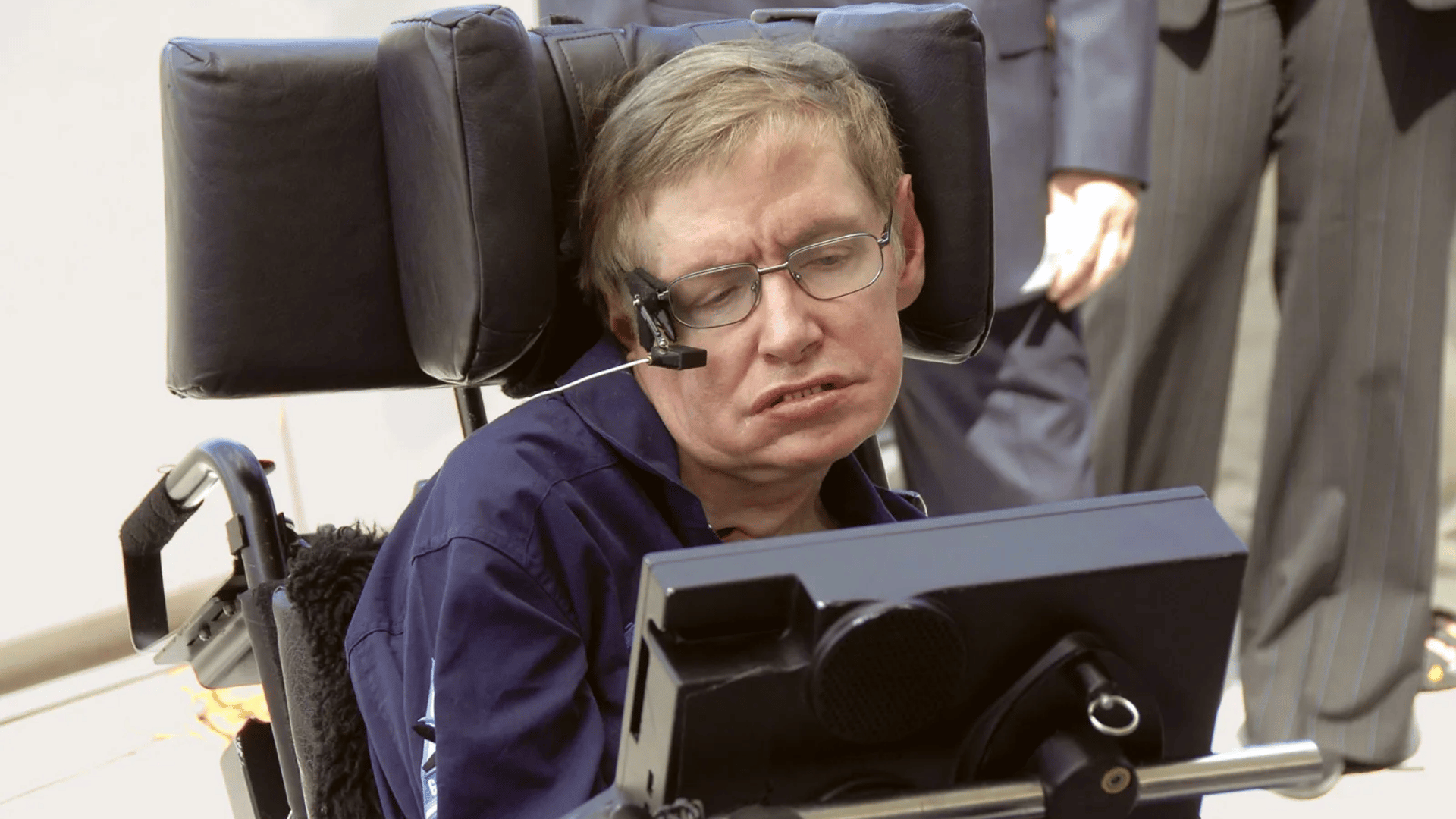

Image Source: Britannica
Stephen Hawking became one of the most famous astrophysicists of modern times, known for his groundbreaking work on black holes.
He showed that black holes emit radiation, now called Hawking radiation, which changed our understanding of these mysterious objects.
Despite physical challenges from ALS, he authored best-selling books, inspiring millions. Hawking’s brilliance brought cosmology into the public eye. His life embodied science and resilience.
- Lifespan: 1942–2018
- Achievement: Discovered Hawking radiation from black holes
19. Carl Sagan
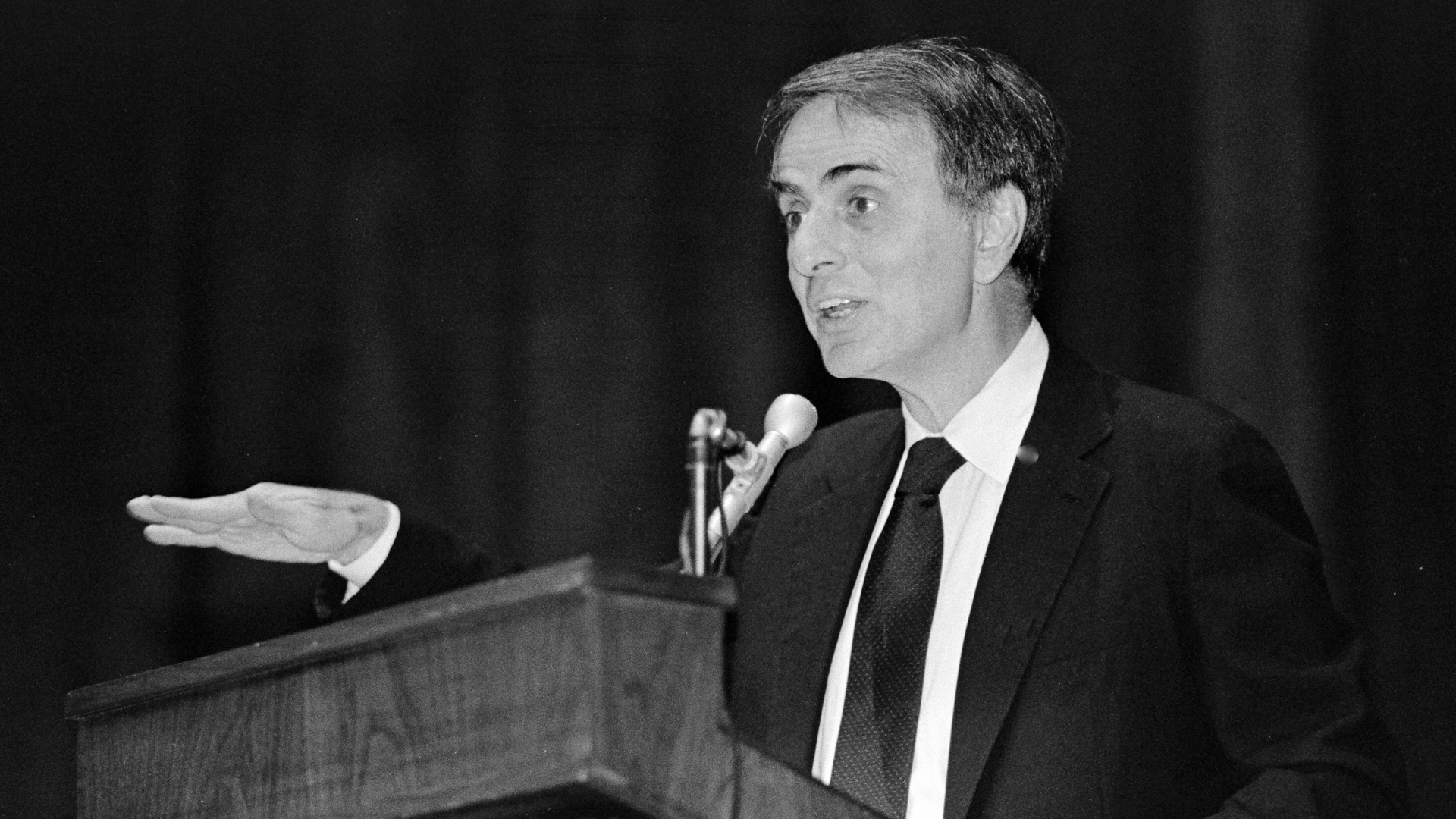

Image Source: Wikiquote
Carl Sagan was a celebrated astrophysicist and science communicator who made the cosmos accessible to millions.
He contributed to planetary science, particularly in understanding Venus, Mars, and the outer planets. His book Cosmos and the accompanying television series inspired public interest in space.
Sagan emphasized the search for extraterrestrial life. His ability to combine science with storytelling made him one of the most famous astrophysicists in history.
- Lifespan: 1934–1996
- Achievement: Popularized science and advanced planetary research
20. Vera Rubin
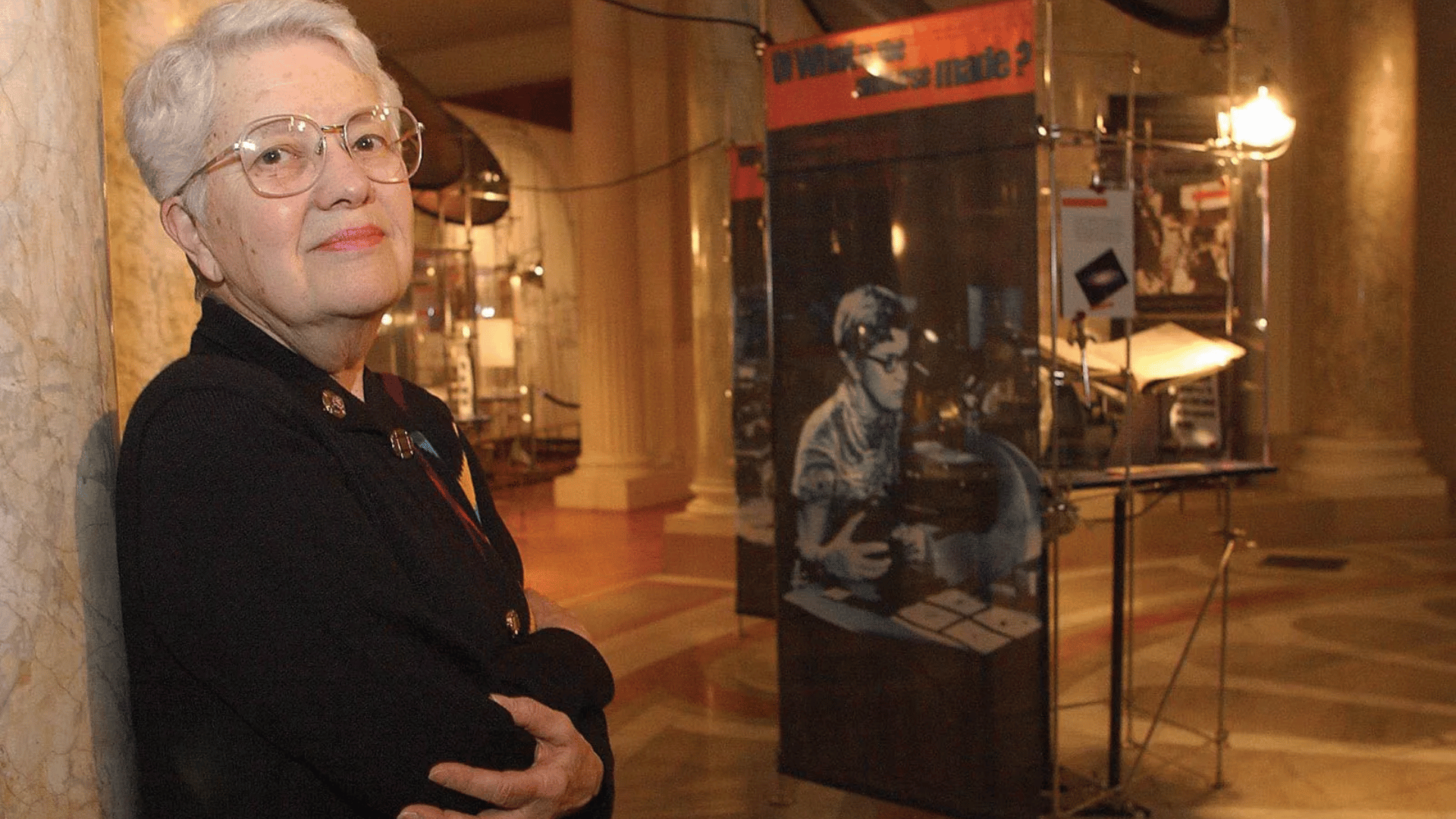

Image Source: Britannica
Rubin was a pioneering female astrophysicist whose work provided the first strong evidence for dark matter.
While studying galactic rotation curves, she observed stars moving faster than expected, pointing to unseen mass. Her discoveries fundamentally changed cosmology. Rubin also broke barriers for women in science.
Her contributions remain a cornerstone in understanding the invisible universe. She reshaped how we view galaxies and their structure.
- Lifespan: 1928–2016
- Achievement: Provided evidence for dark matter
21. Jocelyn Bell Burnell
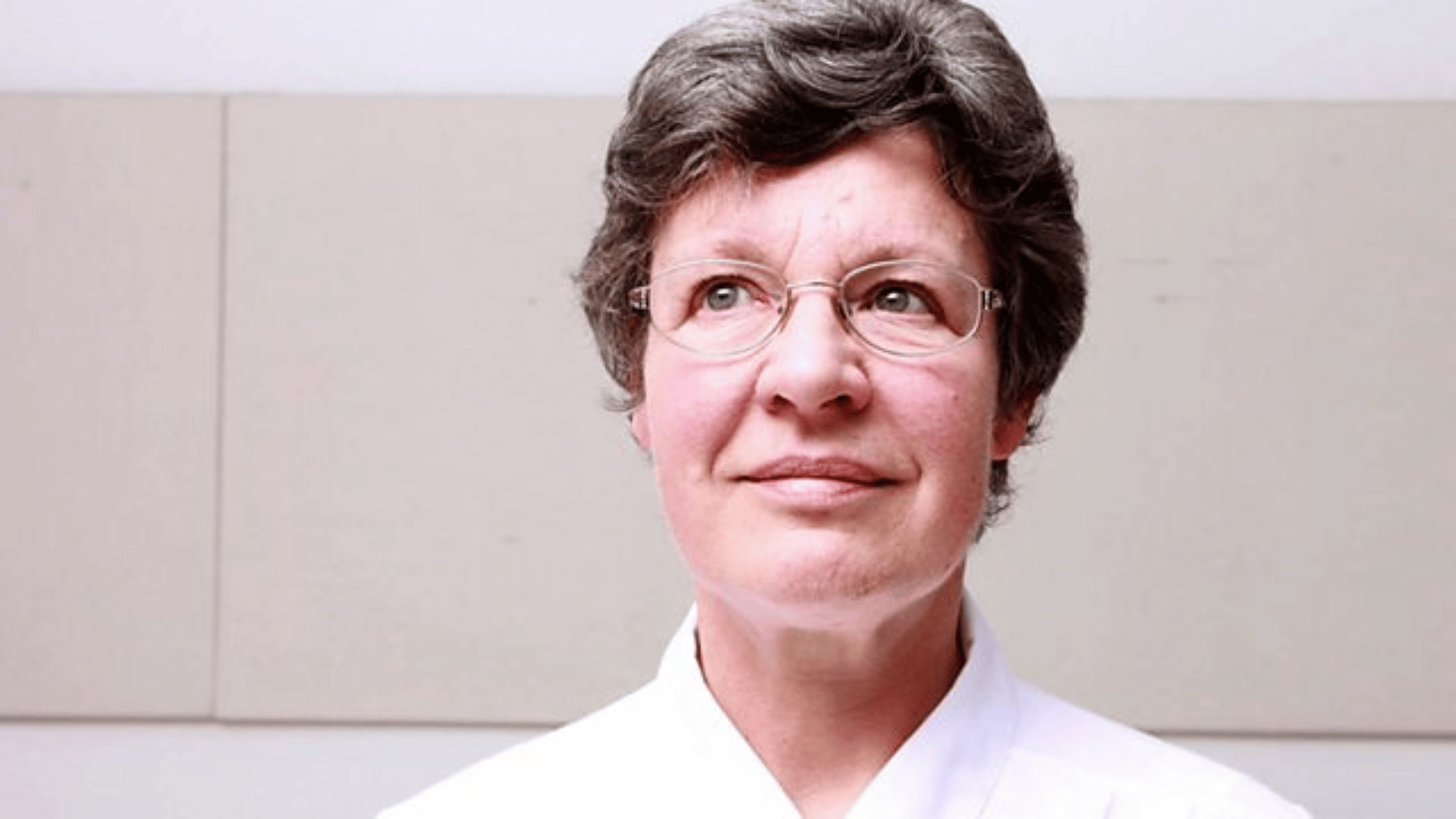

Image Source: BBC
Jocelyn Bell Burnell is credited with discovering pulsars in 1967, while still a graduate student. This breakthrough revealed rapidly rotating neutron stars emitting beams of radiation.
Despite being overlooked for the Nobel Prize, her findings remain one of the most significant in astrophysics.
Bell Burnell later became a strong advocate for women in science. Her contributions embody both brilliance and perseverance.
- Lifespan: 1943–Present
- Achievement: Discovered pulsars
22. Kip Thorne
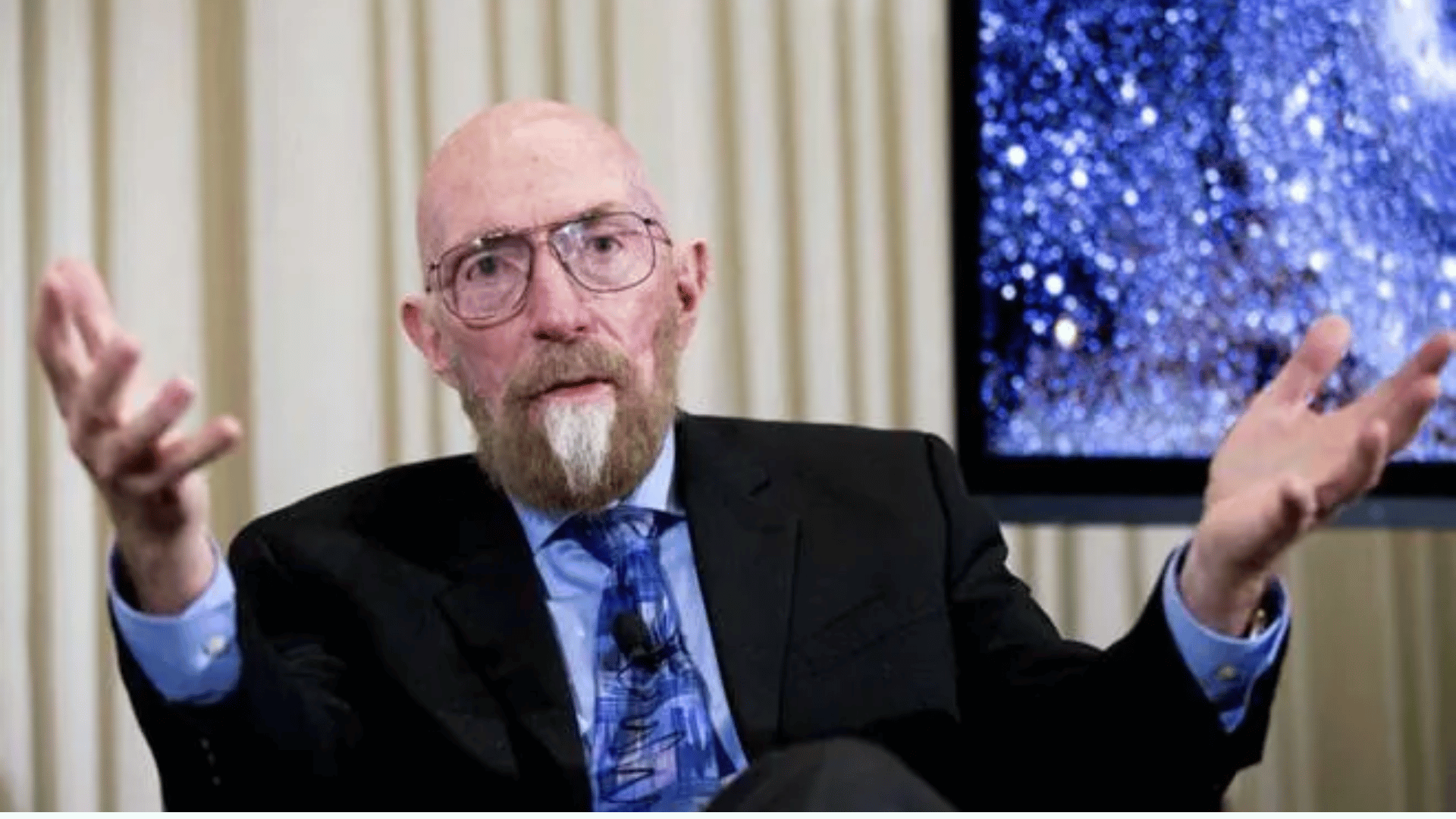

Image Source: The Financial Express
Kip Thorne is a leading theoretical astrophysicist, known for his work on black holes, wormholes, and gravitational waves.
He was a co-recipient of the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics for contributions to the LIGO project, which detected gravitational waves. Thorne also served as a science advisor for the film Interstellar.
His visionary ideas bridged science and imagination. His work continues to push boundaries in astrophysics.
- Lifespan: 1940–Present
- Achievement: Co-discovered gravitational waves with LIGO
23. Andrea Ghez
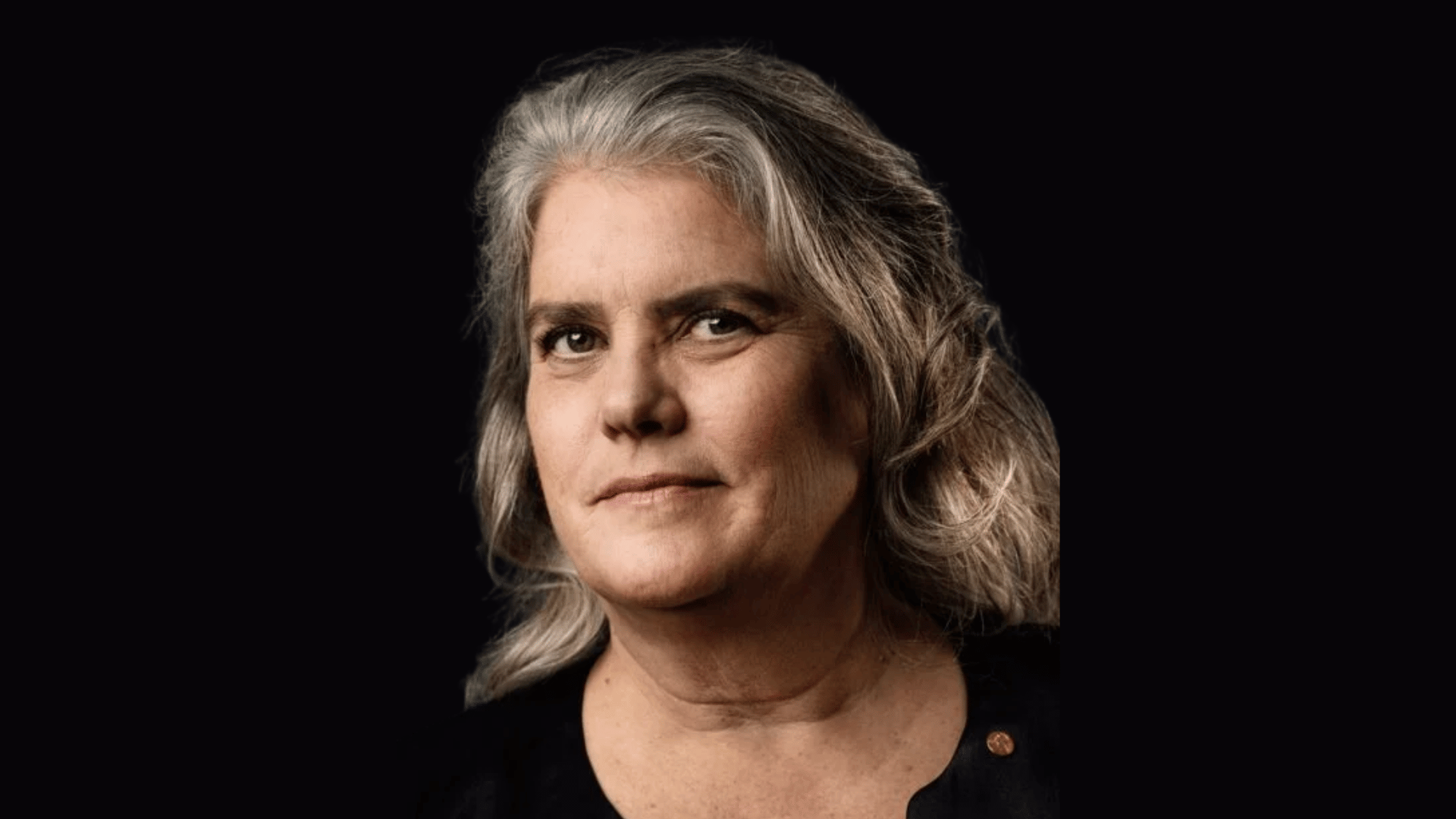

Image Source: Nobel Prize
Andrea Ghez is a modern astrophysicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2020. She is best known for her research proving the existence of a supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy.
Using advanced telescopic techniques, she tracked stellar orbits near Sagittarius A*. Her groundbreaking work confirmed long-suspected theories.
Ghez is also an advocate for women in science. Her achievements inspire future generations.
- Lifespan: 1965–Present
- Achievement: Proved a supermassive black hole exists in the Milky Way
24. Brian Greene

Image Source: NBC News
Brian Greene is an American theoretical physicist and astrophysicist who is widely recognized for his work on string theory.
Beyond academia, he has written bestselling books such as The Elegant Universe, bringing complex topics to the public.
Greene also co-founded the World Science Festival to promote scientific engagement. His ability to explain intricate theories made him a household name. Greene bridges advanced theory with education.
- Lifespan: 1963–Present
- Achievement: Advanced string theory and public science education
25. Michio Kaku

Image Source: The Guardian
Michio Kaku is a renowned American theoretical physicist and futurist who specializes in string theory.
Beyond academia, he has gained global recognition for his engaging books and media appearances that bring astrophysics to the general public.
Kaku blends science with predictions about the future of humanity in space. His charisma makes him a popular science communicator. He continues to inspire curiosity about the universe.
- Lifespan: 1947–Present
- Achievement: Popularized string theory and future space science
26. Neil DeGrasse Tyson

Image Source: CNN
Neil DeGrasse Tyson is one of the big astrophysicists of our time, known for his dynamic communication style.
As the director of the Hayden Planetarium in New York, he has promoted science education and public engagement.
Tyson revived Carl Sagan’s Cosmos series, captivating new generations. He advocates for space exploration and critical thinking. His influence extends beyond academia into mainstream culture.
- Lifespan: 1958–Present
- Achievement: Popularized astrophysics and directed the Hayden Planetarium
27. Georges Lemaître
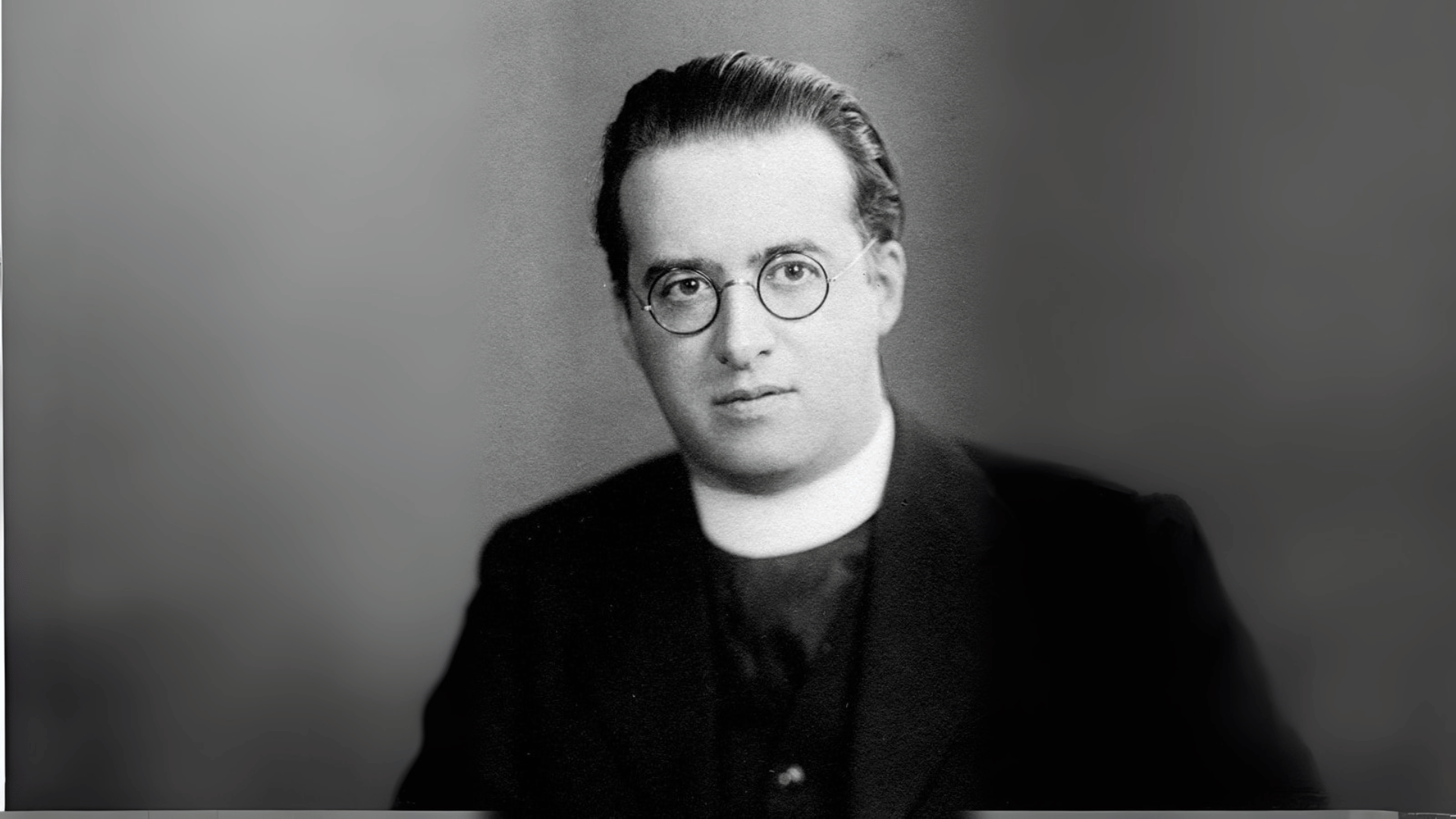
Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Georges Lemaître, a Belgian priest and astrophysicist, first proposed the idea of the expanding universe, which later became the basis for the Big Bang theory.
His work combined faith and science in unique ways, showing that both could coexist. Though initially overlooked, his theories were later confirmed by Hubble’s observations.
Lemaître’s bold insights revolutionized cosmology. He remains a central figure in modern astrophysics.
- Lifespan: 1894–1966
- Achievement: Proposed the Big Bang theory of the universe
28. Arno Penzias

Image Source: Ynetnews
Arno Penzias, along with Robert Wilson, identified the cosmic microwave background radiation in 1964. This monumental finding provided strong evidence for the Big Bang theory.
Using a radio antenna, they detected faint microwave noise that turned out to be the afterglow of the early universe.
Their discovery won them the Nobel Prize. Penzias’s work offered proof of the universe’s origins. He changed cosmology forever.
- Lifespan: 1933–2024
- Achievement: Identified cosmic microwave background radiation
29. Robert Woodrow Wilson
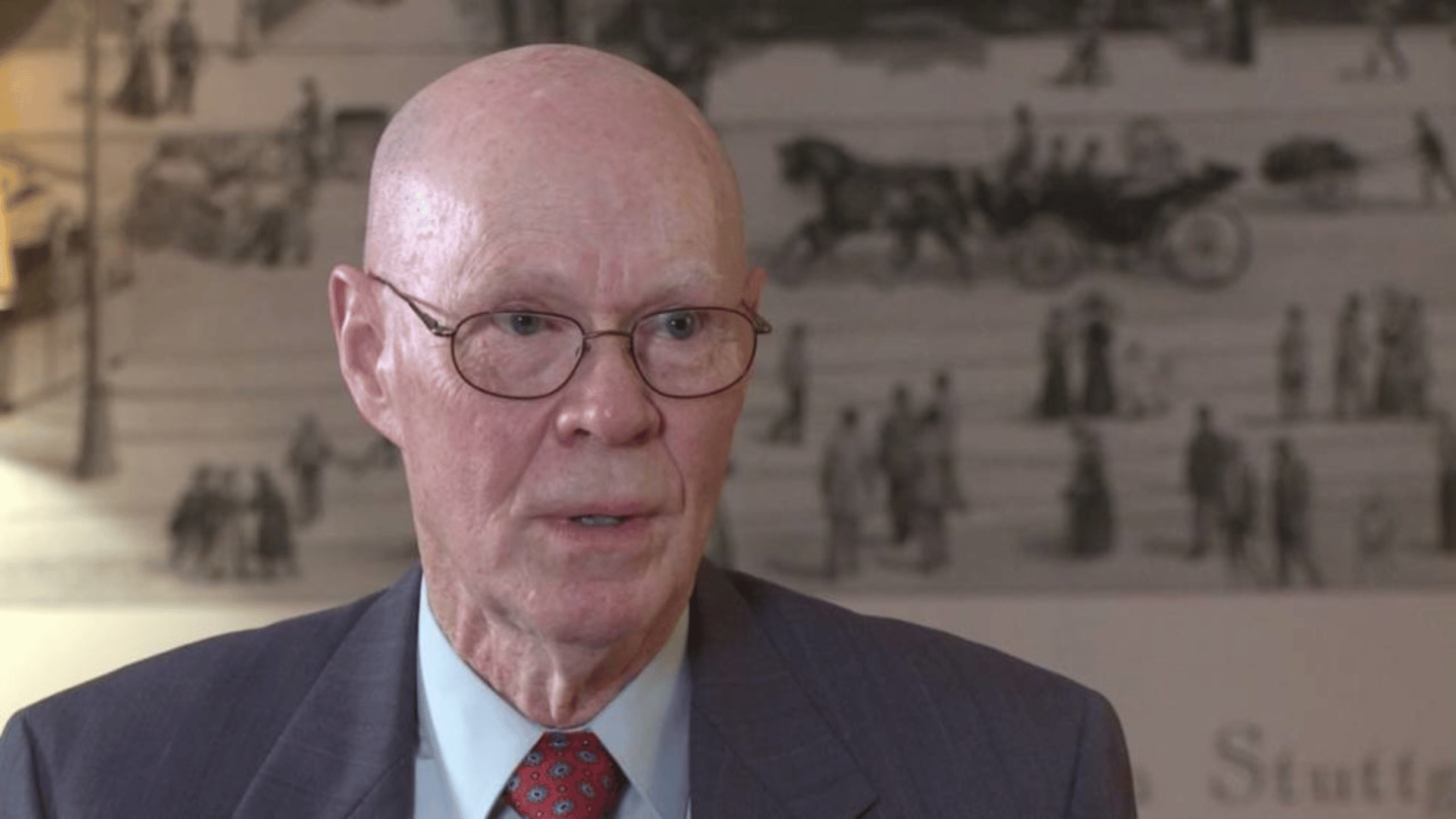

Image Source: Nobel Prize
Robert Wilson partnered with Arno Penzias in the discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, a breakthrough that confirmed the Big Bang theory.
These unexpected findings came while working on satellite communications research. Wilson’s contribution earned him the Nobel Prize and secured his place in astrophysics history.
His work reshaped the study of the universe’s beginnings. Wilson’s legacy is a testament to curiosity and scientific precision.
- Lifespan: 1936–Present
- Achievement: Co-discovered cosmic microwave background radiation
30. John Wheeler

Image Source: The New York Times
John Wheeler was an American theoretical physicist who coined the term “black hole” and made critical contributions to relativity and quantum mechanics.
He helped generations of physicists, including Richard Feynman and Kip Thorne. Wheeler played a vital role in bridging theory and astrophysics, especially in understanding space-time.
His creativity gave modern astrophysics its language. His legacy lives on through his students and ideas.
- Lifespan: 1911–2008
- Achievement: Coined the term “black hole” and advanced relativity
31. Martin Rees
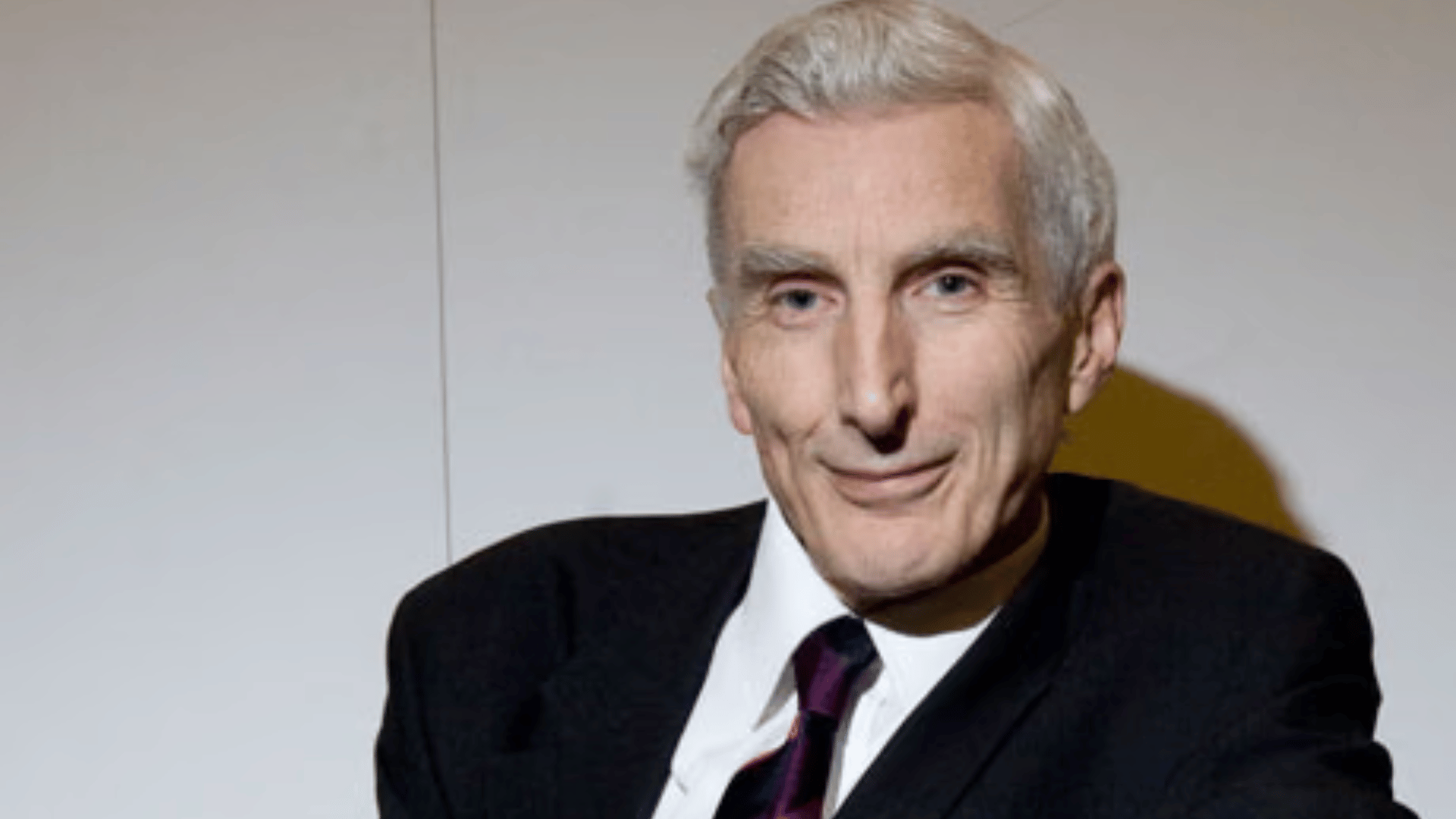

Image Source: The Guardian
Martin Rees, the Astronomer Royal of the United Kingdom, is one of the leading astrophysicists of our time.
His work covers galaxy formation, black holes, and the overall structure of the universe. Rees has also written widely for the public, addressing scientific challenges and future risks.
His influence spans both research and policy. Rees’s insights have shaped how we think about cosmic origins.
- Lifespan: 1942–Present
- Achievement: Advanced theories on galaxy formation and black holes
32. Allan Sandage
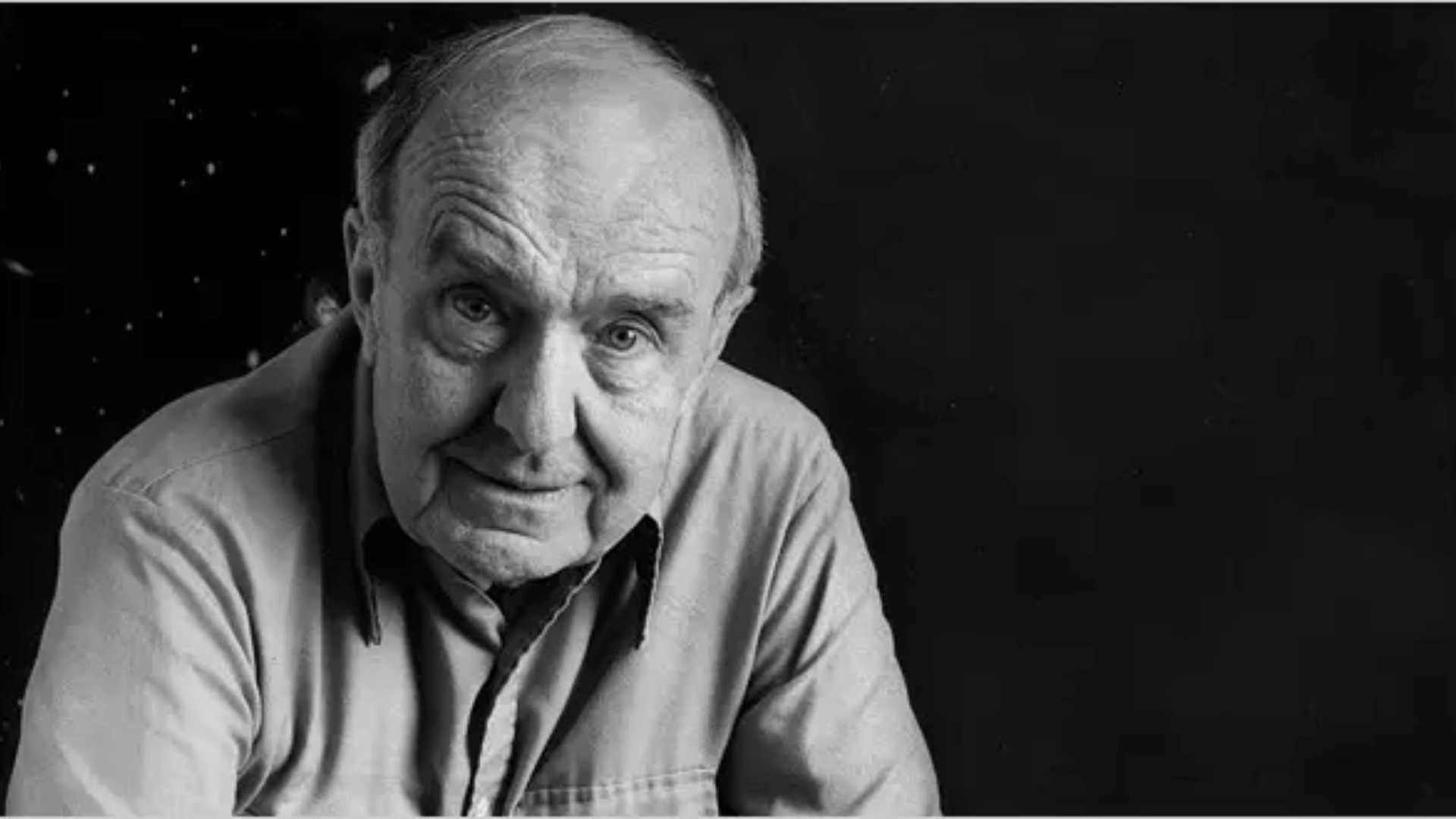

Image Source: The New York Times
Allan Sandage was a key figure in observational cosmology, extending Hubble’s work on the universe’s expansion.
He refined estimates of the Hubble constant and studied the age of the universe. Sandage also mapped distant galaxies and quasars, expanding our cosmic horizon.
His careful measurements provided essential data for modern cosmology. Sandage’s persistence in refining cosmic distances remains legendary.
- Lifespan: 1926–2010
- Achievement: Refined the Hubble constant and studied cosmic expansion
33. Frank Drake
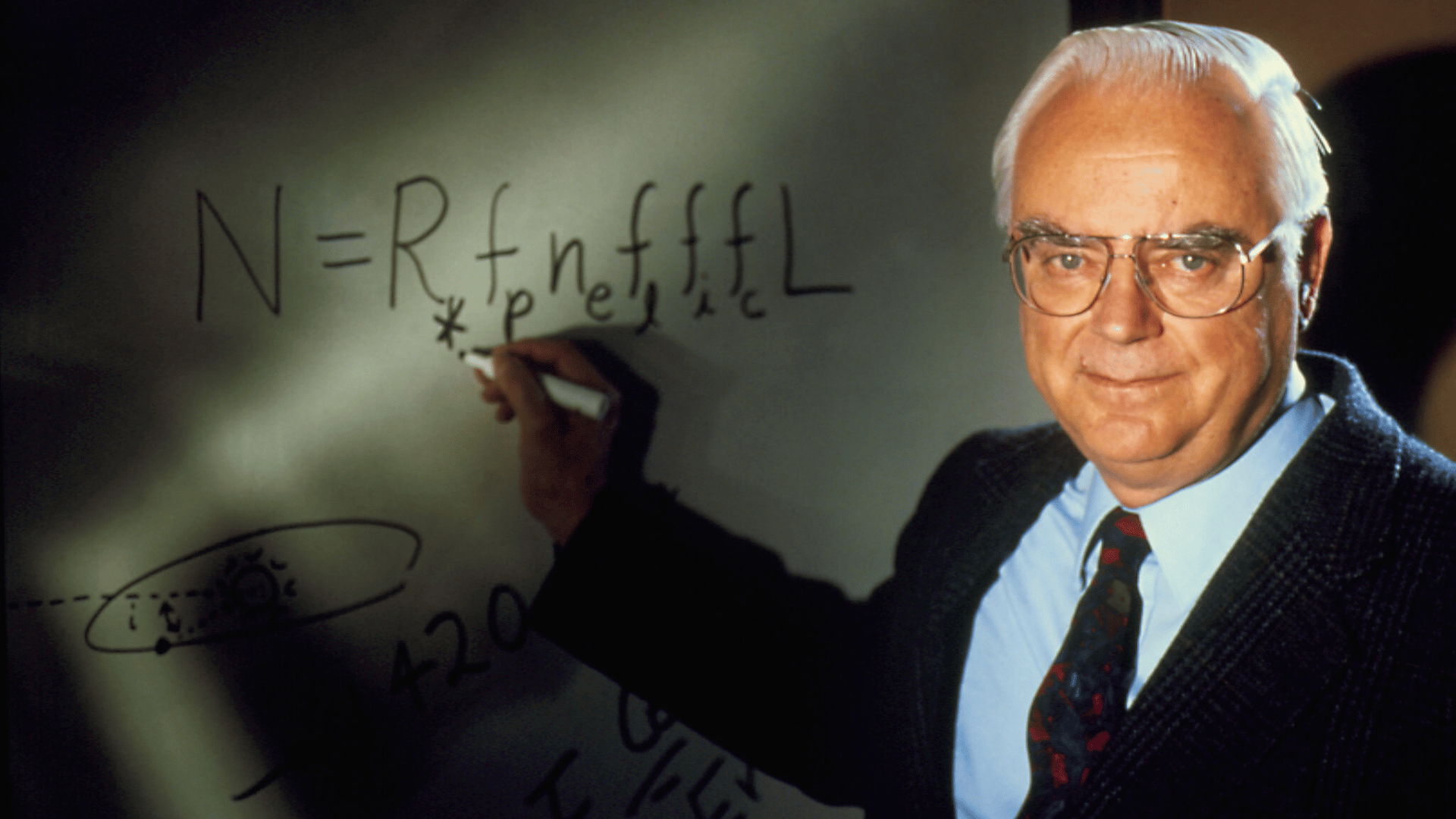
Image Source: The New York Times
Frank Drake was an American astrophysicist who pioneered the scientific search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI).
He developed the Drake Equation, estimating the number of advanced civilizations in the galaxy. Drake also conducted the first modern SETI experiment using radio telescopes.
His vision expanded humanity’s search for life beyond Earth. Drake’s legacy lies in his bold curiosity about the universe.
- Lifespan: 1930–2022
- Achievement: Created the Drake Equation and advanced SETI
34. Margaret Burbidge
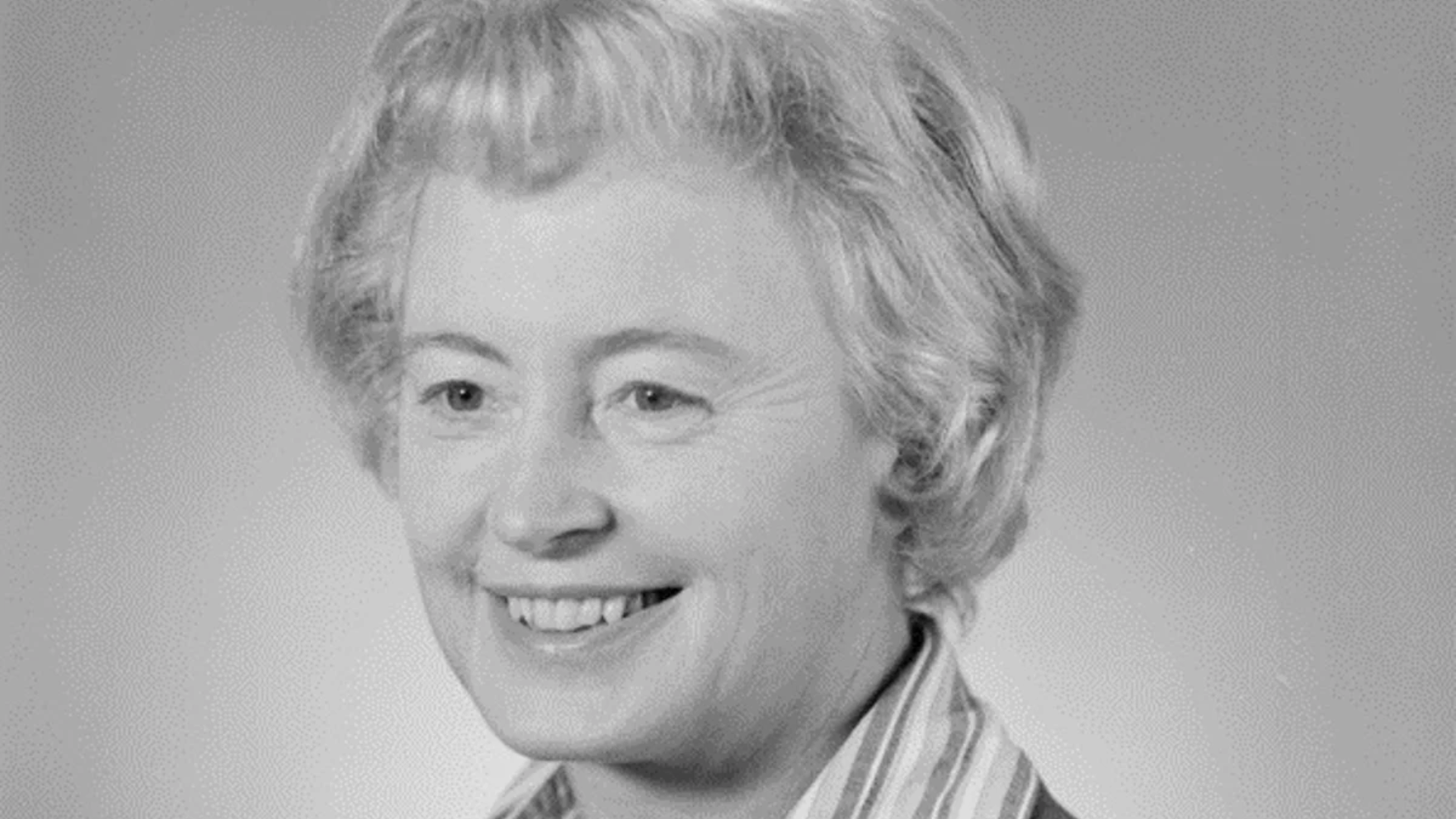

Image Source: The Guardian
Margaret Burbidge was a British-American astrophysicist who made major contributions to stellar nucleosynthesis, the process of creating elements within stars.
She co-authored the landmark B²FH paper, explaining how chemical elements are formed in stars. Burbidge also advanced studies of quasars and galaxies.
She broke barriers for women in astronomy. Her pioneering work reshaped our understanding of the chemical evolution of the cosmos.
- Lifespan: 1919–2020
- Achievement: Co-authored B²FH paper on nucleosynthesis
35. Jan Oort

Image Source: Britannica Kids
Jan Oort, a Dutch astrophysicist, revolutionized our knowledge of the Milky Way.
He discovered evidence for dark matter within galaxies and proposed the existence of the Oort Cloud, a reservoir of icy bodies at the edge of the solar system.
Oort’s research reshaped galactic astronomy. His name lives on in countless astronomical terms. Oort’s insights helped map the invisible structure of the cosmos.
- Lifespan: 1900–1992
- Achievement: Proposed the Oort Cloud and studied galactic dark matter
36. Antony Hewish
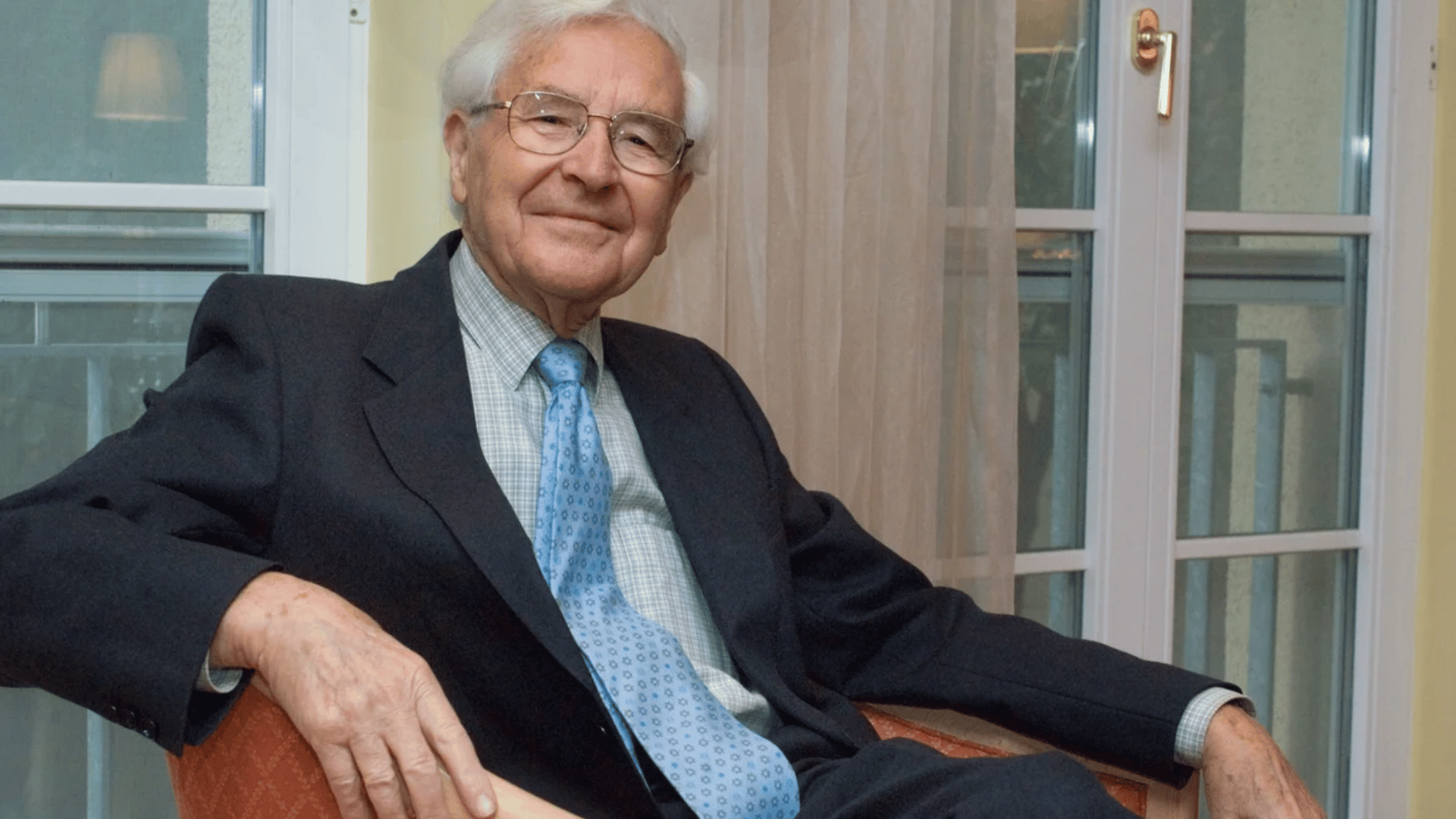

Image Source: The Guardian
Antony Hewish was a British radio astronomer awarded the Nobel Prize for his role in the discovery of pulsars, though the recognition controversially excluded Jocelyn Bell Burnell.
His work in radio astronomy advanced techniques that opened new windows into the universe.
Despite debates, his contributions remain significant. Hewish’s pioneering methods helped capture cosmic phenomena otherwise hidden from view.
- Lifespan: 1924–2021
- Achievement: Shared Nobel Prize for pulsar discovery
37. Charles Messier
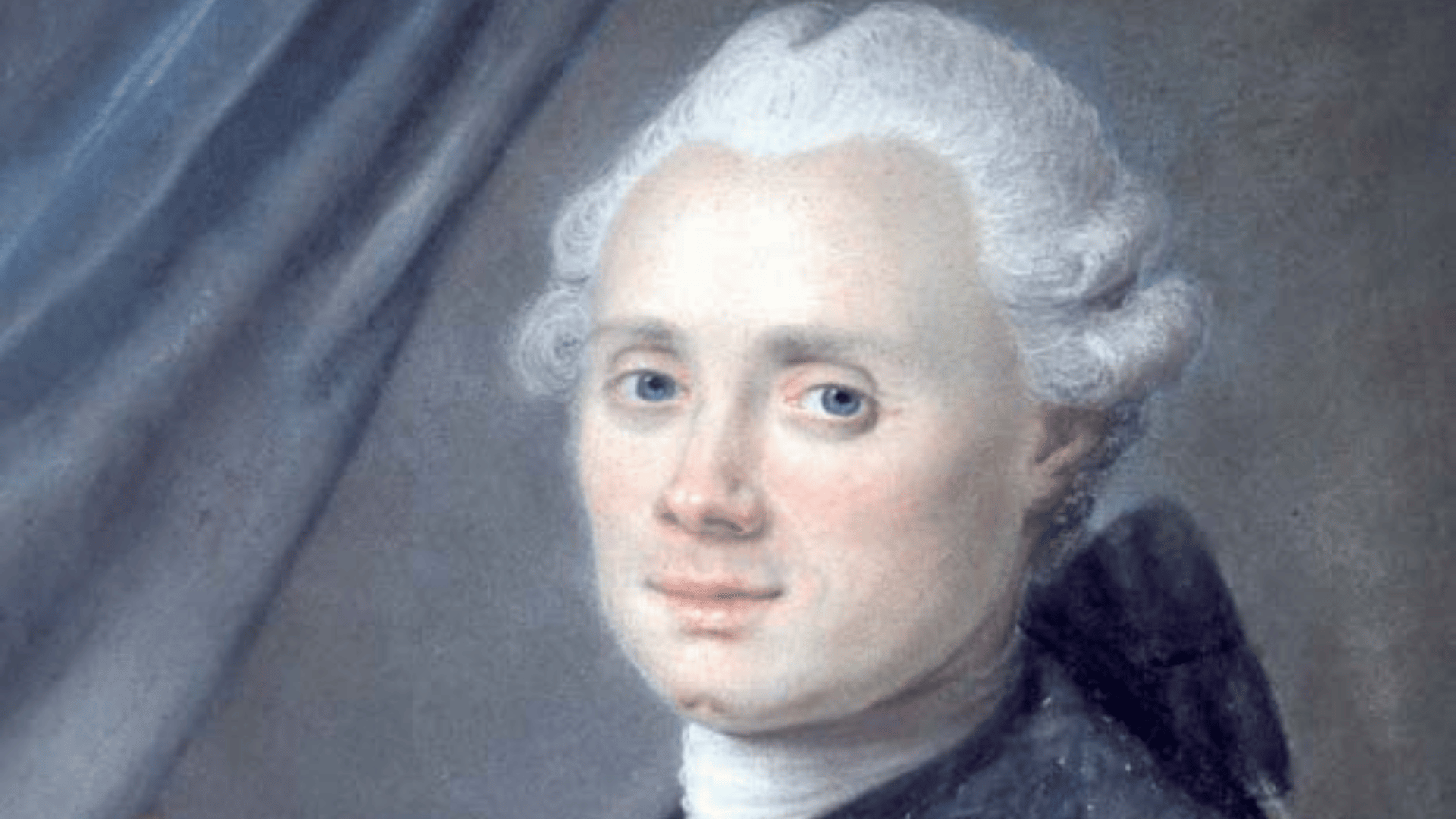

Image Source: Wikipedia
Charles Messier was a French astronomer best known for compiling the Messier Catalog, a list of 110 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies.
His aim was to help comet hunters avoid confusion with fixed deep-sky objects. Ironically, his catalog became one of astronomy’s most valuable tools.
Messier’s work remains widely used by both amateur and professional astronomers. His catalog continues to help stargazers centuries later.
- Lifespan: 1730–1817
- Achievement: Created the Messier Catalog of deep-sky objects
38. Henri Poincaré
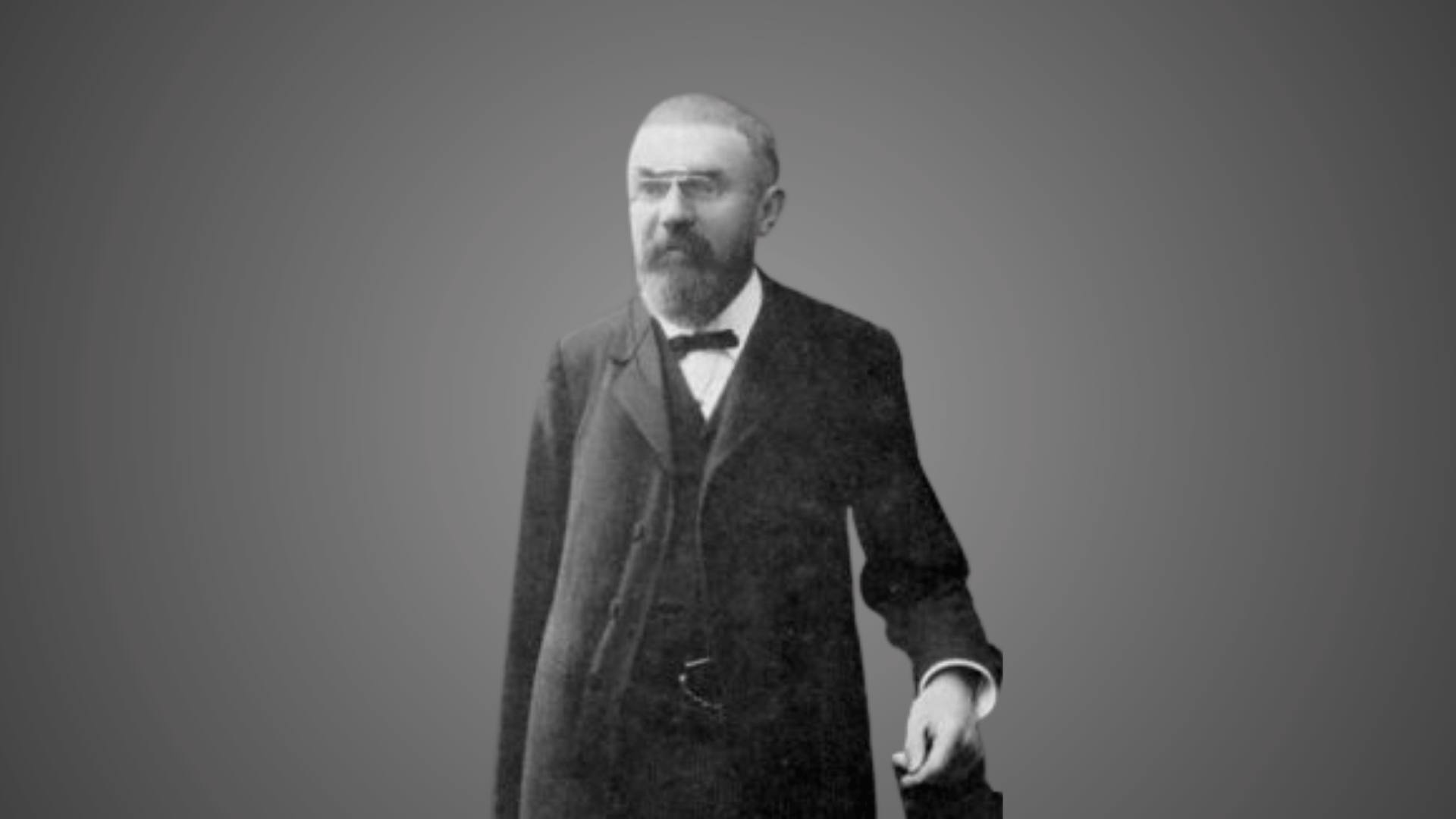

Image Source: Simple Wikipedia
Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician and theoretical physicist whose work influenced celestial mechanics and chaos theory.
He studied the three-body problem, which revealed the complexity of orbital dynamics. Poincaré’s insights foreshadowed ideas that later became central in modern physics and astrophysics.
His deep mathematical thinking reshaped how scientists viewed space and time. Poincaré’s brilliance made him a true giant of theoretical science.
- Lifespan: 1854–1912
- Achievement: Advanced celestial mechanics and chaos theory
39. Harlow Shapley
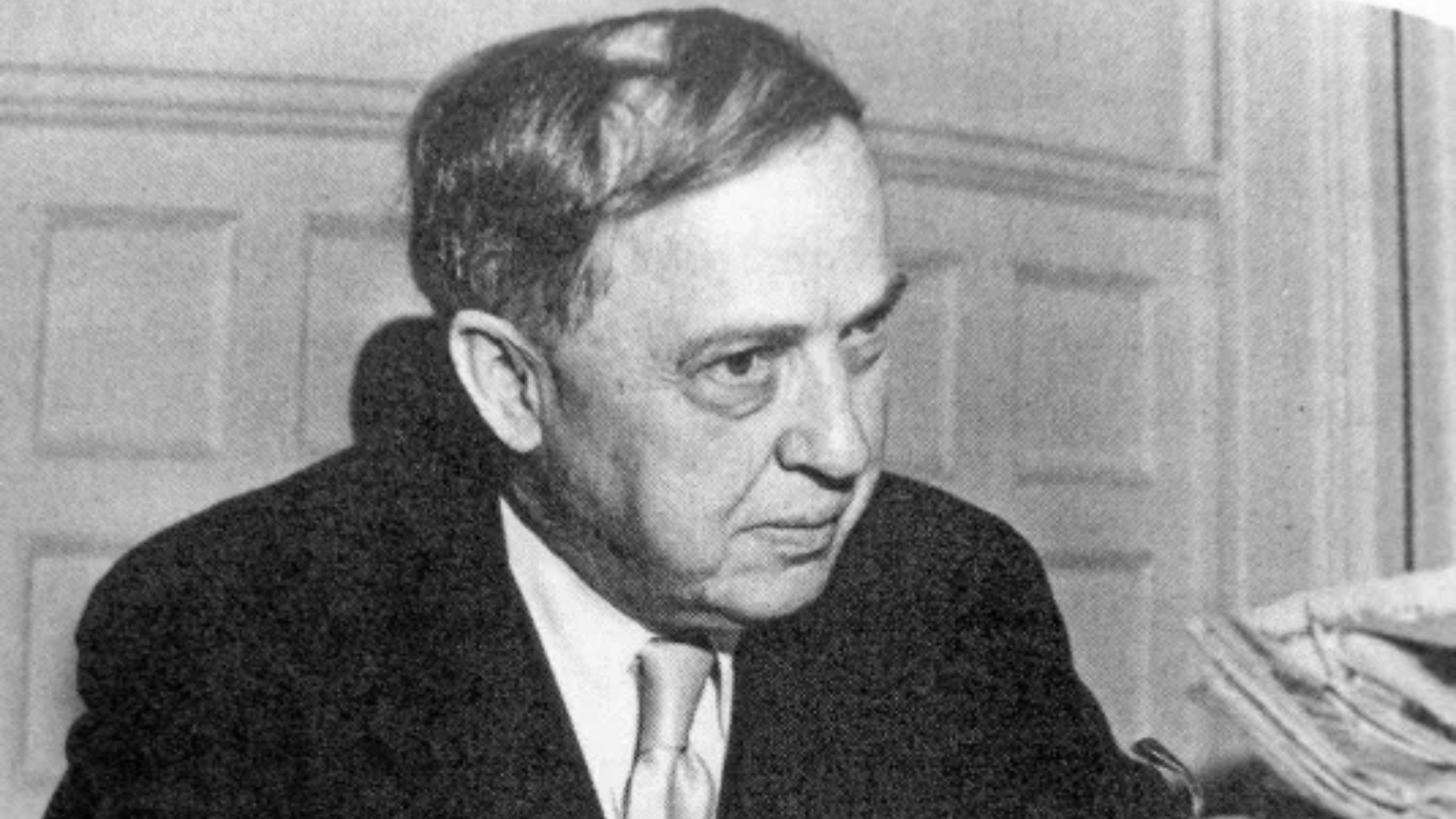

Image Source: Pasadena Star News
Harlow Shapley was an American astrophysicist who mapped the Milky Way and determined our solar system’s location far from the galactic center.
His studies of globular clusters showed the vast scale of the galaxy. Shapley also engaged in public science debates, defending the expanding universe theory.
His work set the stage for modern galactic astronomy. Shapley’s vision redefined humanity’s place in the cosmos.
- Lifespan: 1885–1972
- Achievement: Determined Milky Way structure and solar position
How Their Work Changed Our View of the Universe
The discoveries made by famous astrophysicists completely changed how humans understand their place in the universe and what exists beyond Earth.
Before these scientists, people believed Earth was the center of everything, but astrophysicists proved that our planet is just one small world orbiting an average star in a vast galaxy.
Their work revealed that the universe is billions of years old, constantly expanding, and contains trillions of galaxies with countless stars and planets.
They discovered black holes, dark matter, and dark energy that make up most of the universe but remain invisible to human eyes.
These discoveries showed that humans know very little about space and that countless mysteries still wait to be solved by future generations of scientists.
Conclusion
Famous astrophysicists have given humanity an incredible gift by revealing the wonders and mysteries of the universe through their tireless dedication and brilliant minds.
Their work continues to inspire young people to pursue careers in science and helps everyone appreciate the beauty and complexity of space.
From understanding how stars create the elements that make up human bodies to discovering planets orbiting distant stars, these scientists have shown that anything is possible with curiosity and hard work.
The legacy of astrophysicists reminds people that there is always more to learn and explore in the vast cosmos that surrounds our tiny planet.
Start your own space learning journey today by reading astronomy books or watching documentaries about these amazing scientists.