Living in space is very different from life on Earth, especially for astronauts who spend months aboard the International Space Station (ISS), orbiting 250 miles above the planet.
They work, eat, sleep, and stay healthy while floating in zero gravity. It takes a lot of planning to live in space.
Even simple tasks like sleeping or brushing teeth are not the same. Every part of the ISS is built with care, including the bedroom area.
This blog gives a simple look at daily life inside the ISS. It focuses on how the bedroom works and what it’s like to sleep in space.
What is the International Space Station?
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space lab that orbits Earth. It travels at about 17,500 miles per hour. That means it circles the Earth about 16 times every day.
The ISS is a home and workplace for astronauts. They live there for weeks or even months. Astronauts from different countries work together on science experiments, health studies, and space missions.
Living in space is not like living on Earth. Everything floats because there is almost no gravity.
Even simple tasks, like sleeping or eating, become tricky. That’s why the space station has special areas for sleep, food, hygiene, and work.
Before understanding how astronauts sleep, it helps to understand why rest in space is so challenging. Microgravity changes how the body functions, including how it senses position, pressure, and time.
Why Sleeping in Space is Hard?
On Earth, gravity helps the body stay on the bed. In space, there is no gravity to pull you down. That means your arms, legs, and even your head can float around.
You can’t just lie down on a mattress and fall asleep. Without gravity, your body does not know which way is up or down.
Also, the ISS orbits Earth many times a day. That causes 16 sunrises and 16 sunsets every 24 hours.
The light can confuse the body clock, making it hard to know when to sleep. Astronauts need to follow a strict schedule to stay healthy and rested.
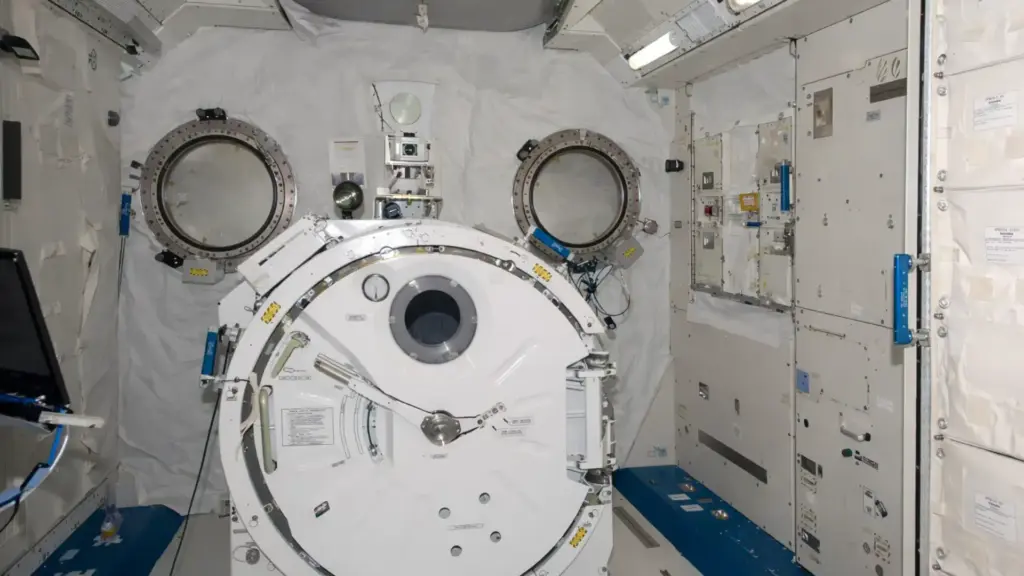
What is the International Space Station Bedroom Like?
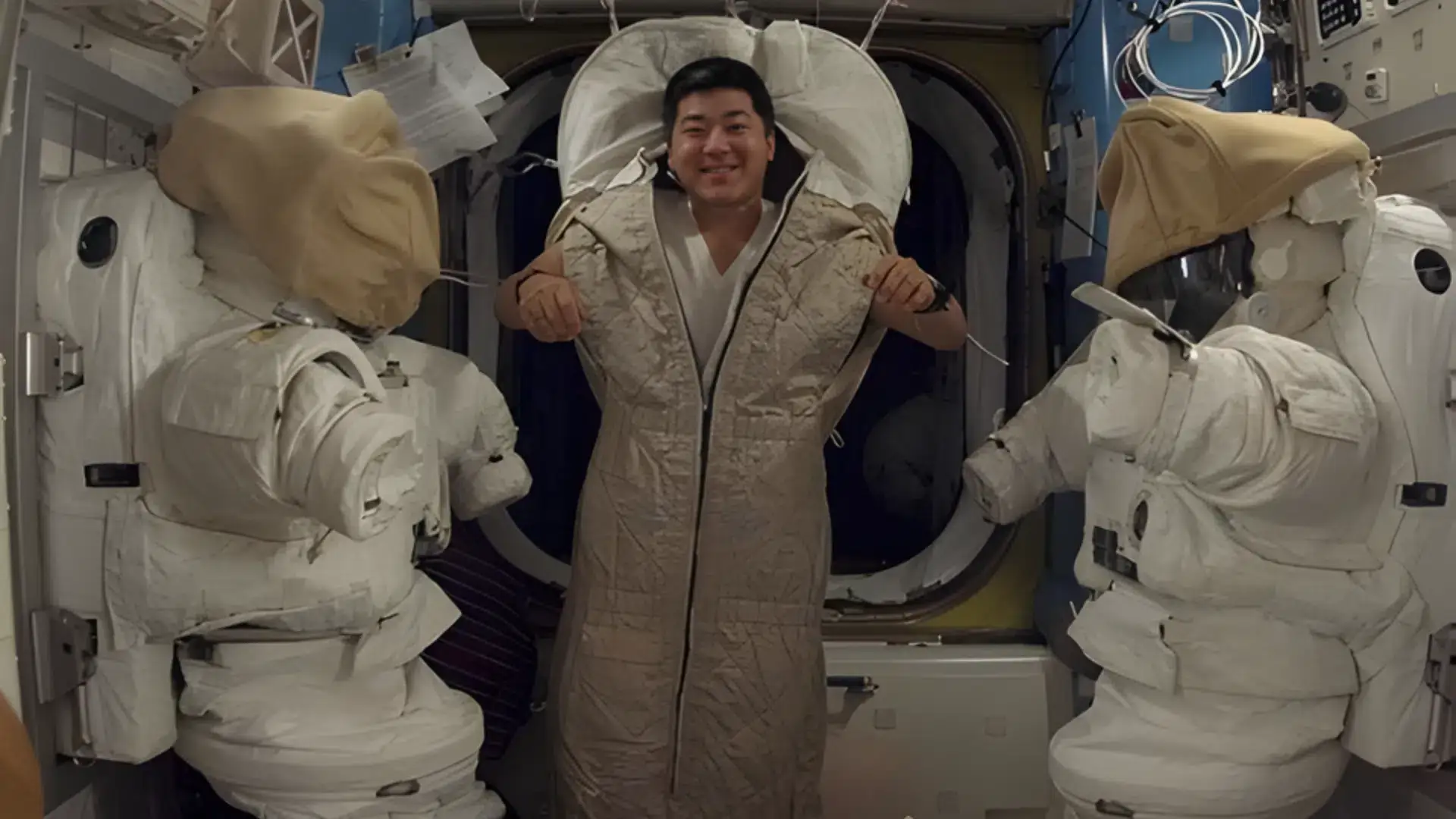

Image Source: Let’s Talk Science
The “bedroom” inside the ISS is not like a bedroom on Earth. There are no large beds, pillows, or nightstands. Instead, each astronaut gets a small sleeping pod or crew quarters. These are tiny, private areas about the size of a phone booth or a small closet.
Each sleeping pod is just big enough for one person. It usually includes:
- A sleeping bag fixed to the wall
- A reading light
- A small window (in some pods)
- A fan for air flow
- Personal items like photos or notes
- A laptop or tablet for work and messages
This area is called the International Space Station bedroom. It is quiet, private, and made for rest.
Watch NASA astronaut Suni Williams give a tour of the ISS crew quarters:
Earth Bedroom vs ISS Bedroom
| Feature | Earth Bedroom | ISS Crew Quarters |
|---|---|---|
| Gravity | Yes | Microgravity |
| Bed Type | Mattress & frame | Wall-mounted sleeping bag |
| Size | Varies | ~2m x 1m pod |
| Noise Level | Usually quiet | Constant machine hum |
| Window | Optional | Only some pods |
| Sunrises | 1 per day | 16 per day |
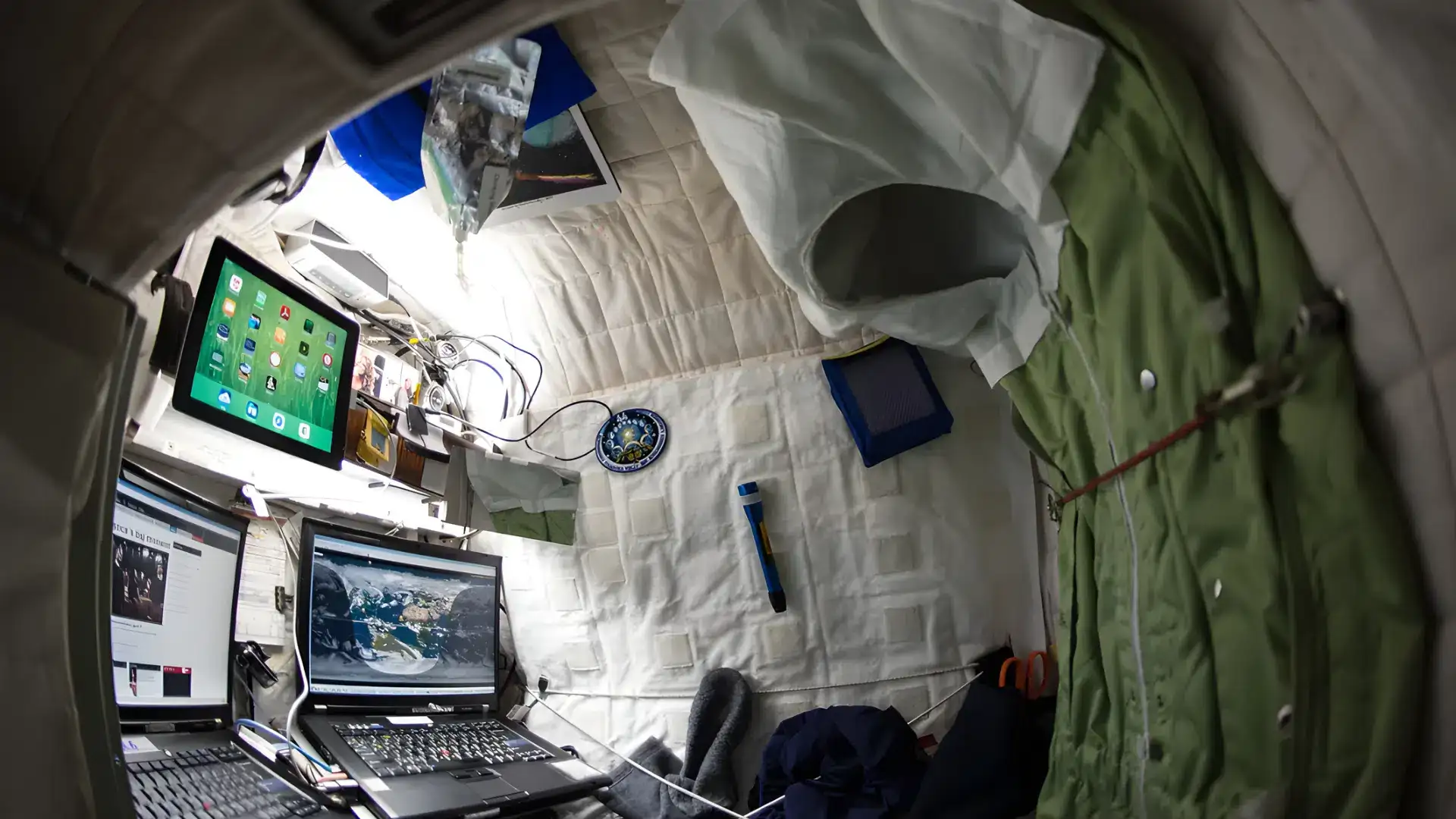
Sleeping in the International Space Station Bedroom

Image Source: Reddit
The International Space Station bedroom is specially designed to help astronauts rest in zero gravity. It includes private sleep pods, special sleeping bags, and a set routine to support healthy sleep habits.
Sleeping Bags Replace Regular Beds
Astronauts use sleeping bags that are attached to the wall, ceiling, or floor of the ISS. In space, there is no real “up” or “down,” so any direction works.
The sleeping bag keeps the astronaut from floating away during sleep. It also gives a cozy, wrapped feeling, like a soft cocoon.
Some astronauts like to keep their arms inside the bag, while others let them float freely. These bags do not need pillows or mattresses because there’s no pressure on the back or neck in zero gravity.
Eight Hours of Sleep is the Goal
Astronauts are scheduled to sleep for around eight hours each night. Getting enough sleep is important for their health and focus.
However, studies published in the journal Sleepand indexed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) show that astronauts typically sleep an average of 6 hours per night, often with reduced REM sleep cycles due to stress and circadian rhythm disruption. [NCBI Study Citation]
NASA has studied these patterns for years to improve crew performance on long missions.
Sleepingin space can be harder than on Earth. Lights, sounds, or motion in the station can interrupt rest. That’s why astronauts follow a set routine and use tools to help them rest better.
Tools That Help with Sleeping
Astronauts use different tools to help them sleep well. These include:
- Eye masks to block out light
- Earplugs to lower noise
- Fans inside the sleeping pod to make a steady background sound
Sometimes, NASA doctors allow mild sleep medicine, but it’s only used when needed. Most astronauts focus on good habits, such as relaxing before bed and keeping a quiet space.
Short Naps are Sometimes Allowed
Astronauts are allowed to take short naps if they are tired or have had a long day. Naps can help them feel more alert.
However, naps are not a full replacement for deep nighttime sleep. NASA continues to study sleep patterns in space to improve rest and focus for astronauts.
Pajamas are Simple and Comfortable
Most astronauts wear simple, loose-fitting clothes to bed. This may include a T-shirt and shorts or soft pajamas. There are no thick blankets in space because the station stays at a comfortable temperature, about 72°F (22°C).
Because they float, astronauts do not turn over in their sleep. Their body stay mostly still, and many say space sleep feels calm and peaceful.
Private Pods Offer Quiet and Comfort
Every astronaut gets a personal sleep pod. Each one includes a sleeping bag, a fan, and space for personal items like photos, journals, or a tablet. The pod has a curtain or door that can be closed for quiet and privacy.
This setup makes it easier to rest without floating into others or being disturbed.
Sharing a sleeping space would be hard in zero gravity, so these pods give astronauts both comfort and space of their own.
Each ISS crew quarter measures approximately 2 meters (6.5 feet) long and 1 meter (3.3 feet) wide, roughly the size of a small closet. The compartments are located inside modules such as Node 2 (Harmony) and the Japanese Kibo laboratory.
Background Noise is Always Present
The ISS is never fully quiet. It has fans, machines, and computers that run all the time. This creates a soft humming or buzzing sound. While it’s not loud, it can be distracting for some people.
That’s why many astronauts use earplugs or listen to white noise. The sleeping pod itself also blocks out some of the sound, creating a better space for rest.
Wake-Up Time Follows a Set Clock
Astronauts follow a shared schedule based on Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Everyone on the ISS sticks to the same time zone to keep things organized.
Wake-up calls are given with alarms. The ISS also uses lighting systems that change brightness during the day to help the body stay on track.
These small changes in light help signal when it’s time to sleep or wake up, which supports the body’s internal clock.
Sleeping is only one part of daily survival in orbit. Basic human needs like using the bathroom also require engineering solutions that are very different from those on Earth.
How Do Astronauts Use the Bathroom?
Using the bathroom in space takes training. The toilet on the ISS uses air flow instead of water. It has:
- A small seat with straps
- A funnel and hose for urine
- A canister for solid waste
Astronauts must hold themselves in place with foot straps or handholds. Fans pull waste away and store it safely. Some of the water from urine is cleaned and reused for drinking or washing.
There are no showers on the ISS. Instead, astronauts stay clean with rinse-free wipes, no-rinse shampoo, wet towels, and small amounts of liquid soap.
Since water floats in space, they must use it carefully to avoid spills or equipment issues.
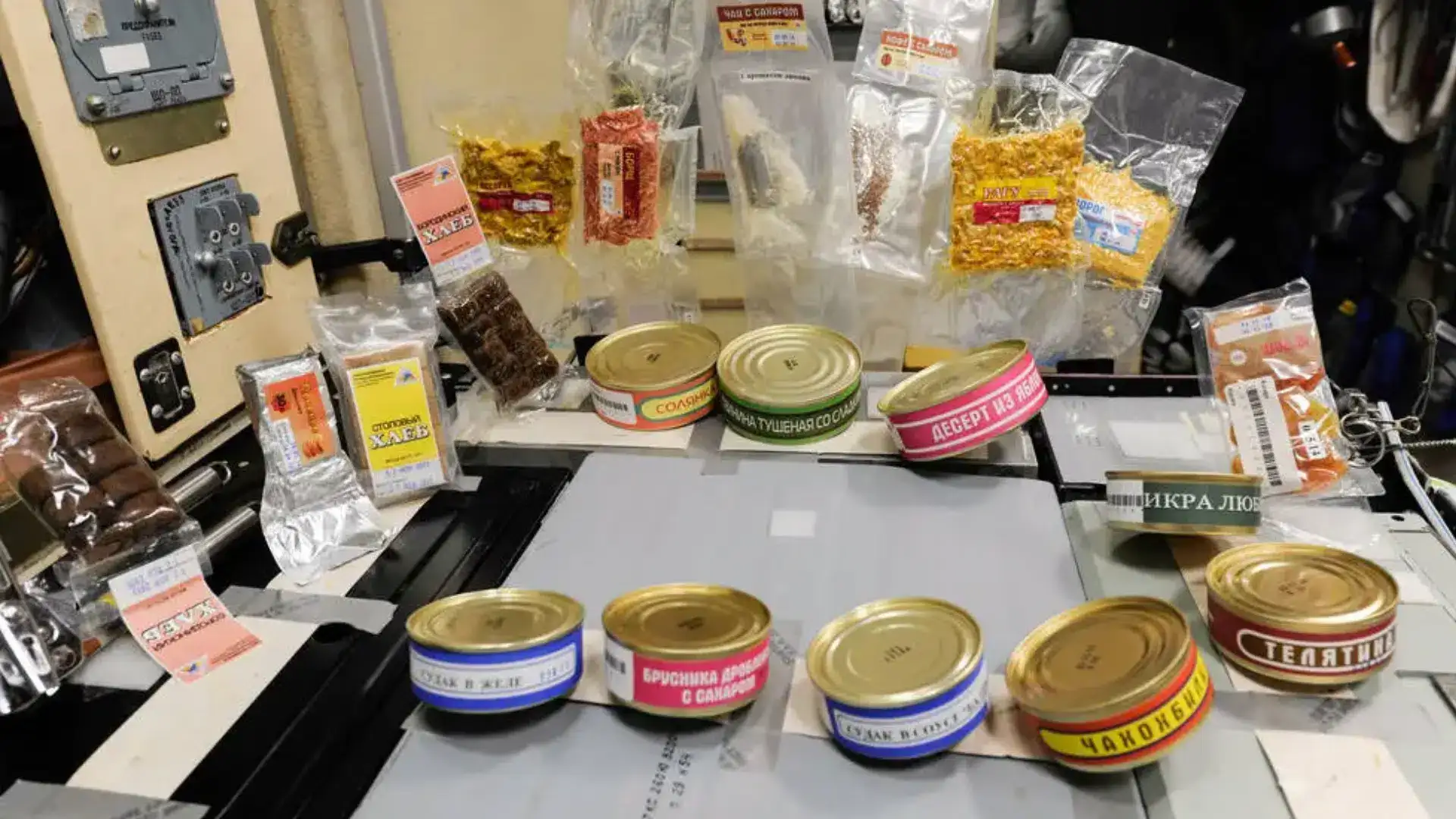
Food and Mealtime on the Space Station

Image Source: NASA
Eating in space is different from eating on Earth because of zero gravity. The kitchen on the ISS is very small but includes all the basics.
It has a table with straps, a water dispenser, food packets, and a heater for warming meals. Astronauts eat three meals a day plus snacks.
The food is packed to last a long time and includes soups, pasta, rice, fruit, meat, and drinks like coffee or juice. Many items are freeze-dried and need water added before eating.
They use special forks, spoons, and knives that stick to the table with Velcro or magnets to keep them from floating away.
Astronauts often eat together, floating near the table and talking about their day. Sharing meals helps build teamwork and keeps everyone feeling connected and healthy.
How the ISS Supports Mental Health
Being in space can be hard. Astronauts miss their families, fresh air, and outdoor spaces. That’s why sleep, food, and daily tasks matter so much. They keep the mind strong.
Astronauts also:
- Talk to a counselor on Earth
- Share thoughts with their team
- Stay busy with fun projects
- Watch movies or read books
Mental health is as important as physical health. The ISS is designed to support both.
Final Thoughts
Life aboard the International Space Station is a remarkable blend of human adaptation and advanced engineering.
From wall-mounted sleeping bags to airflow-powered toilets, every detail is carefully designed to support life in microgravity.
Decades of research from NASA and international space agencies continue to improve how astronauts rest, work, and stay healthy, lessons that may one day help humans live on the Moon or Mars.
Want to learn more about life beyond Earth? Keep reading our space blogs for simple, fun facts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the ISS Lighting System Help Astronauts Sleep?
The ISS uses a special LED lighting system designed to support circadian rhythms. The lights can shift between bright blue-white light (which promotes alertness) and warmer tones (which signal the body to prepare for sleep). NASA introduced this system to reduce sleep disruption caused by 16 sunrises and sunsets each day.
What Happens if An Astronaut Cannot Sleep?
If an astronaut struggles with sleep, NASA flight surgeons monitor the situation carefully. Short-term sleep aids may be approved, but they are used cautiously. More often, astronauts adjust their light exposure, workload timing, and relaxation routines to improve rest naturally.
How is Sleep Monitored During Space Missions?
Astronauts sometimes wear wrist devices similar to actigraphy monitors that track movement and rest cycles. NASA researchers use this data to study sleep quality, performance, and long-term health effects in microgravity.