Since 1976, NASA has published over 2,000 documented “spinoff” technologies, inventions first created for space missions that later improved life on Earth.
Many people think space travel only benefits astronauts. But the truth is, technologies developed for extreme space conditions now help people sleep better, drink cleaner water, survive emergencies, and even take photos with their phones.
Space missions face harsh challenges: no gravity, extreme temperatures, limited power, and life-or-death safety risks.
To solve these problems, engineers create tools that are lighter, stronger, and smarter than ordinary equipment. When those solutions return to Earth, they often become everyday products.
In this article, we’ll look at real space-related inventions, with the specific missions, companies, and stories behind how they made the leap from orbit to everyday life.
What are Space-Related Inventions?
Space-related inventions are the result of space research and engineering made to meet the extreme needs of space missions.
These inventions often focus on saving weight, using less power, working in zero gravity, or handling extreme heat and cold. To solve these problems, scientists create new materials, tools, and systems.
While built for space, many of these inventions turn out to be useful on Earth, too. They are later adapted for regular use in homes, hospitals, cars, and more.
What makes them special is their smart design, made under pressure, that later benefits millions of people in daily life without space travel.
Why Do Space Programs Create New Inventions?
Space is a very hard place to live or work in. Astronauts face problems like:
- Extreme heat and cold
- Lack of air or water
- Limited space for tools or food
- Weight limits for cargo
- No way to call for help right away
To solve these problems, scientists and engineers build special tools. These tools must be light, strong, safe, and easy to use. Many of these tools are so helpful that people later use them in everyday life.
Everyday Items That Came from Space Missions
Let’s look at some common things that were first made for space missions.
1. Memory Foam

Memory foam was developed in 1966 at NASA’s Ames Research Center. It was originally designed to improve crash protection for aircraft seats, not for rocket launches. The material, called “temper foam,” could absorb shock and slowly return to its shape.
In the 1980s, companies like Fagerdala World Foams licensed the technology and adapted it for consumer mattresses and pillows.
Today, memory foam is used in:
- Mattresses
- Pillows
- Car seats
- Helmets
- Shoes
It helps with comfort and support.
2. Cordless Tools

Black & Decker introduced cordless tools in 1961. However, NASA later partnered with the company to develop a special battery-powered drill for the Apollo missions. Astronauts used this drill to collect lunar rock samples.
The improvements made for NASA helped advance battery efficiency and lightweight motor design, influencing modern cordless tools.
Today, cordless drills and tools are used by:
- Builders
- Mechanics
- Homeowners
You can find them in garages and toolkits everywhere.
3. Scratch-Resistant Lenses

In the 1970s, NASA needed helmet visors that would not scratch easily during missions. Engineers worked on protective coatings to keep astronaut face shields clear and durable.
Later, companies like Foster Grant licensed this coating technology for eyewear. Today, scratch-resistant coatings are standard on:
- Eyeglasses
- Sunglasses
- Safety glasses
It helps people see clearly and protects their eyes.
4. Water Purifiers

Clean water is critical in space, where astronauts must recycle nearly every drop. NASA developed advanced filtration systems for spacecraft and the International Space Station to remove bacteria, chemicals, and particles.
These purification technologies were later adapted for use on Earth. Today, similar systems help:
- Make clean water at home
- Help in emergencies
- Support clean water in poor areas
Water is safer thanks to this invention.
5. Freeze-Dried Food

Freeze-drying existed before NASA, but space missions helped refine and popularize the process. For astronauts, food had to be lightweight, compact, and long-lasting without refrigeration.
NASA improved packaging and preservation methods so that nutrients and taste were maintained. Today, freeze-dried foods are common in:
- Camping
- Military meals
- Emergency kits
Many of your snacks may have come from this space idea.
6. Infrared Ear Thermometers
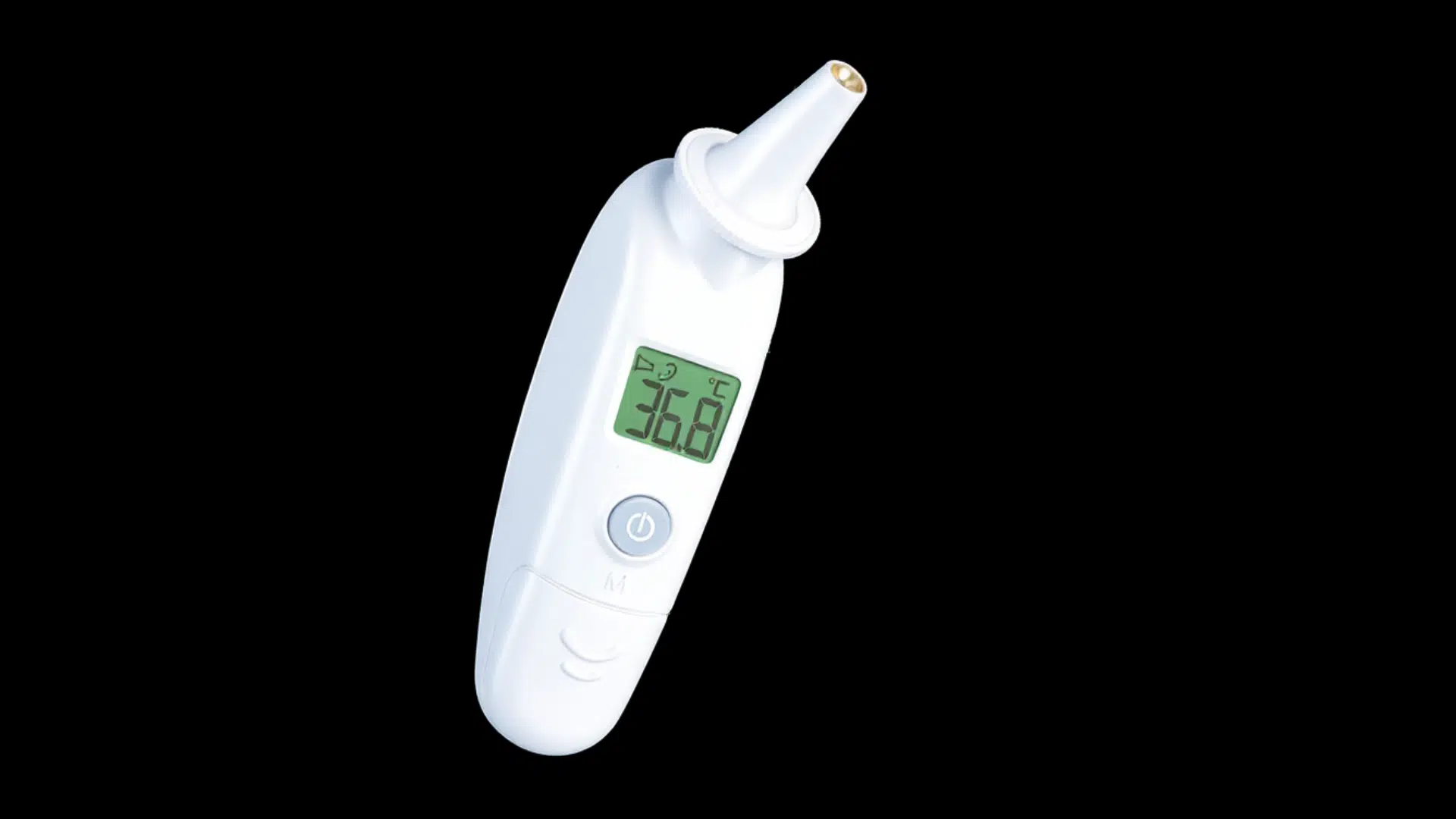
NASA developed infrared sensing technology to measure the temperature of distant stars and planets. These sensors detect heat without touching the object.
In the 1990s, the company Diatek adapted this technology into the first infrared ear thermometer. It allowed doctors and parents to measure body temperature quickly and safely.
Today, infrared thermometers are:
- Fast
- Safe
- Good for babies
You’ll find them in homes and hospitals everywhere.
7. Emergency Blankets

Also known as “space blankets,” these were developed using lightweight reflective materials originally designed to protect spacecraft from extreme temperature swings.
The thin material reflects up to 90% of body heat. Emergency responders quickly adopted the technology.
Today, they are used by:
- First aid teams
- Campers
- Runners after races
They save lives during cold weather or accidents.
8. Fire-Resistant Materials

After the tragic Apollo 1 cabin fire in 1967, NASA redesigned spacecraft materials to improve fire safety. Engineers developed flame-resistant fabrics and materials for astronaut suits.
These advancements later influenced the protective clothing used in:
- Firefighter suits
- Military uniforms
- Car racing outfits
They make dangerous jobs safer.
9. Improved Baby Formula

In the 1980s, NASA funded research into algae-based nutrients for long-duration space missions. Scientists discovered a way to produce DHA and ARA, fatty acids important for brain and eye development.
These nutrients were later added to infant formula. Most baby formulas include DHA and ARA to support healthy development. Today’s formula includes:
- Healthy fats
- Brain-boosting ingredients
Many babies benefit from this science today.
Space Inventions in Health and Safety
Some inventions were made to keep astronauts healthy. Now, they help people on Earth.
10. Long-Distance Health Monitoring

NASA needed to monitor astronauts’ heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs from Earth. This required reliable remote medical tracking systems.
The same principles are now used in:
- Remote heart monitors
- Health-tracking smartwatches
- Tools for checking blood pressure at home
People with health problems now use this tech every day.
11. Air Purifiers

To keep astronauts safe, NASA developed advanced air purification systems that could remove contaminants in closed spacecraft environments.
NASA research later contributed to the development of improved HEPA filtration and air-cleaning systems.
Today, air purifiers are widely used in:
- Homes
- Schools
- Hospitals
They help people with asthma and allergies breathe easier.
12. Artificial Limbs
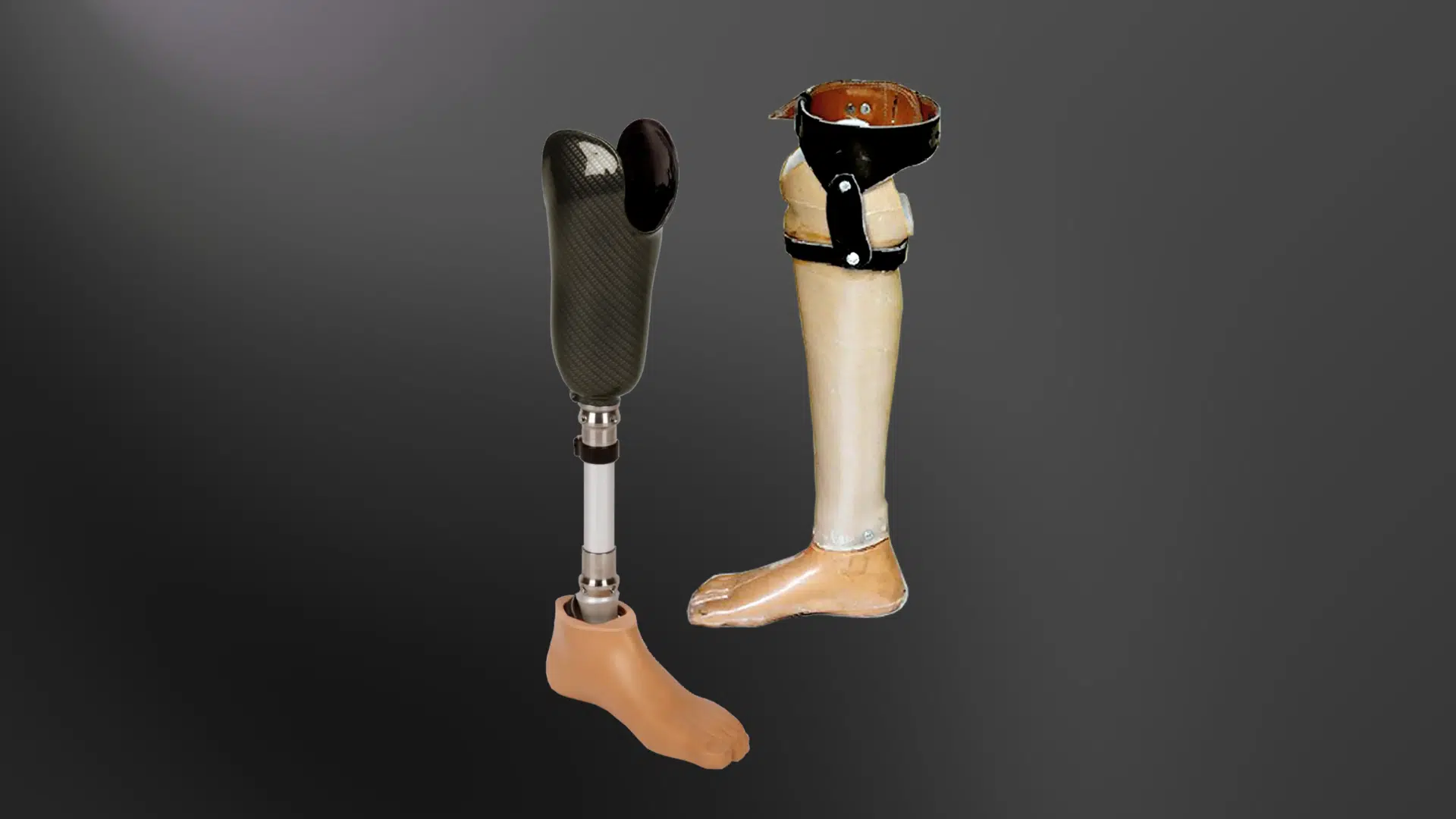
Robotic technology developed for space missions, including the Canadarm used on the Space Shuttle, helped advance precision control systems.
These innovations influenced modern prosthetic limb development. Today’s artificial limbs are:
- Lighter
- Stronger
- Easier to use
People with lost limbs can move better because of space tech.
13. Adjustable Smoke Detectors

Spacecraft required extremely sensitive smoke detection systems that could work in zero gravity. NASA helped refine smoke detection technology to reduce false alarms.
Modern smoke detectors now better distinguish between real smoke and harmless steam.
This improvement helps:
- Homes avoid false alarms
- Buildings react faster to fires
This tech keeps more people safe.
Space Inventions in Technology and Tools
Space missions helped create many tools and tech items we now use every day.
14. GPS and Satellite Navigation

GPS was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, not NASA. However, space-based satellite research and precision tracking work by NASA helped improve positioning accuracy.
NASA’s expertise in orbital mechanics and satellite calibration contributed to more precise navigation systems.
Today, GPS supports:
- Drivers
- Delivery workers
- Farmers
- Hikers
It is one of the most used space-related inventions in the world.
15. Wireless Headsets

During early missions, astronauts needed reliable, hands-free communication inside spacecraft and during spacewalks.
NASA helped advance wireless communication systems that improved clarity and durability in extreme environments.
Modern wireless devices now include:
- Bluetooth headsets
- Earbuds
- Gaming headsets
These devices make it easy to talk, listen, or play without wires, all thanks to space constraints.
16. Camera Phones

In the 1990s, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory engineer Eric Fossum helped develop CMOS image sensor technology. These sensors were smaller, lighter, and required less power than older camera systems.
Originally designed for space probes, CMOS sensors became the foundation for modern digital cameras.
Today, this technology powers:
- Phone cameras
- Laptop webcams
- Doorbell cameras
Most people take photos every day using this camera tech from space research.
17. Solar Panels

Solar cells existed before NASA, but space missions accelerated their development. Spacecraft needed lightweight, efficient solar panels to generate power far from Earth.
NASA’s investment helped improve solar cell efficiency and durability.
Today, solar panels power:
- Homes
- Outdoor lights
- Emergency gear
They save money, reduce power bills, and are better for the environment.
18. Portable Computers

Space missions required compact, durable computing systems capable of operating in confined and harsh environments.
While NASA did not invent laptops, its demand for smaller and more efficient onboard computers accelerated miniaturization and reliability improvements.
Modern portable computing benefits from decades of aerospace-driven innovation in hardware durability and power efficiency.
- Lightweight
- Easy to carry
- Used in schools, homes, and while traveling
Space Tech That Helps Transportation
Some inventions made for space travel are now used to make transportation safer and more reliable on Earth.
19. Anti-Icing Systems
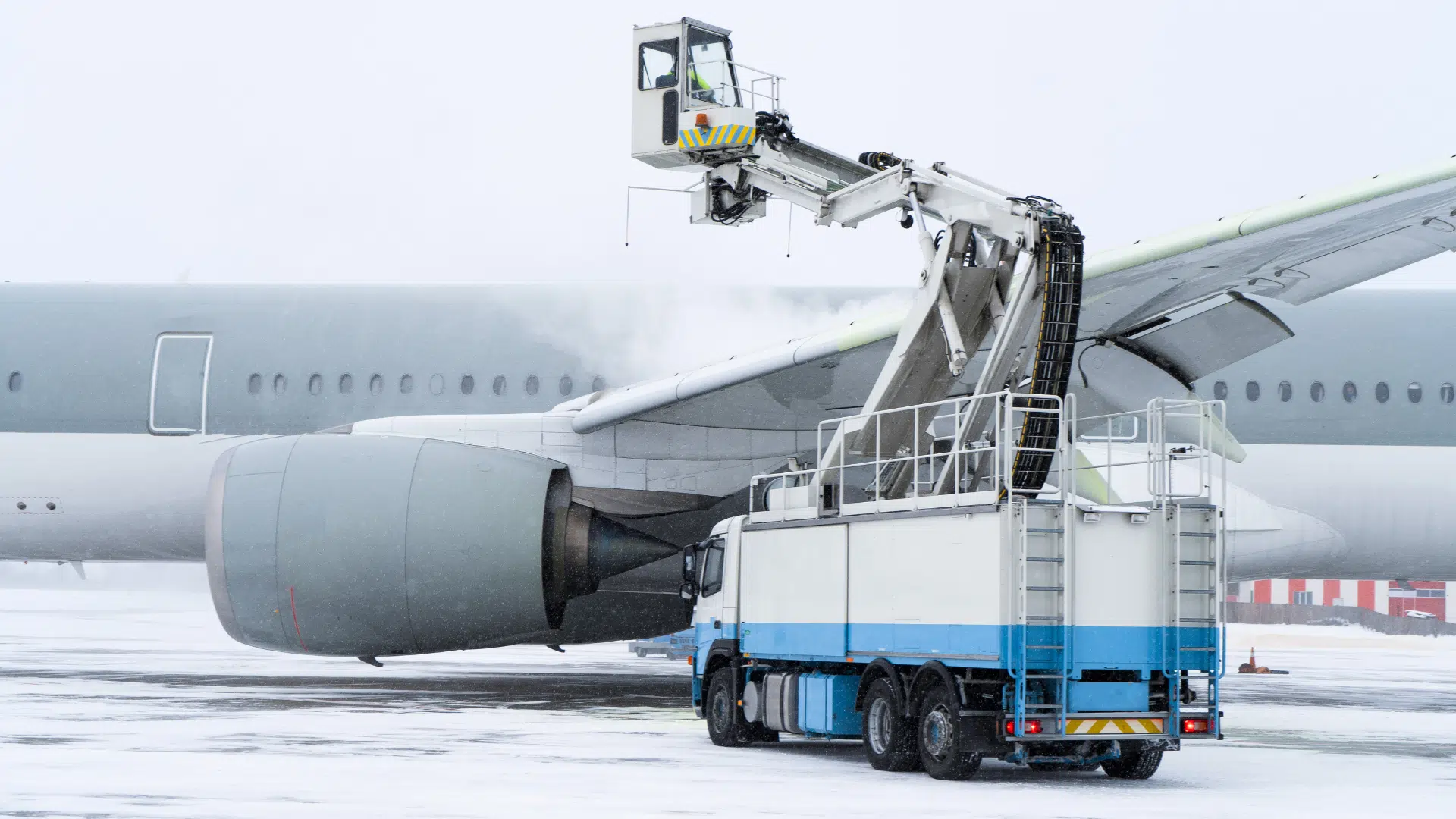

Space shuttles faced ice buildup risks during launch preparation. NASA developed monitoring and ice-detection systems to prevent dangerous accumulation.
Similar technologies are now used on:
- Airplane wings
- Wind turbines
- Power lines
These systems help prevent damage and reduce the risk of accidents caused by ice buildup. They help keep travel safe in cold weather.
20. Stronger Car Tires

When designing lunar rovers, NASA needed tires that could handle rough terrain without air. Working with companies like Goodyear, engineers developed durable, flexible tire designs.
Research into lightweight materials and improved tread design influenced later tire innovations.
Today, drivers benefit from:
- Better grip
- Longer-lasting tires
- Safer travel in rain, snow, and rough roads
This space-related invention helps people drive more safely and with more control every day.
What These Inventions Mean for Everyday Life
Space-related inventions are more than just high-tech tools; they solve real problems on Earth. They help people sleep better, travel safer, and stay healthy in simple ways.
Many items, like GPS or water filters, are now so common that people forget they started with space programs.
These inventions also push companies to make smarter, stronger, and lighter products. They improve comfort, safety, and even save lives in emergencies.
From hospitals to homes, their impact is wide. Space missions may be far away, but the results are close to home, improving daily life without most people even noticing.
Final Thoughts
The next time you use a GPS, slip on a pair of sunglasses, or turn on clean water, remember that space science helped make it possible.
These inventions may seem normal now, but they began with bold ideas and big challenges. Space research isn’t just about rockets; it’s about solving problems in smart, lasting ways.
As new missions continue, even more useful tools may come into our daily lives. It’s a reminder that science in one place can make life better everywhere.
Curious about how else space has shaped the world around you? Browse our other blogs for more simple, useful insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
Did NASA Invent Tang?
No. Tang was created in 1957 by General Foods. NASA used it on early missions, which made it popular.
Did NASA Invent Velcro?
No. Velcro was invented in 1941 by Swiss engineer George de Mestral. NASA used it widely in spacecraft, increasing public awareness.
Did NASA Invent Teflon?
No. Teflon was discovered in 1938 by DuPont chemist Roy Plunkett. NASA later used it in spacecraft components because it resists heat.