Space has always bewitched humanity, sparking curiosity and wonder about what lies beyond our planet.
From breathtaking images of galaxies to the mysteries of black holes, the universe continues to inspire both scientists and dreamers alike.
This blog brings together a collection of cool facts about space that are not only surprising but also genuinely fun and educational.
These space facts go beyond the usual trivia, offering readers a chance to learn details that are overlooked yet deeply attractive.
Why Space Feels Almost Endless?
One of the most fascinating facts about space is its unimaginable vastness.
The observable universe stretches an estimated 93 billion light-years across, containing billions of galaxies, each one filled with countless stars, planets, and cosmic wonders.
To truly grasp this scale, it helps to understand what a light-year means. It’s the distance light travels in a single year, which is about 5.88 trillion miles.
That’s an almost impossible number to picture. Even the closest star beyond our Sun, Proxima Centauri, sits more than 4 light-years away, so the light we see from it tonight actually left years ago.
For perspective, if a person could drive a car at highway speeds all the way to the Moon, it might take a few months, but reaching the nearest star would still take tens of millions of years!
Amazing Space Facts You Should Know
Space is full of surprises, from mysterious black holes to wandering planets. These cool facts reveal the universe’s wonders while making science fun and fascinating.
1. The Universe Is 93 Billion Light-Years Wide
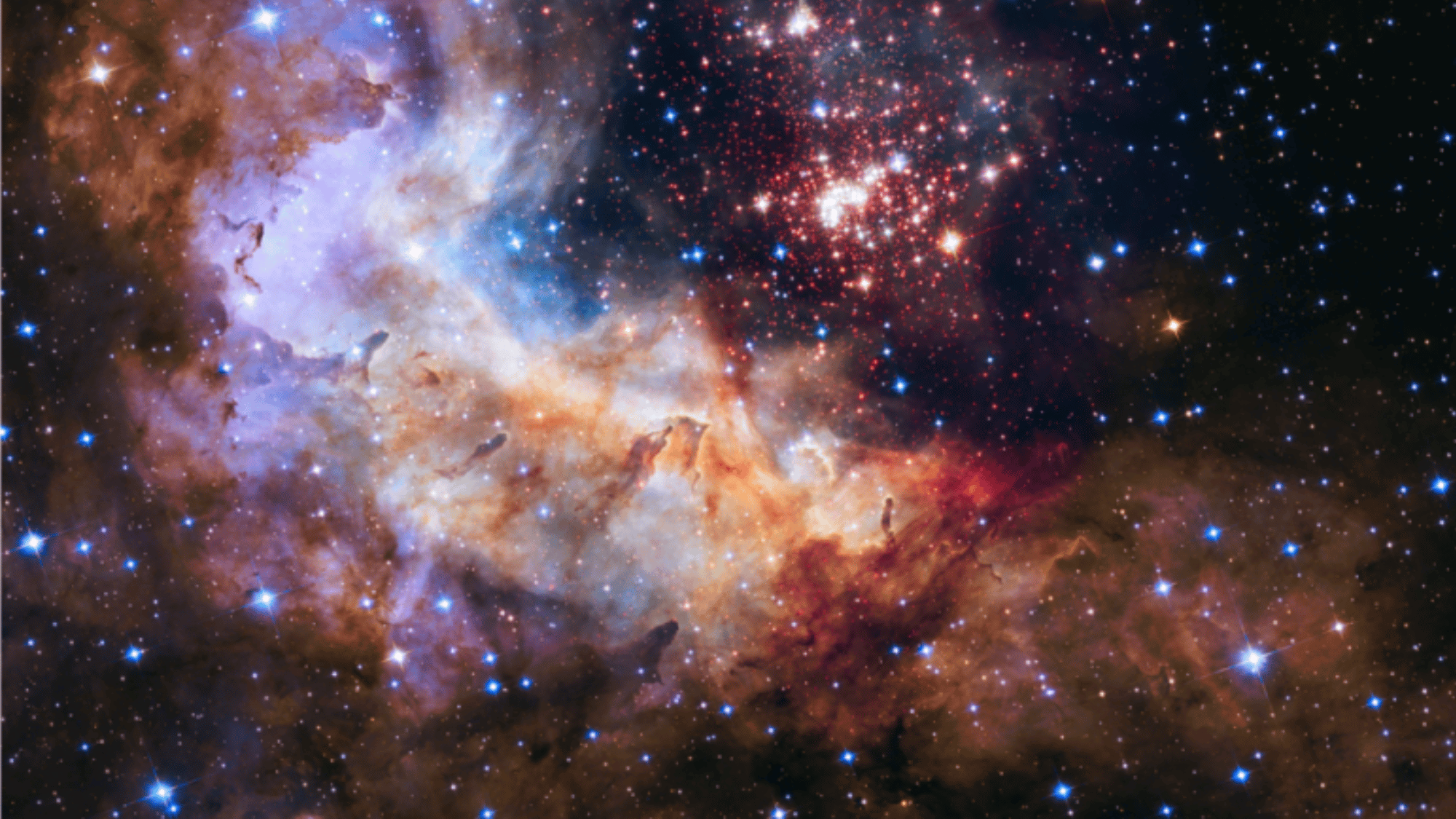

Image Source: NASA
The observable universe is estimated to span approximately 93 billion light-years, encompassing billions of galaxies, each comprising countless stars and planets.
This doesn’t mean the universe ends there; it’s simply the part we can currently observe. What lies beyond is still a mystery.
Astronomers believe the universe could be infinite, but because light takes time to travel, we only see a portion of its vastness, making space truly mind-boggling.
2. A Day on Venus Is Longer Than a Year
Venus rotates so slowly that one day on the planet lasts about 243 Earth days. But it orbits the Sun faster than it spins, meaning its year lasts just 225 Earth days.
This bizarre timing results in a day on Venus being longer than its year.
To make things even stranger, Venus spins backward compared to most planets, so the Sun rises in the west and sets in the east.
3. Neutron Stars Are Incredibly Dense
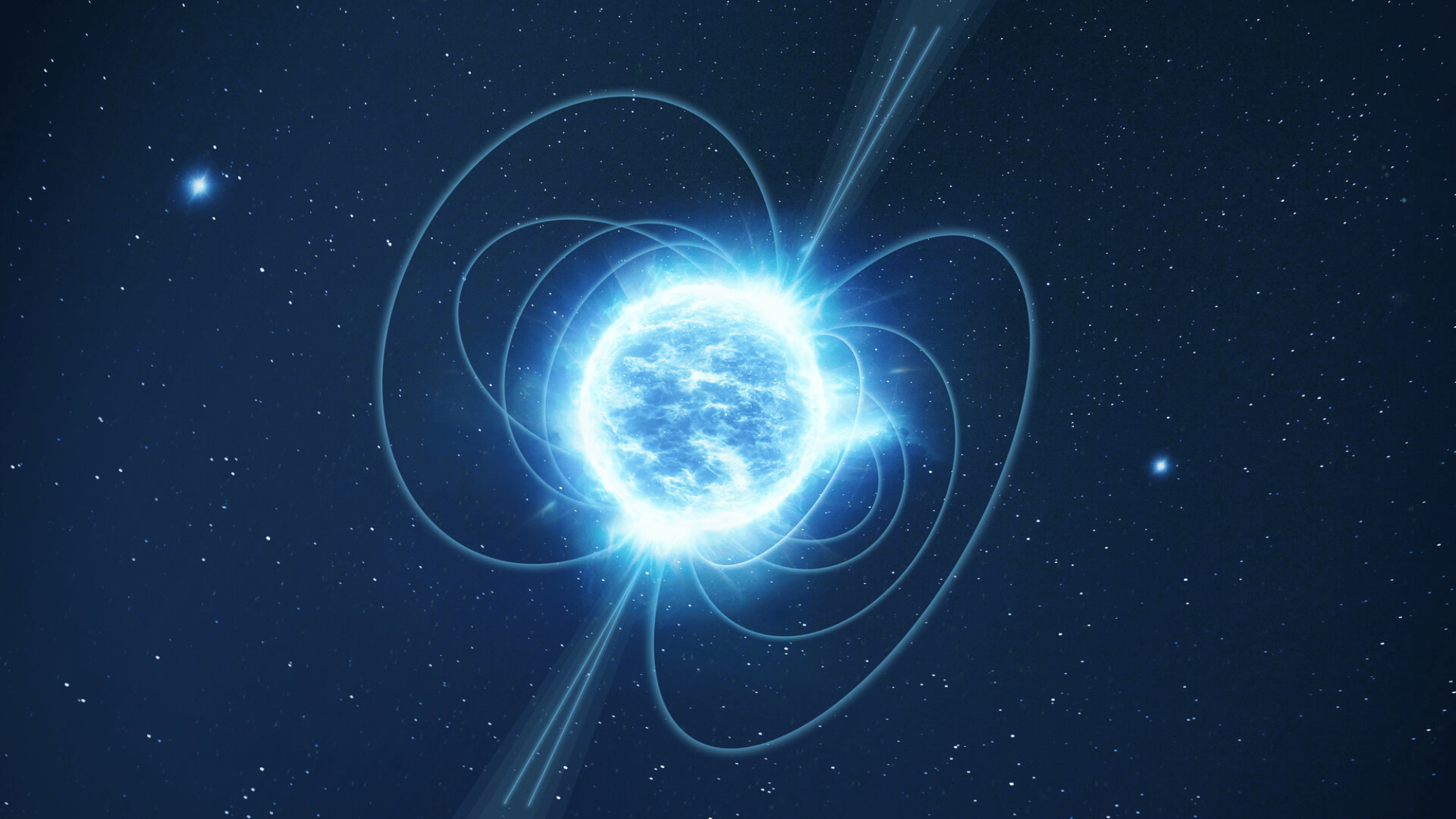
Image Source: European Space Agency
When massive stars collapse, they sometimes form neutron stars. These are so dense that a teaspoon of their material would weigh billions of tons on Earth.
Neutron stars are only about 12 miles across but pack more mass than our Sun. Some spin rapidly, emitting beams of radiation known as pulsars, which scientists use as cosmic lighthouses to study space.
Their extreme density challenges our understanding of physics and the nature of matter itself.
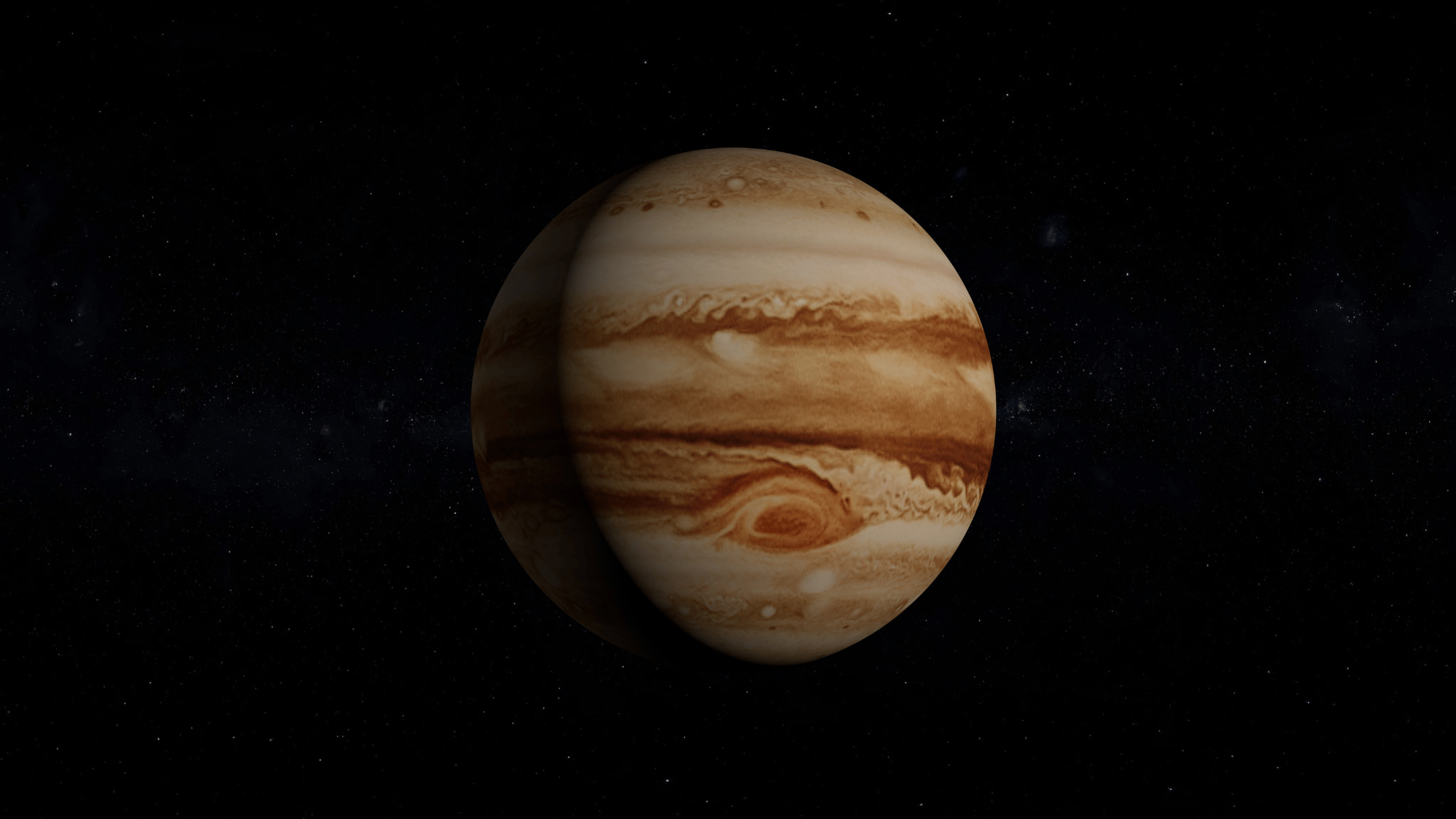
4. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is Shrinking
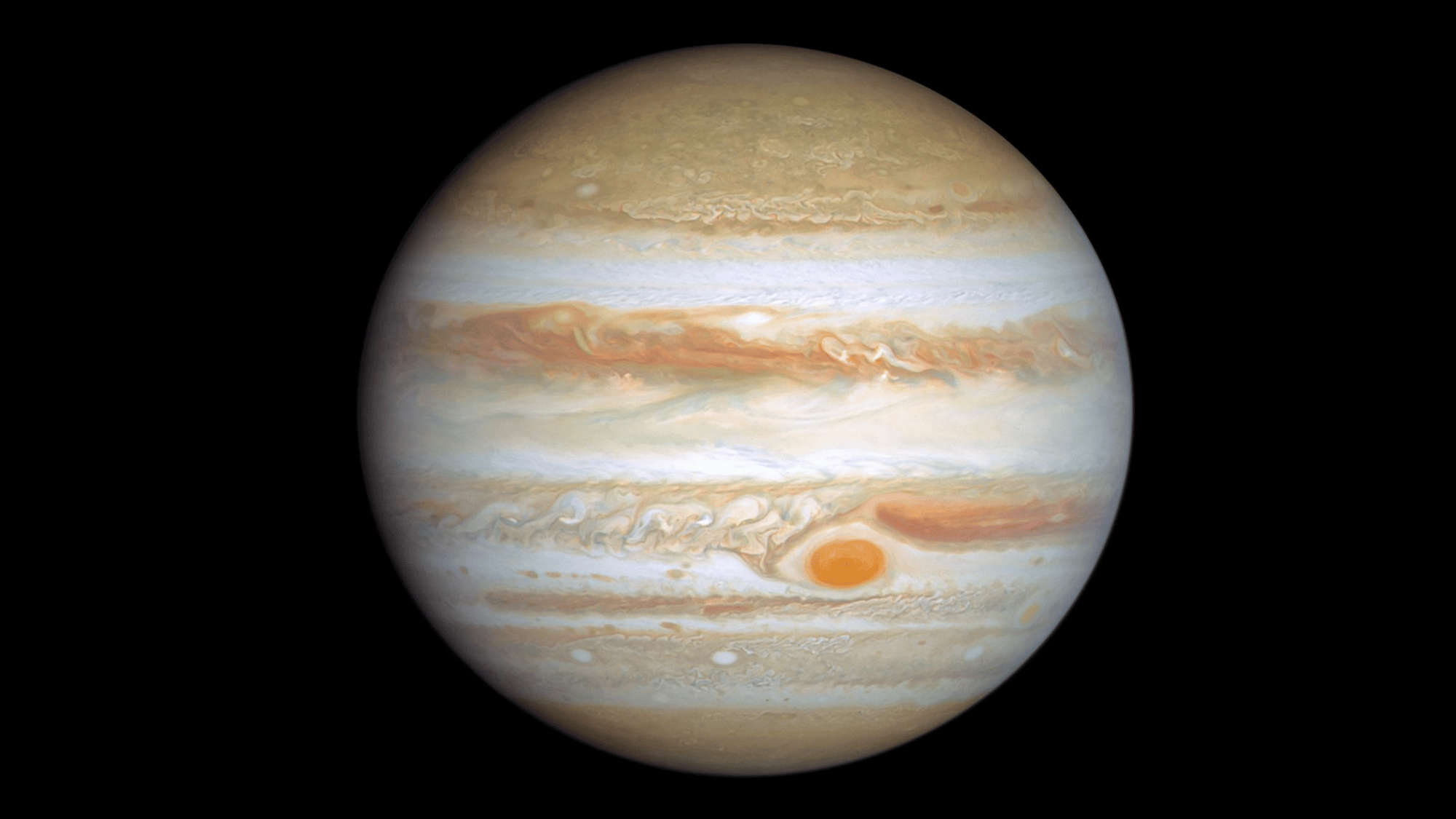
Image Source: Wikipedia
The Great Red Spot on Jupiter, a massive storm larger than Earth, has been raging for centuries.
However, scientists have observed that it’s been shrinking over the past few decades. Once wide enough to fit three Earths across, it’s now just about one Earth in size.
Even so, it remains an incredibly powerful storm system with winds up to 400 miles per hour, making Jupiter’s atmosphere one of the most violent.
5. Saturn Could Float in Water
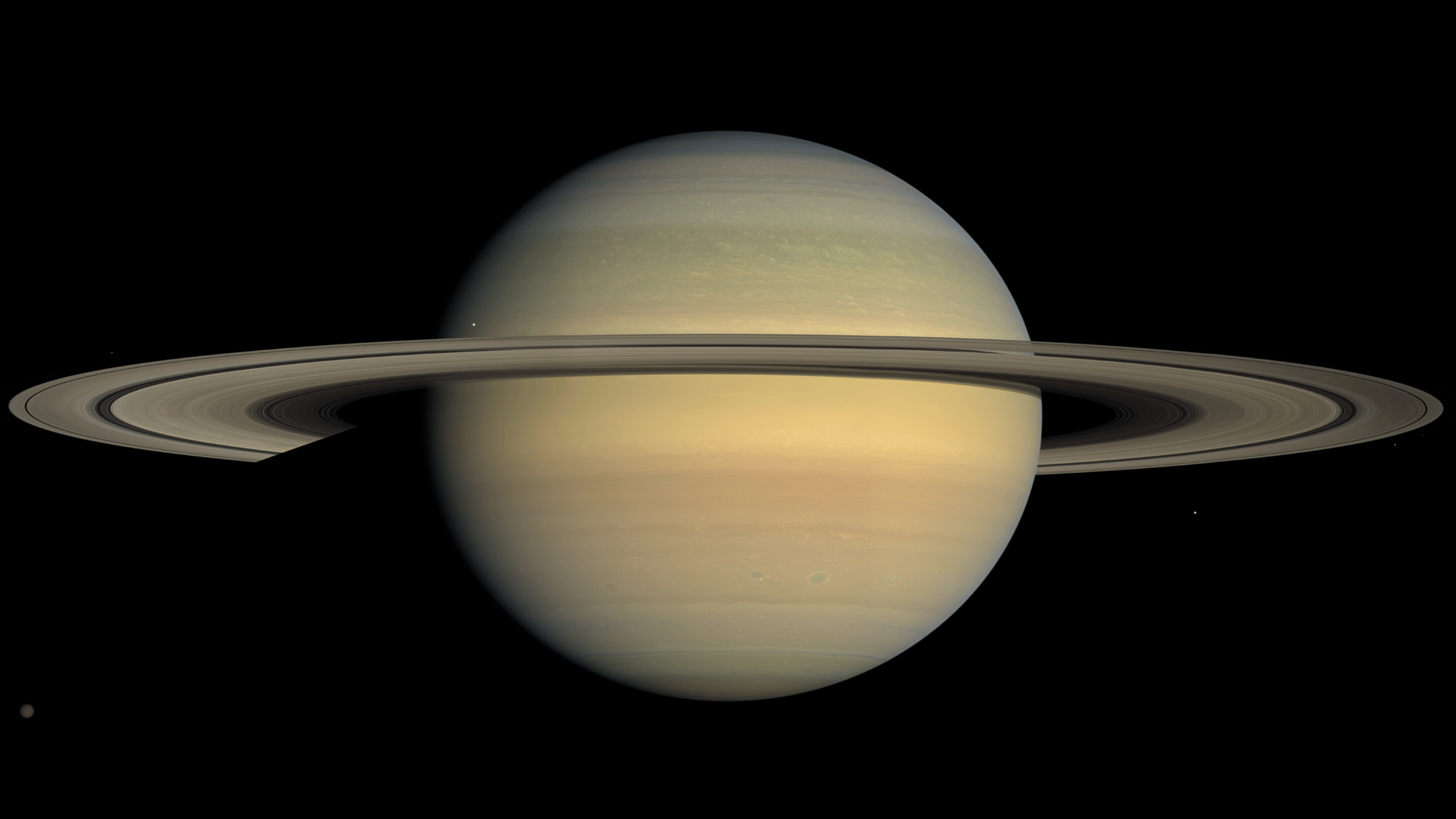
Image Source: Wikipedia
Saturn is mostly made of hydrogen and helium, making it less dense than water. If someone could find a bathtub big enough, Saturn would float!
Its average density is just 0.687 grams per cubic centimeter, which is lower than water’s 1 gram per cubic centimeter.
While this is purely theoretical, it highlights the differences between gas giants and rocky planets like Earth. Saturn’s massive rings, made of ice and rock, add to its stunning uniqueness in our solar system.
6. The Moon Is Slowly Drifting Away
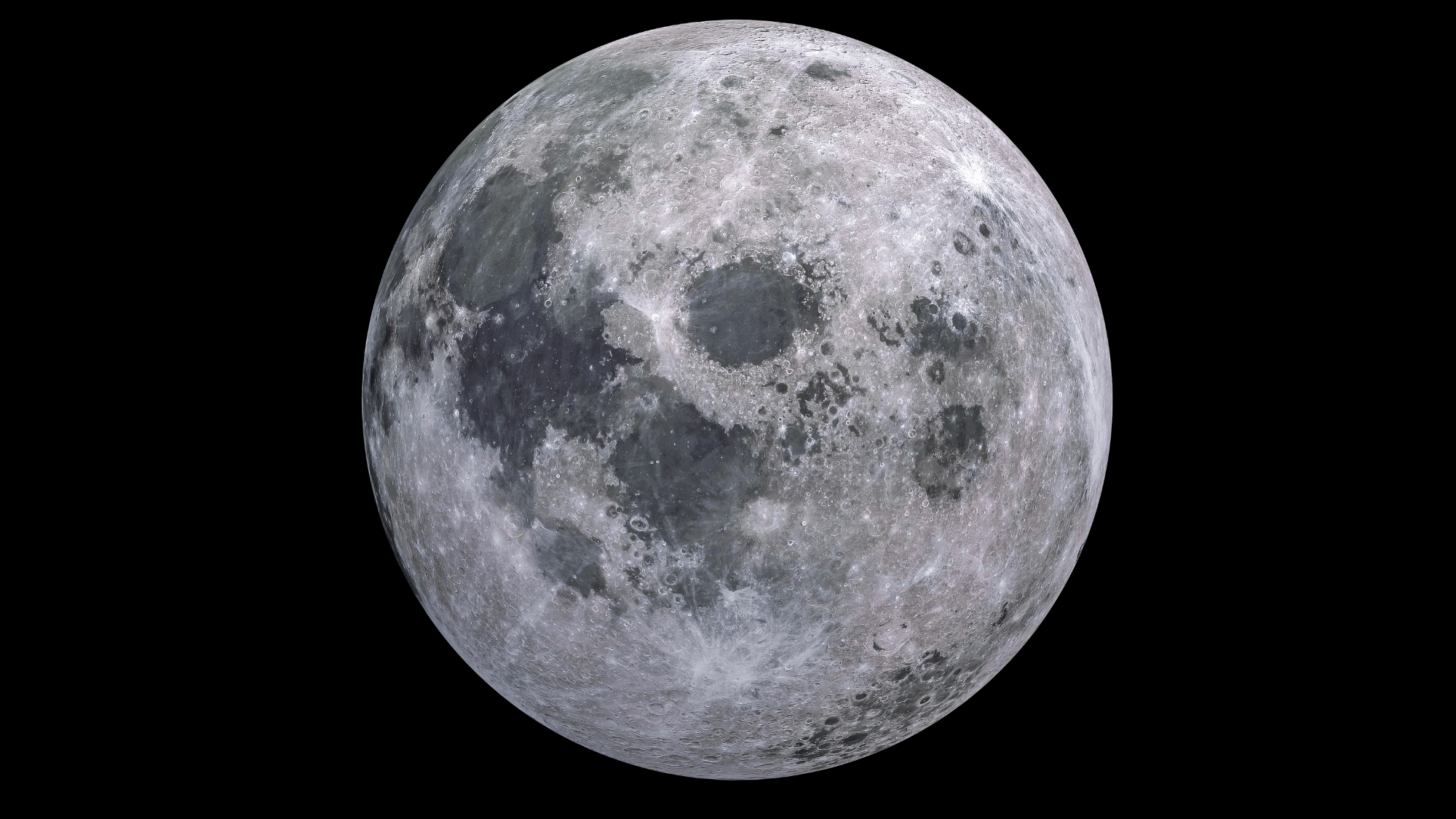

Our Moon is moving about 1.5 inches farther from Earth every year. This occurs because tidal interactions between Earth and the Moon gradually transfer energy, causing the Moon to move outward.
In the distant future, this slow drift will make total solar eclipses impossible, as the Moon will no longer appear large enough to completely block the Sun’s disk.
Luckily, this process takes billions of years, so eclipses remain a spectacular sight for now.
7. The Milky Way Will Collide with Andromeda
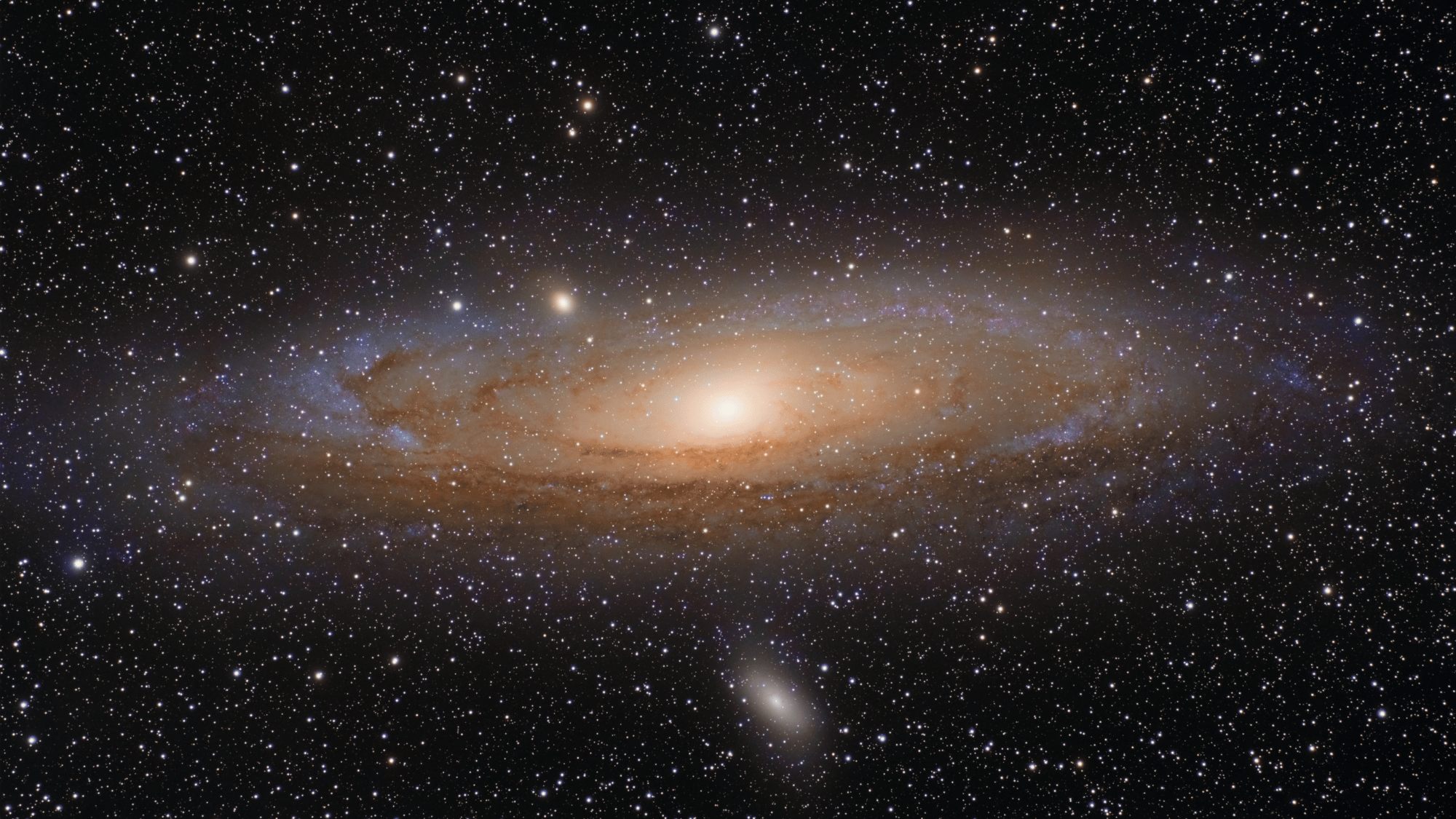
Image Source: Wikipedia
In about 4.5 billion years, our galaxy, the Milky Way, is set to collide with the neighboring Andromeda Galaxy.
Though it sounds catastrophic, stars are so far apart that very few will actually collide. Instead, the galaxies will merge, forming a new, larger galaxy often called “Milkomeda.”
This cosmic dance is a natural part of galaxy evolution, illustrating the universe’s dynamic and ever-changing nature over billions of years.
8. Space is Completely Silent

Unlike Earth, space has no atmosphere for sound waves to travel through, making it completely silent. Astronauts rely on radios to communicate, as their voices can’t carry in the vacuum of space.
However, scientists can still “hear” space by detecting electromagnetic vibrations with special instruments.
These signals are converted into sound waves, allowing us to experience eerie “space sounds” recorded from planets, stars, and cosmic phenomena across the universe.
9. Mars Has the Tallest Volcano in the Solar System
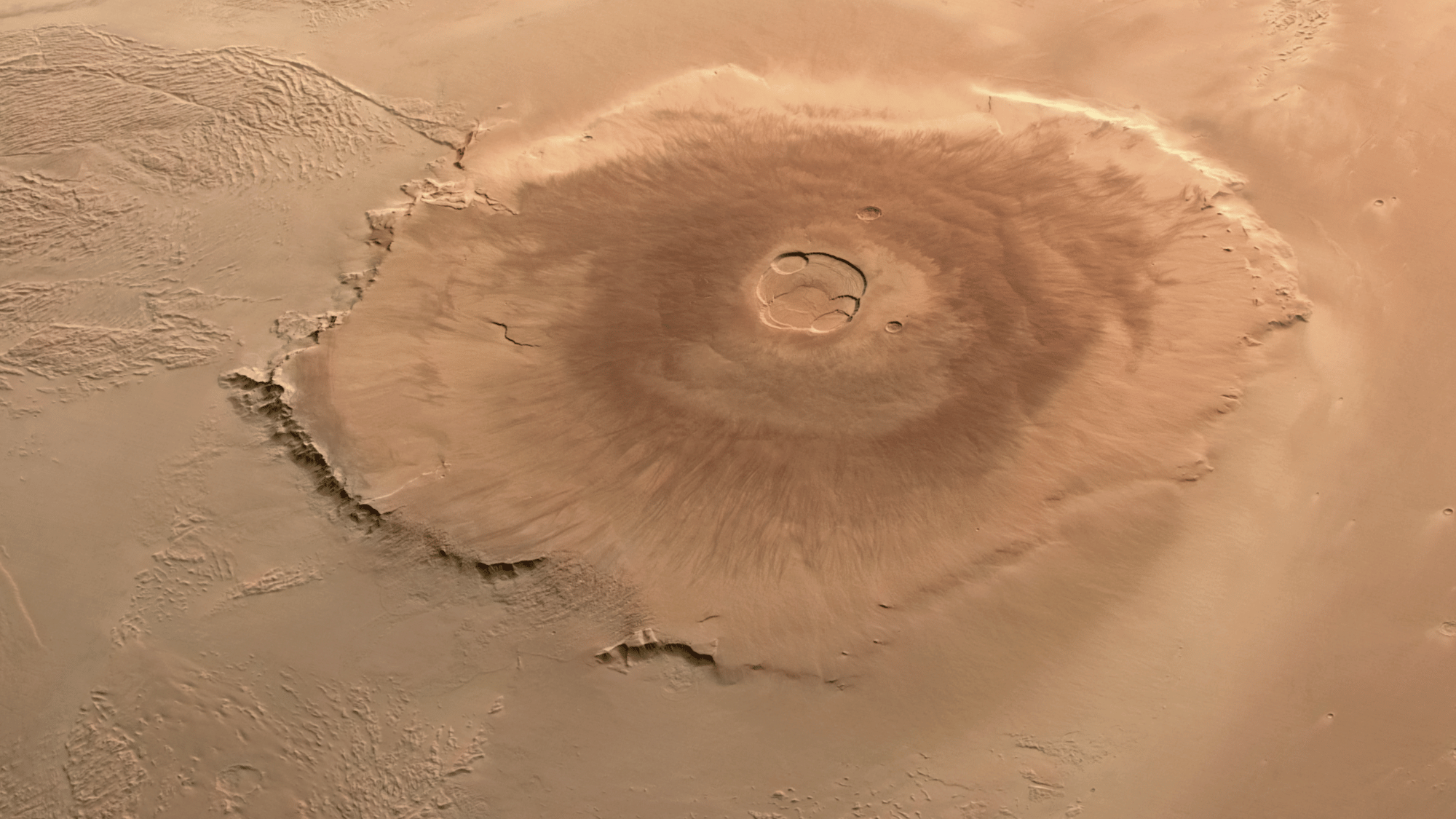

Olympus Mons on Mars is the largest volcano known, standing about 13.6 miles high, nearly three times taller than Mount Everest.
It’s also incredibly wide, spanning about 370 miles, roughly the size of the state of Arizona. This massive shield volcano formed from countless lava flows over billions of years.
Because Mars lacks tectonic plate movement like Earth, volcanoes there can grow to enormous sizes without being disrupted by shifting crust.
10. A Year on Neptune Lasts 165 Earth Years
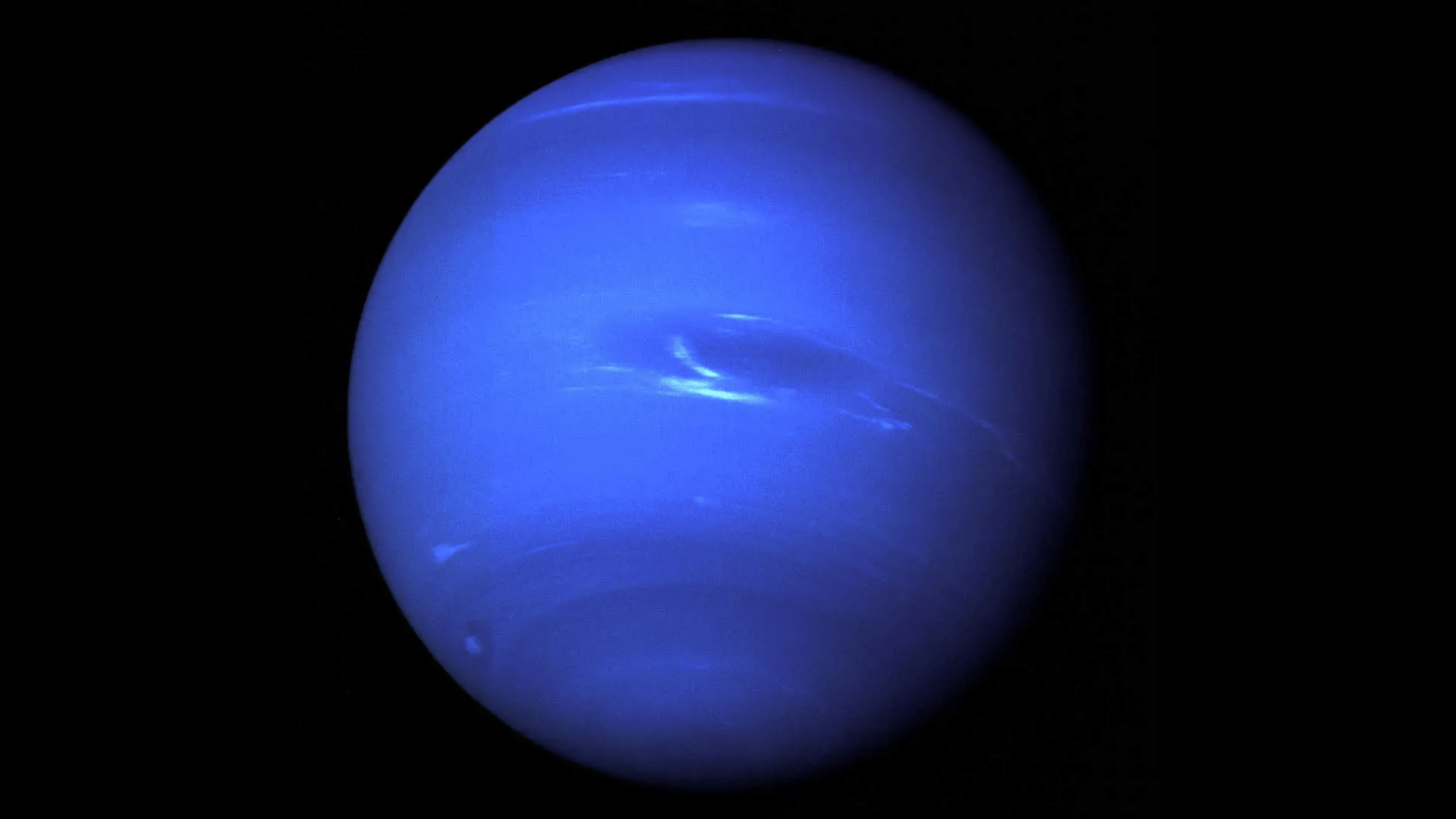
Image Source: NASA
Neptune, the farthest planet from the Sun, takes about 165 Earth years to complete one orbit.
That means it has only circled the Sun once since its discovery in 1846. Despite its long years, Neptune’s days are short, lasting about 16 hours.
Its atmosphere is also known for the fastest winds in the solar system, reaching up to 1,300 miles per hour, making Neptune one of the most dynamic outer planets.
11. A Day on Mercury Has Two Sunrises
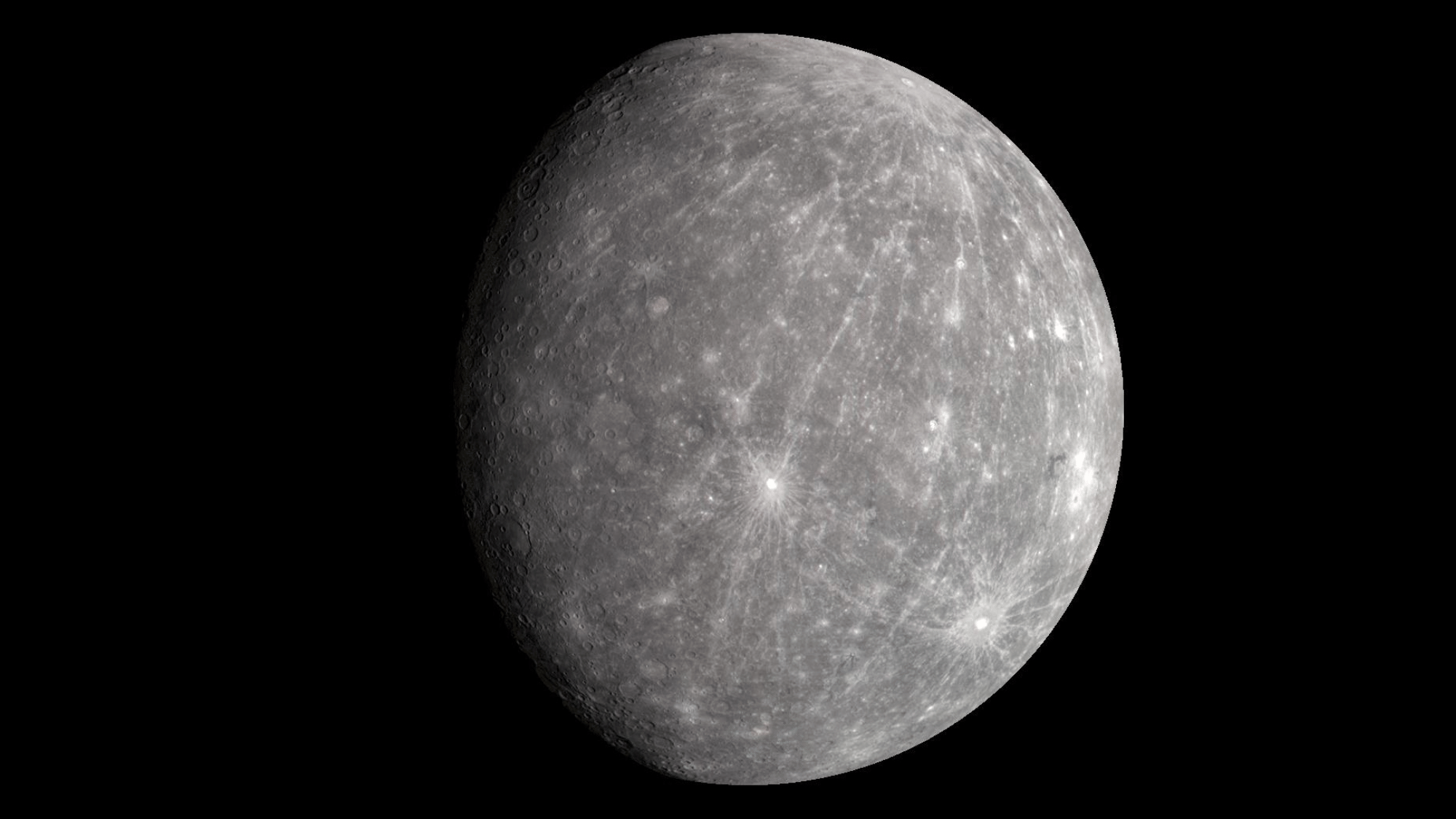
On Mercury, a day is unusual because the planet rotates slowly but orbits the Sun quickly.
A single day on Mercury lasts 176 Earth days. Combined with its elliptical orbit, this creates a strange effect:
If you stood on Mercury’s surface, you could see the Sun rise, set, and then rise again in the same day. This bizarre timing makes Mercury’s skies one of the most unusual in the solar system.
12. There are More Stars Than Grains of Sand on Earth

Image Source: European Space Agency
Astronomers estimate there are about 200 billion stars in the observable universe. To compare, Earth’s beaches and deserts hold far fewer grains of sand.
This staggering number underscores the vastness and star-filled nature of the cosmos. Each star may host planets, moons, and possibly life, making the universe an incredibly diverse place.
The comparison between stars and sand is one of the most famous yet humbling facts about space.
13. Uranus Spins on Its Side
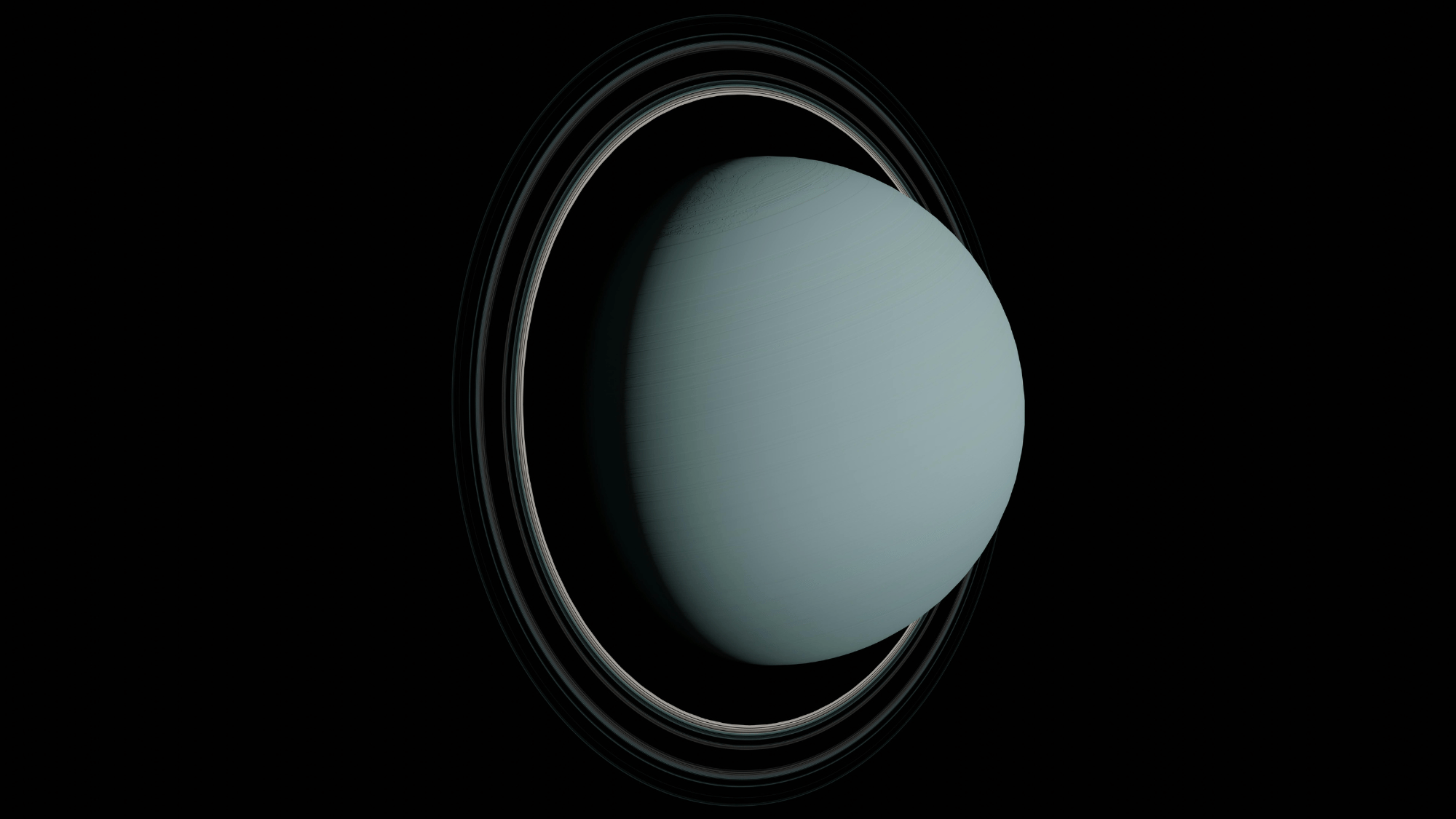

Unlike other planets, Uranus rotates on its side with an axial tilt of 98 degrees. This means it essentially rolls around the Sun rather than spinning upright like Earth or Mars.
Scientists think a massive collision with another celestial body caused this tilt.
As a result, Uranus has extreme seasons, with each pole experiencing 42 years of continuous sunlight followed by 42 years of complete darkness. It’s one of the strangest rotations in the solar system.
14. The Coldest Place in the Universe is the Boomerang Nebula
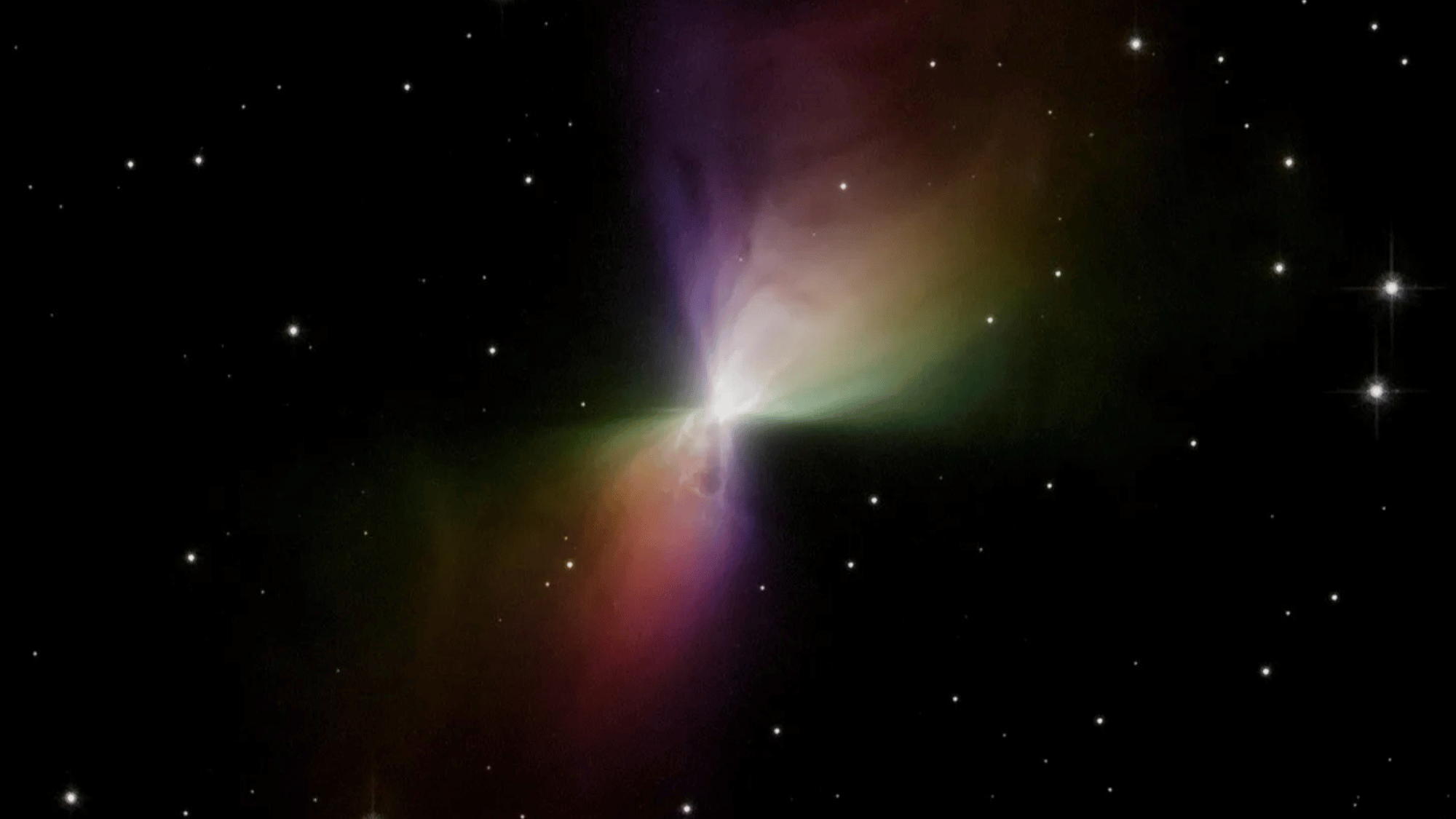

Image Source: NASA
The Boomerang Nebula, about 5,000 light-years away, holds the record as the coldest natural place in the universe.
Its temperature drops to just one Kelvin above absolute zero (–458°F). This extreme cold is caused by the rapid expansion of gas as it flows out of a dying star.
Even the background temperature of space, at 2.7 Kelvin, is warmer than this nebula, making it one of the universe’s most chilling locations.
15. Comets Are “Dirty Snowballs” from Deep Space
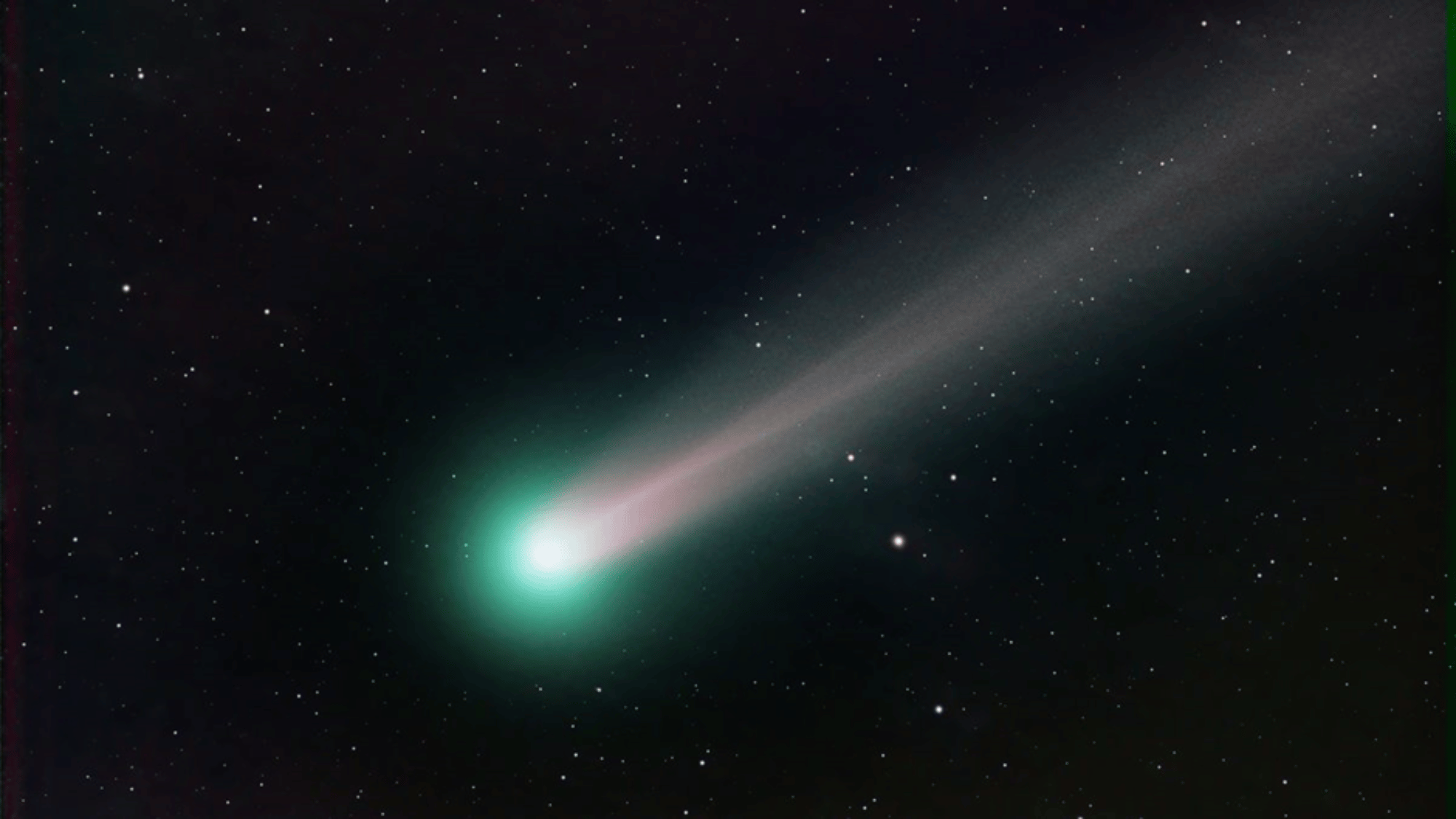

Comets are icy bodies made of frozen gases, dust, and rock, often called “dirty snowballs.”
When they approach the Sun, heat causes them to release gas and dust, forming glowing tails that can stretch for millions of miles.
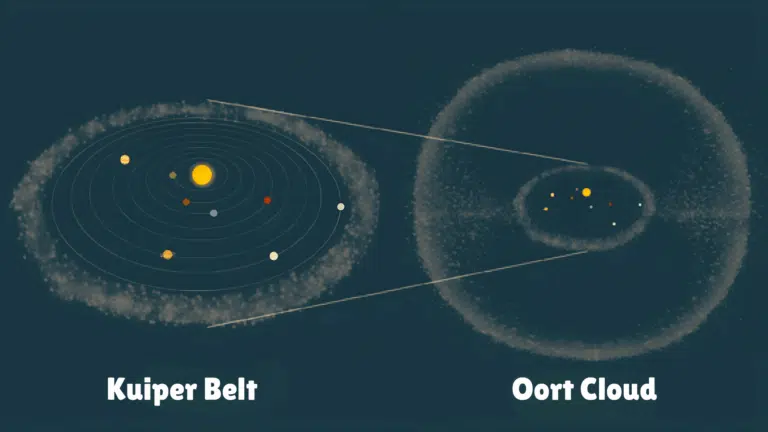
These tails always point away from the Sun, pushed by solar wind. Comets originate in the Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt, distant regions filled with icy objects left over from the solar system’s formation.
16. Space Travel Makes You Taller
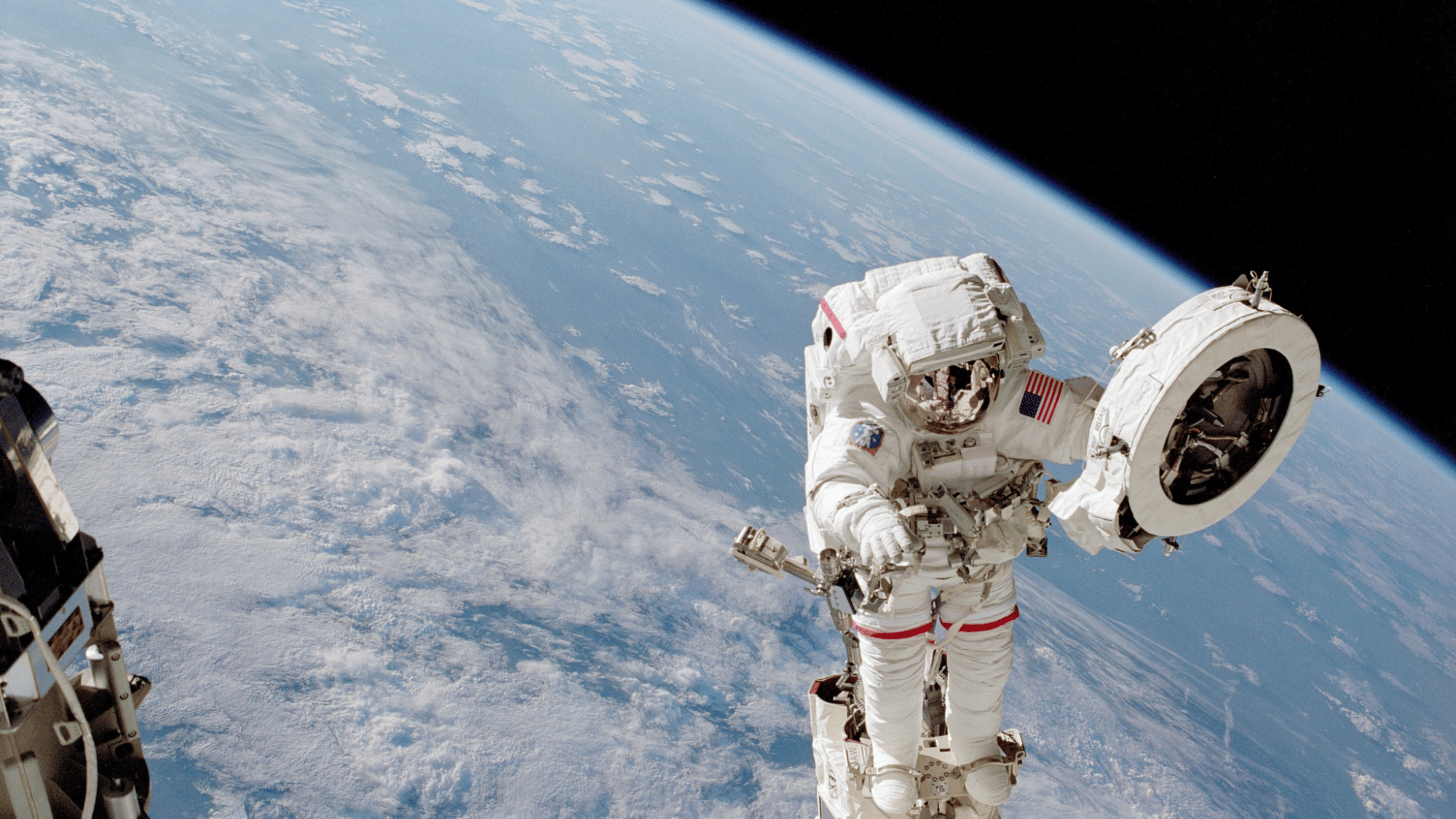

Image Source: NASA
Astronauts often grow about two inches taller while living in microgravity. Without Earth’s gravity compressing their spines, the vertebrae expand slightly, making them taller.
However, this change is temporary; once astronauts return to Earth, gravity pulls them back to their original height within a few months.
This phenomenon demonstrates how space not only alters machines and environments but also affects the human body in fascinating and sometimes surprising ways.
17. There Are Rogue Planets Wandering Alone

Not all planets orbit stars. Scientists have discovered rogue planets drifting freely through the galaxy without a host star.
These dark, cold worlds may have formed near stars but were later ejected by gravitational interactions. Some estimates suggest there could be more rogue planets than stars in the Milky Way.
Though they’re hard to detect, their existence shows that planetary systems are far more dynamic and unstable than we once thought.
18. Time Moves Differently in Space
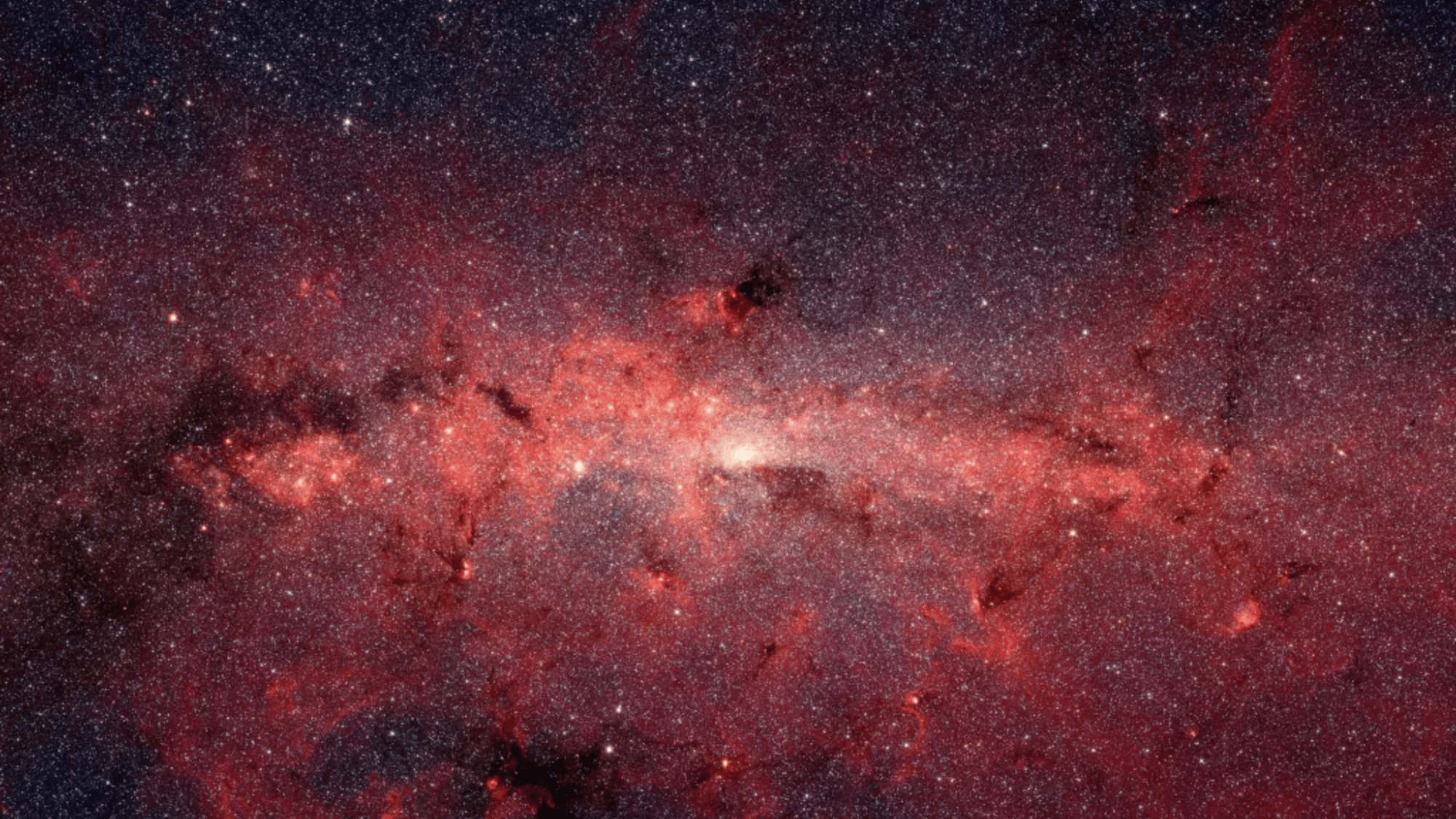
Image Source: NASA
Einstein’s theory of relativity demonstrates that time passes at different rates depending on the presence of gravity and velocity.
In stronger gravitational fields, like near black holes, time moves more slowly, a phenomenon known as time dilation.
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station actually age slightly slower than people on Earth, though only by fractions of a second.
19. The Sun Makes Up 99.8% of Our Solar System’s Mass
The Sun is enormous, containing 99.8% of all the mass in the solar system. Its sheer gravity keeps planets, asteroids, and comets in orbit.
To put it in perspective, about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the Sun. Without it, the solar system as we know it wouldn’t exist.
Even though it’s just one of billions of stars, for us, the Sun is the ultimate powerhouse of life.
20. Pluto Has a Heart-Shaped Glacier
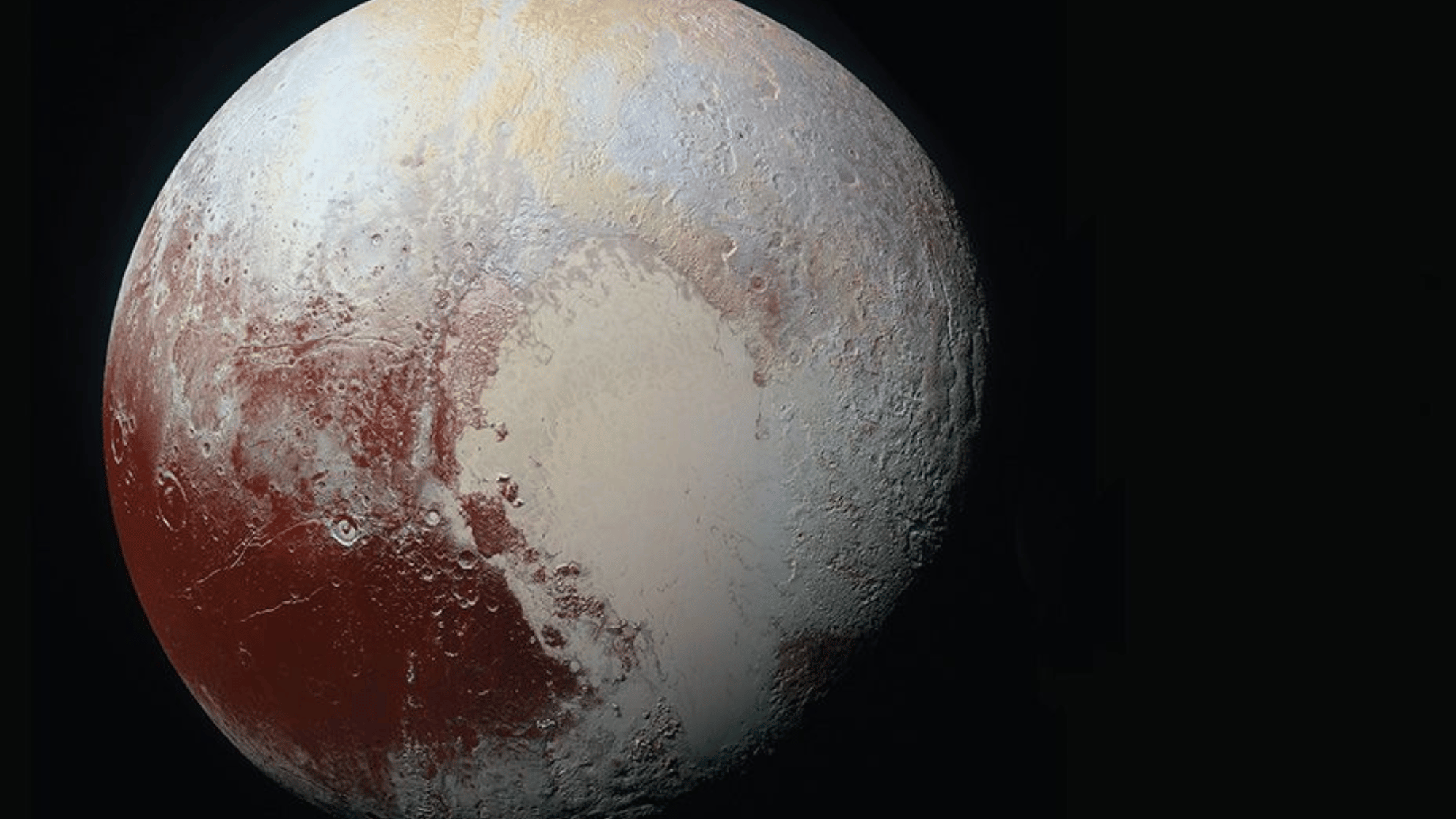
Pluto, once considered the ninth planet, continues to surprise scientists. Its surface features a massive heart-shaped glacier called Tombaugh Regio.
Made largely of nitrogen ice, this iconic feature spans approximately 1,000 miles. Images from NASA’s New Horizons mission in 2015 revealed the glacier in stunning detail, sparking renewed fascination with this distant world.
Despite its reclassification as a dwarf planet, Pluto continues to capture imaginations with its beauty and mysteries.
21. Venus Is the Hottest Planet in the Solar System
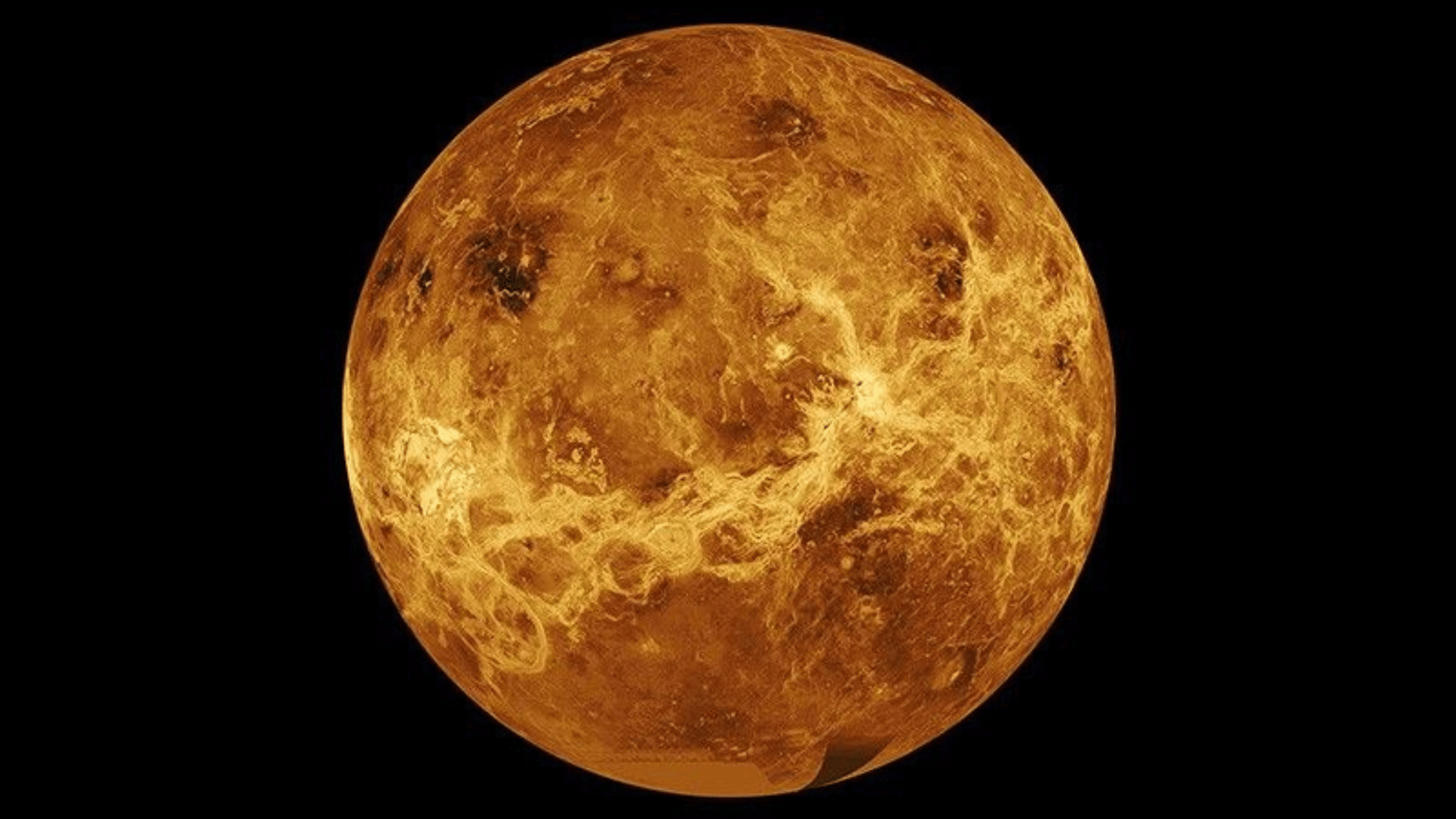
Image Source: NASA
Although Mercury is closer to the Sun, Venus is the hottest planet, with surface temperatures averaging 900°F (475°C).
Its thick atmosphere traps heat in a runaway greenhouse effect, making the planet hotter than even Mercury. The extreme heat and crushing pressure on Venus mean that spacecraft survive only a few hours on its surface.
These harsh conditions show how climate can drastically shape a planet’s environment, offering insights into Earth’s own atmospheric future.
22. A Day on Saturn’s Moon Titan Looks Earth-Like
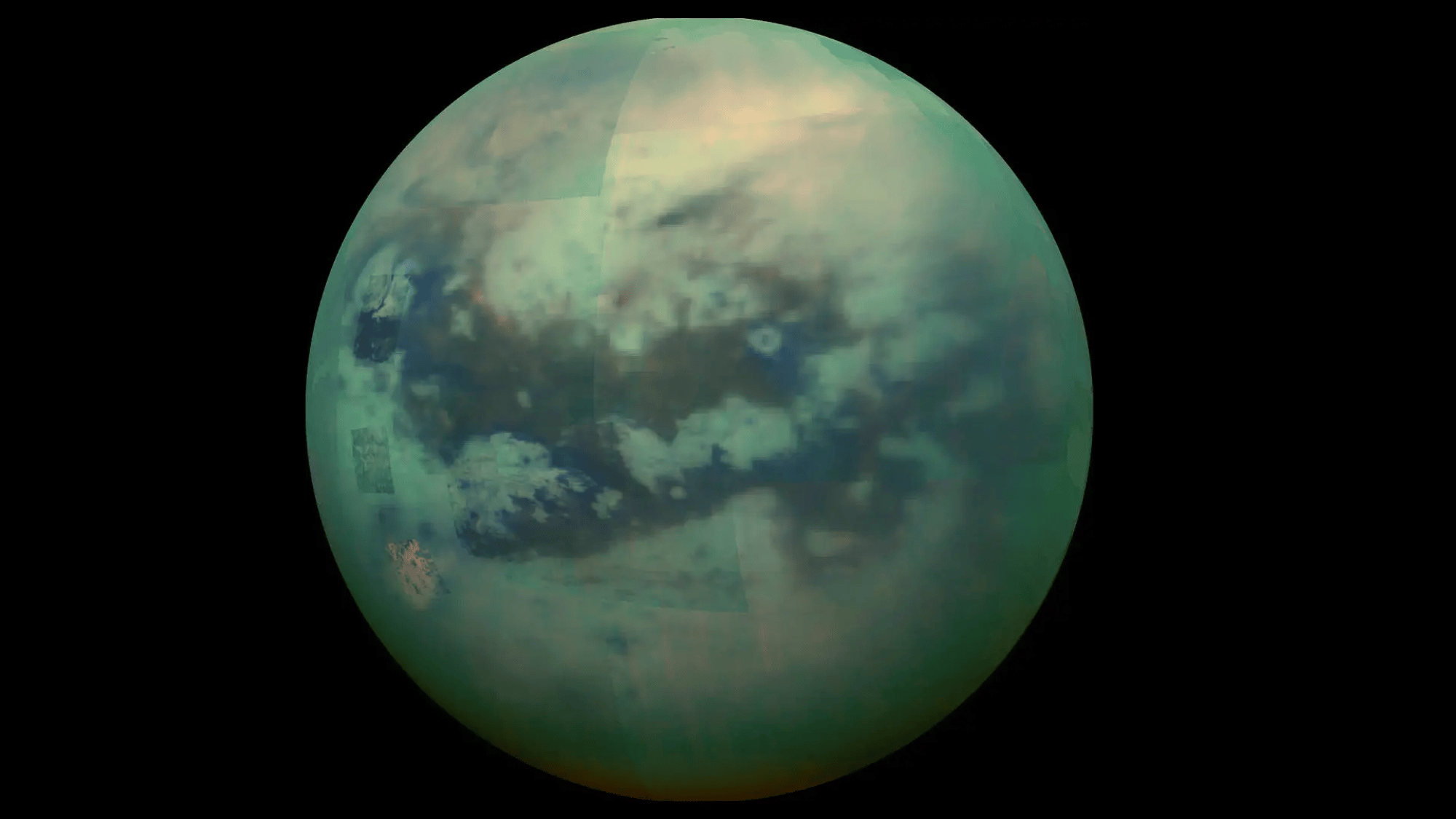
Image Source: NASA
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, is the only place besides Earth known to have stable liquids on its surface.
However, its rivers, lakes, and seas are made of liquid methane and ethane instead of water. Titan also has a thick atmosphere, giving it an orange haze.
Scientists believe its chemistry could resemble early Earth, making Titan a prime candidate in the search for life and understanding how conditions for habitability may develop elsewhere.
23. The Largest Known Star Is UY Scuti
UY Scuti, a red supergiant located about 9,500 light-years away, is the largest known star by radius. If placed at the center of our solar system, its outer edge would extend beyond Jupiter’s orbit.
Despite its enormous size, it’s not the most massive star, since red supergiants are expanded and relatively low in density.
Its unimaginable scale demonstrates the diversity of stars and how they evolve through different life stages in the cosmos.
24. The Moon Has Earthquakes, or Moonquakes
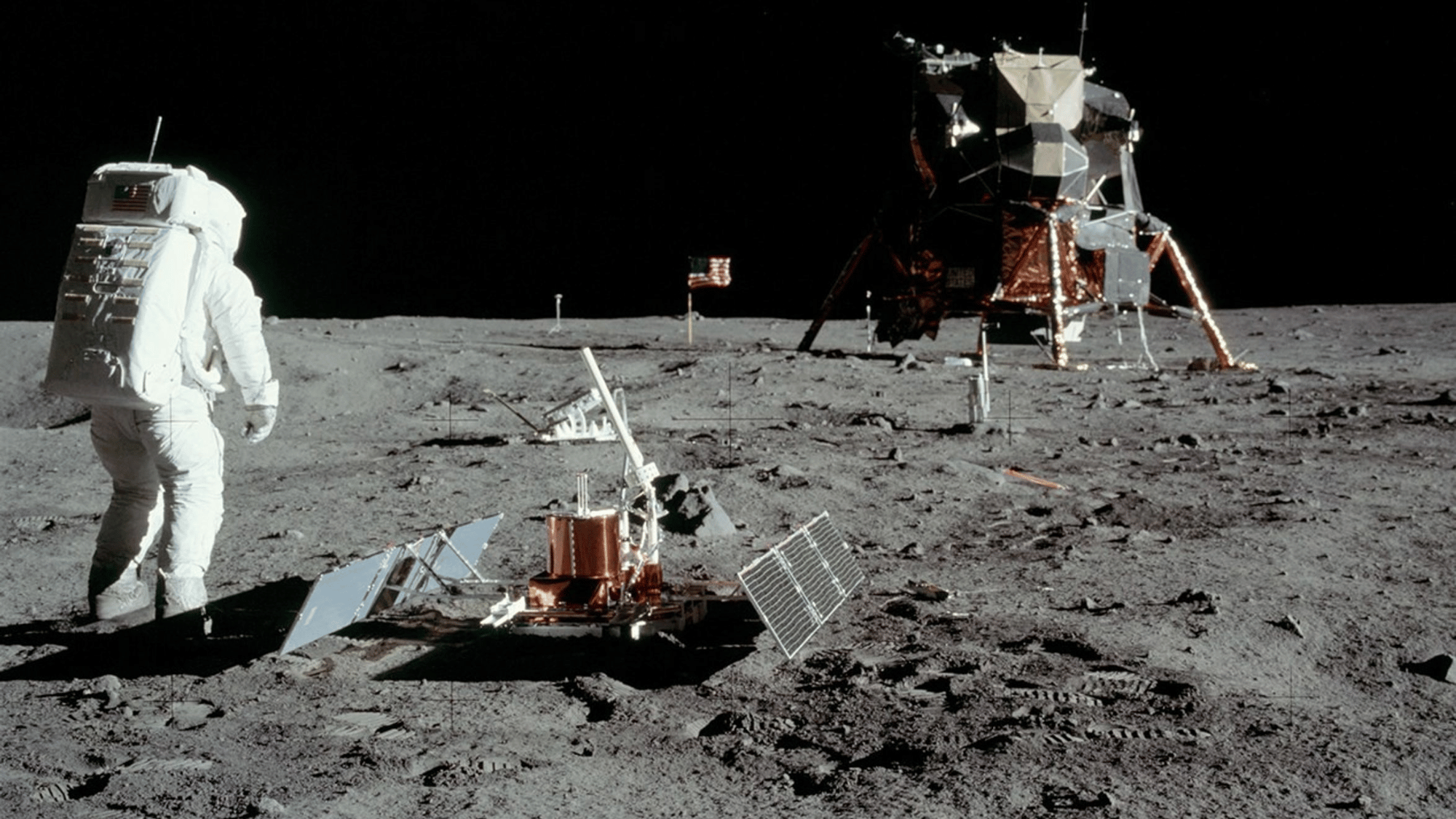
Image Source: NASA
Just like Earth, the Moon experiences quakes, though on a smaller scale.
These moonquakes are caused by tidal forces from Earth’s gravity, meteorite impacts, and even thermal expansion as the Moon’s surface warms and cools. Some shallow moonquakes can be surprisingly strong, lasting up to 10 minutes.
These tremors reveal that the Moon is more geologically active than once believed and highlight the challenges future lunar bases may face with ground stability.
25. The Largest Canyon in the Solar System Is on Mars
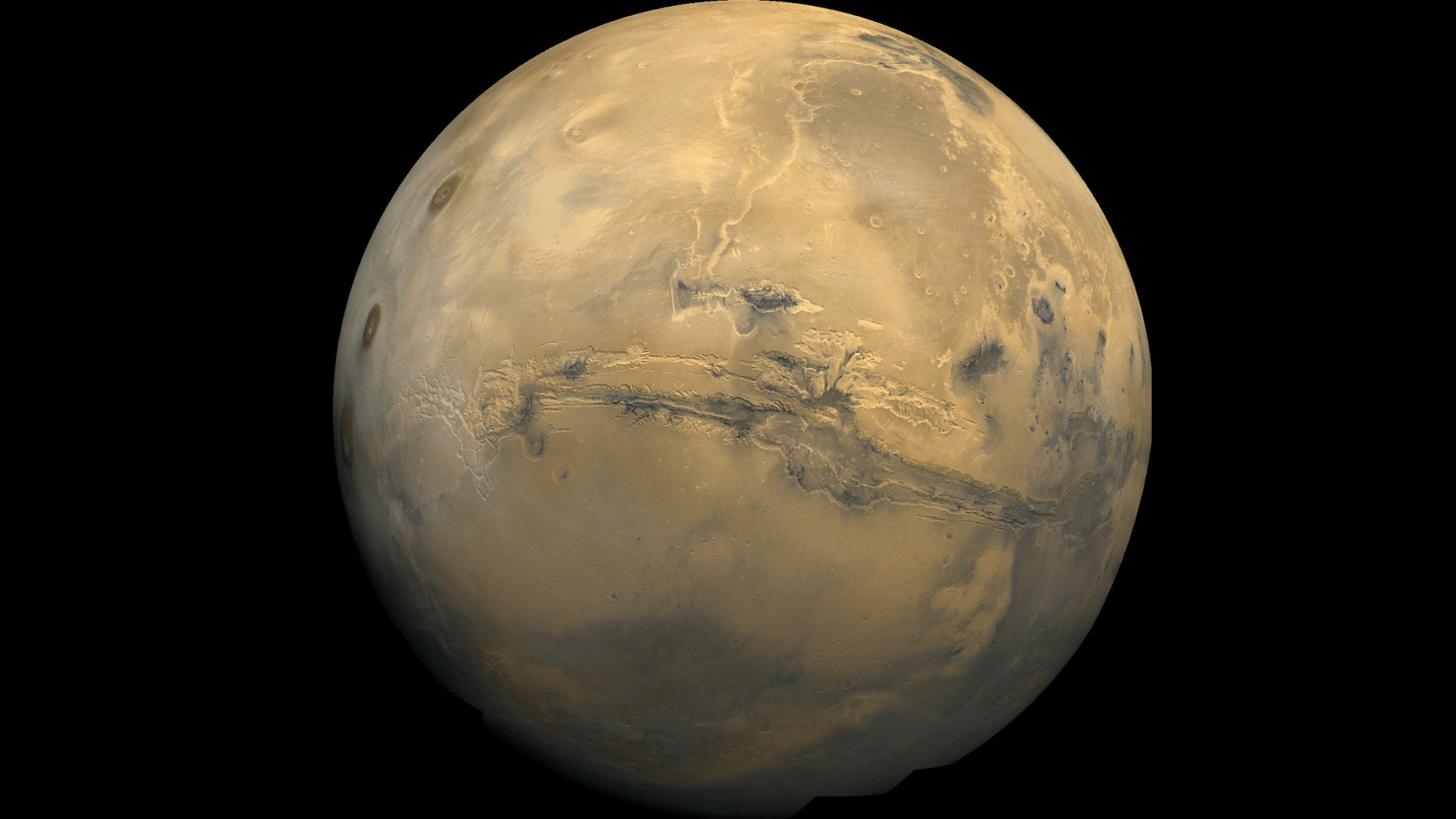
Image Source: Wikipedia
Mars is home to Valles Marineris, a canyon system stretching over 2,500 miles long and up to 7 miles deep. That’s nearly ten times longer and four times deeper than Earth’s Grand Canyon.
Scientists believe it formed through a combination of tectonic activity and erosion.
The canyon reveals billions of years of Martian history, providing clues about the planet’s geology, water activity, and potential habitability in the distant past.
26. Space Debris is Becoming a Growing Problem

Image Source: European Space Agency
Earth’s orbit is filled with space debris, including defunct satellites, rocket parts, and fragments from collisions.
Currently, over 36,000 pieces larger than 10 cm are being tracked, along with millions of smaller fragments. Traveling at speeds up to 17,000 miles per hour, even tiny pieces pose serious risks to spacecraft and satellites.
This growing issue, known as the “Kessler syndrome,” could make space exploration and satellite operations increasingly hazardous in the future.
27. Some Galaxies Have Supermassive Black Holes at Their Centers
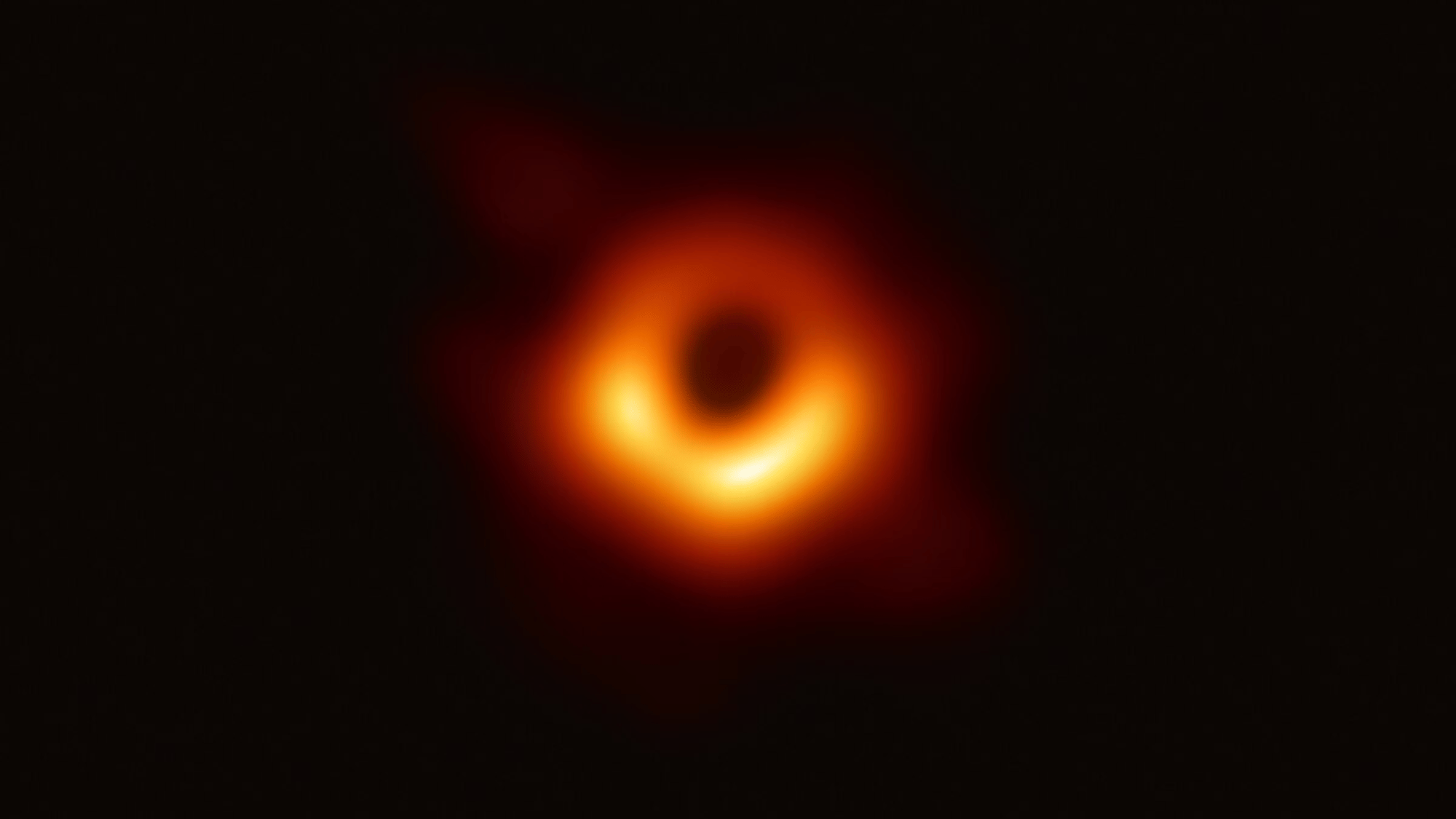

Image Source: Wikipedia
Almost every large galaxy, including the Milky Way, hosts a supermassive black hole at its core. The one in our galaxy, Sagittarius A*, has a mass equivalent to about 4 million Suns.
These black holes shape the growth and structure of galaxies, influencing star formation and the dynamics of galactic systems.
When active, they can power quasars, some of the brightest objects in the universe, outshining entire galaxies with their incredible energy output.
28. The International Space Station Travels at 17,500 MPH
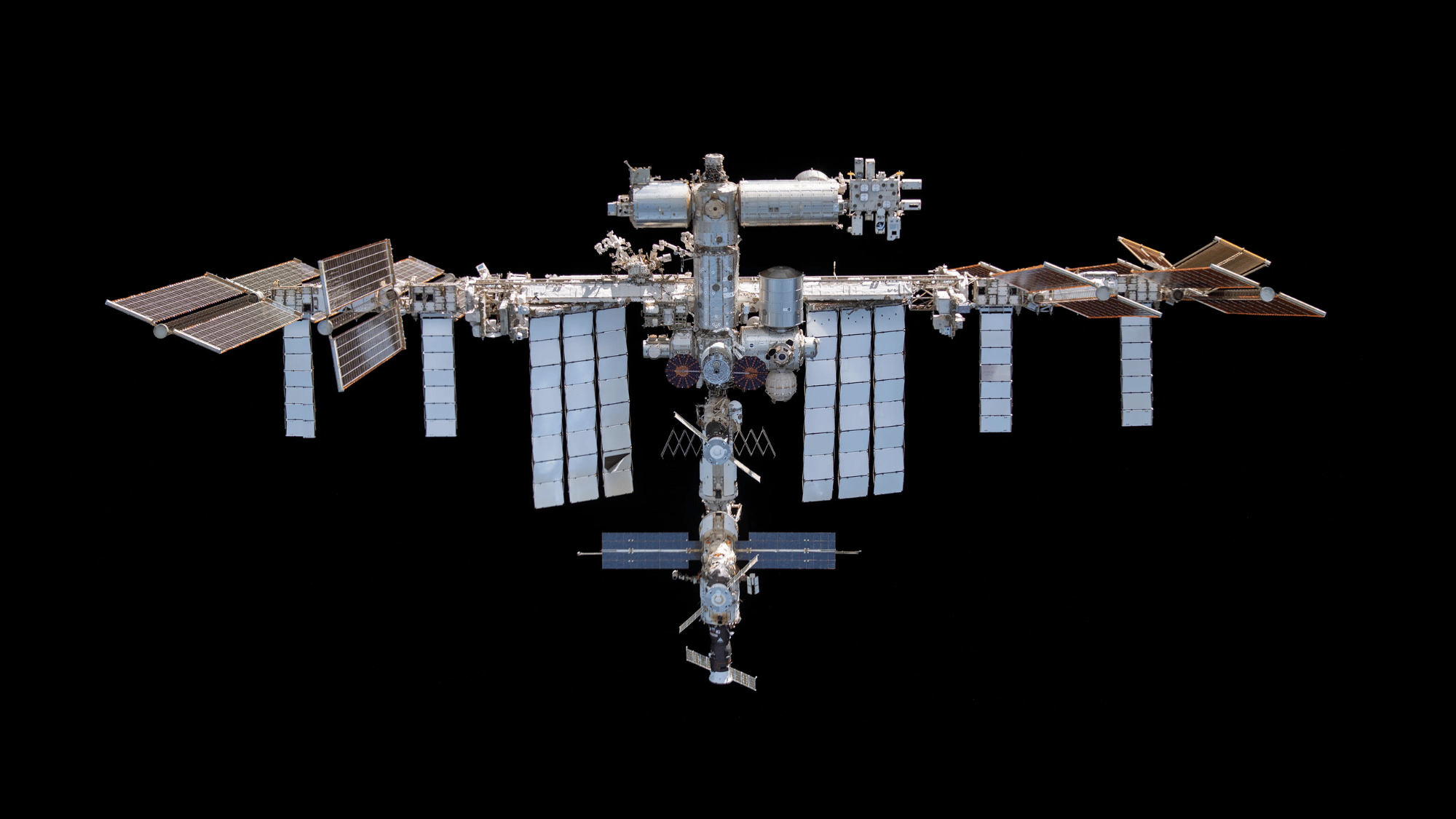
Image Source: NASA
The International Space Station (ISS) orbits Earth at a speed of about 17,500 miles per hour, circling the planet every 90 minutes.
Astronauts on board witness 16 sunrises and sunsets each day. This incredible speed allows the ISS to conduct groundbreaking research in microgravity, advancing science in medicine, engineering, and space exploration.
It also serves as a unique international collaboration, uniting space agencies from around the world in pursuit of discovery.
29. Jupiter’s moon, Lo, is the Most Volcanically Active Body in The Solar System
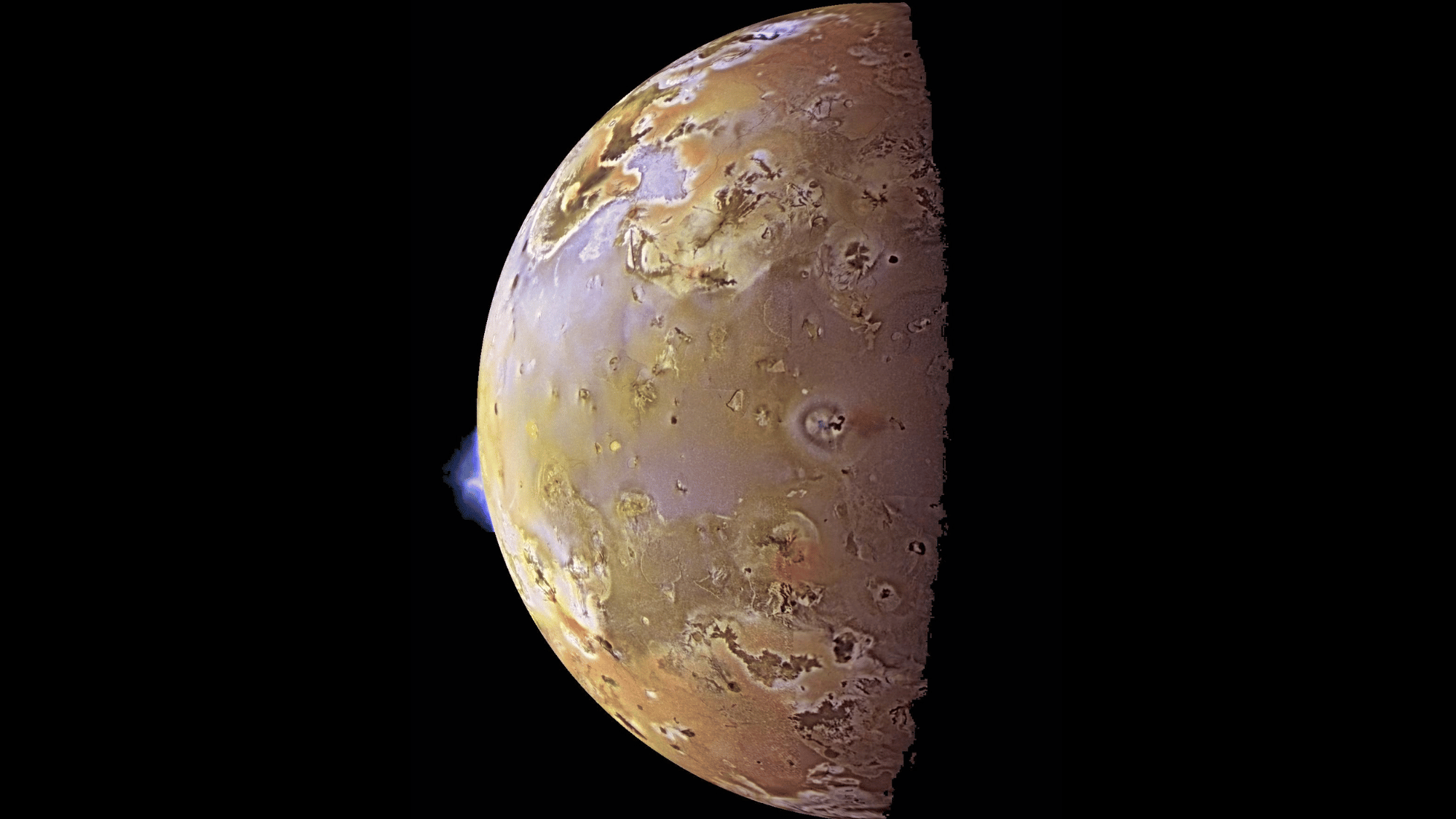
Image Source: Wikipedia
Lo, one of Jupiter’s moons, is the most volcanically active body in the solar system with over 400 active volcanoes, including the largest volcano on Io named Loki.
While Mars has Olympus Mons, Jupiter’s moon Io has volcanoes that erupt regularly due to tidal heating caused by Jupiter’s immense gravity.
Some eruptions spew lava fountains dozens of miles high. This relentless activity constantly reshapes Io’s surface, erasing impact craters and leaving a colorful, molten landscape.
30. Dark Matter Makes Up Most of the Universe
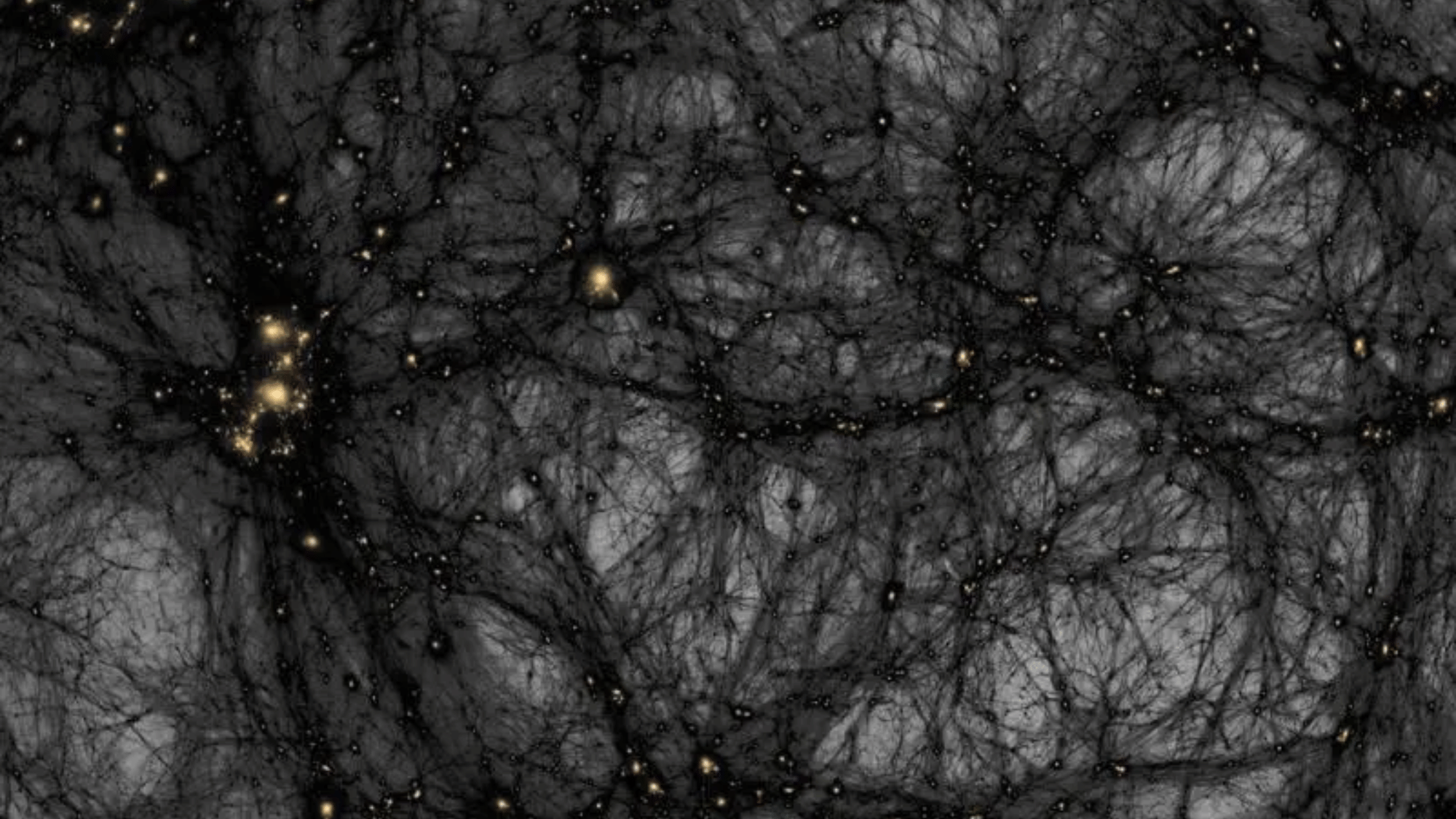
Image Source: NASA
Scientists estimate that dark matter accounts for approximately 27% of the universe, while dark energy comprises about 68%.
The matter we can see stars, planets, and galaxies accounts for less than 5%. Although invisible and undetectable by light, dark matter reveals itself through its gravitational effects, which hold galaxies together.
Despite decades of study, scientists still don’t know what dark matter is, making it one of the greatest cosmic mysteries yet to be solved.
Space Technology in Everyday Life
Space technology isn’t just for astronauts; it powers everyday tools like GPS, satellites, and medical advances, showing how discoveries beyond Earth shape life here.
- Space technology provides tools such as GPS and satellites, which aid in navigation, weather forecasting, global communication, and disaster management.
- Cosmic rays, high-energy particles from outer space, constantly bombard Earth, subtly influencing our atmosphere, climate, and electronic systems.
- Everyday conveniences, such as accurate maps, TV broadcasting, and mobile connections, are made possible by advancements in space research and satellite technology.
- Space exploration drives innovations in healthcare, such as the development of improved medical imaging and monitoring technologies derived from studies on astronaut health.
- Preparing for human survival on Mars and the Moon inspires the development of new technologies that also benefit daily life on Earth.
Conclusion
From black holes to distant galaxies, these interesting facts about space remind readers of the vastness of knowledge yet to be found beyond our planet.
Each of these space facts adds a new layer of understanding, proving that knowledge of the cosmos is as limitless as space itself.
For those who enjoy expanding their horizons about space, these can be both enjoyable and deeply educational.
Readers are encouraged to continue learning, ask bold questions, and share their favorite facts or curiosities about the universe in the comments below.