Story Musgrave is one of NASA’s most well-known astronauts. His path to space was long and full of learning. He worked in many fields and wore many hats during his career.
From fixing machines to flying space shuttles, he did it all with care and skill. His story is not just about space; it’s about hard work, curiosity, and never giving up.
This blog takes a closer look at his time at NASA, his space missions, and the impact he left behind.
Story Musgrave’s journey is one worth knowing. He shows what is possible when a person stays focused and keeps going.
Early Life of Story Musgrave
Story Musgrave was born on August 19, 1935, in Stockbridge, Massachusetts. He grew up in a rural area and spent a lot of time outdoors.
As a child, he was curious about how things worked. He enjoyed building, fixing, and learning by doing. These early years shaped his way of thinking and helped him later in life.
Musgrave had a difficult childhood. His father struggled with alcohol, and Story often had to take care of himself.
But he did not let his problems hold him back. He kept moving forward and worked hard in school. He believed that learning could open doors, and he never stopped learning.
Education and Path to NASA
Before Story Musgrave ever flew in space, he built a strong background in school, the military, and medicine. Each part of his early path helped prepare him for his future at NASA.
Education

Image Source: Academy of Achievement
Story Musgrave was not a traditional student. He dropped out of high school but later earned a GED and began college studies. Over the years, he earned six college degrees, showing his deep interest in both science and the humanities. His degrees included:
- Mathematics and statistics
- Operations analysis
- Physiology and biophysics
- Literature
- Medicine
- Computer programming
Early Career
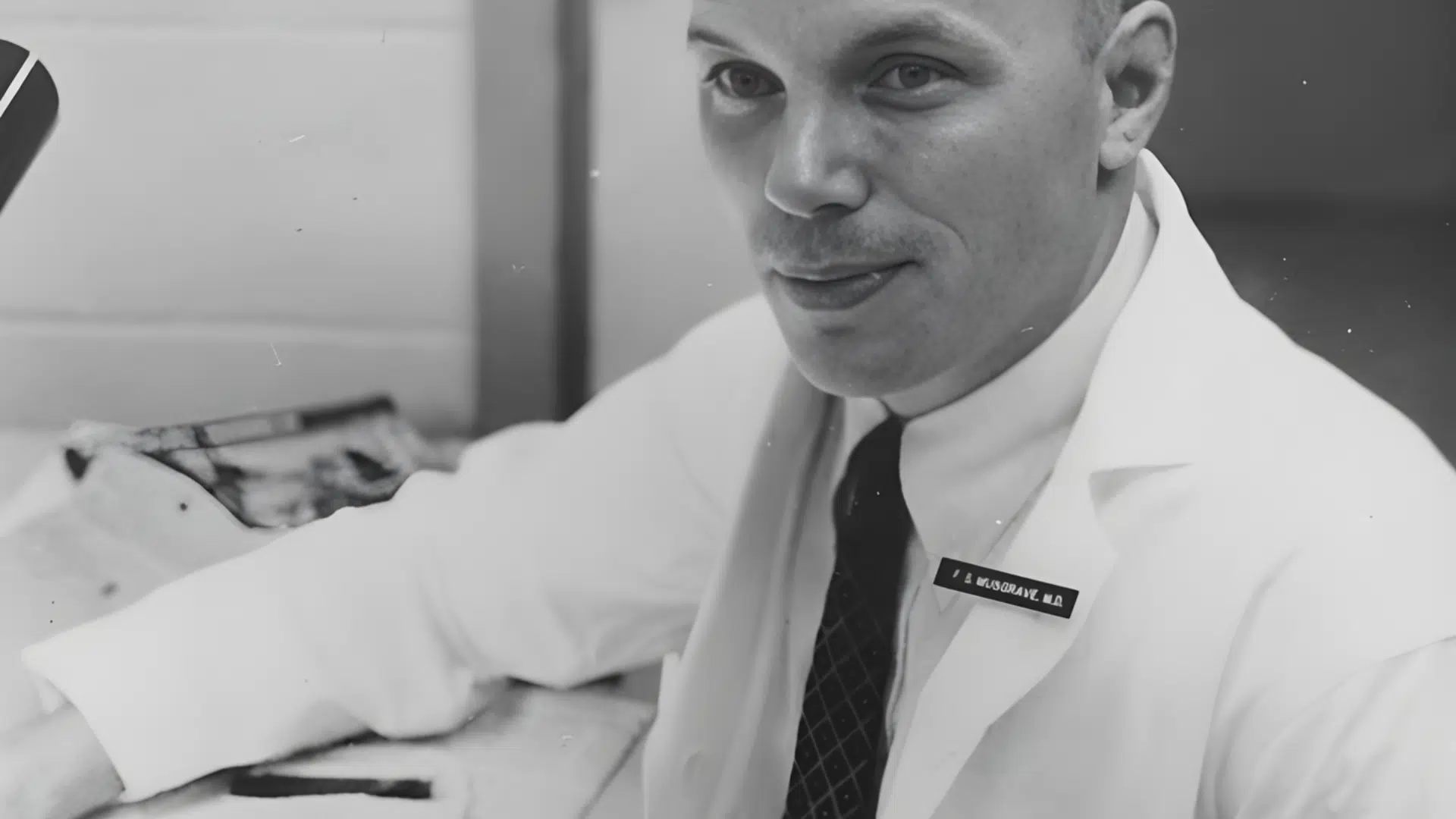
Image Source: University of Kentucky
Musgrave joined the U.S. Marine Corps, where he worked as an aviation electrician and learned how to repair and fly planes. His time in the Marines taught him discipline, technical skills, and how to stay calm under pressure.
After leaving the military, he studied medicine and became a doctor.
He worked in hospitals and emergency rooms, treating injuries and understanding how the human body works. These skills later helped him become a medical expert on space missions.
Joining NASA

Image Source: Academy of Achievement
In 1967, Musgrave was selected by NASA as part of its sixth astronaut group. Unlike earlier astronauts, many in this group had strong science and medical backgrounds.
Musgrave stood out because of his wide range of knowledge and his ability to work across fields.
At the time, NASA was preparing for future shuttle missions, and they needed astronauts who could work with complex systems. Musgrave’s mix of skills in flying, fixing machines, and medicine made him a perfect choice.
Work at NASA Before Flying
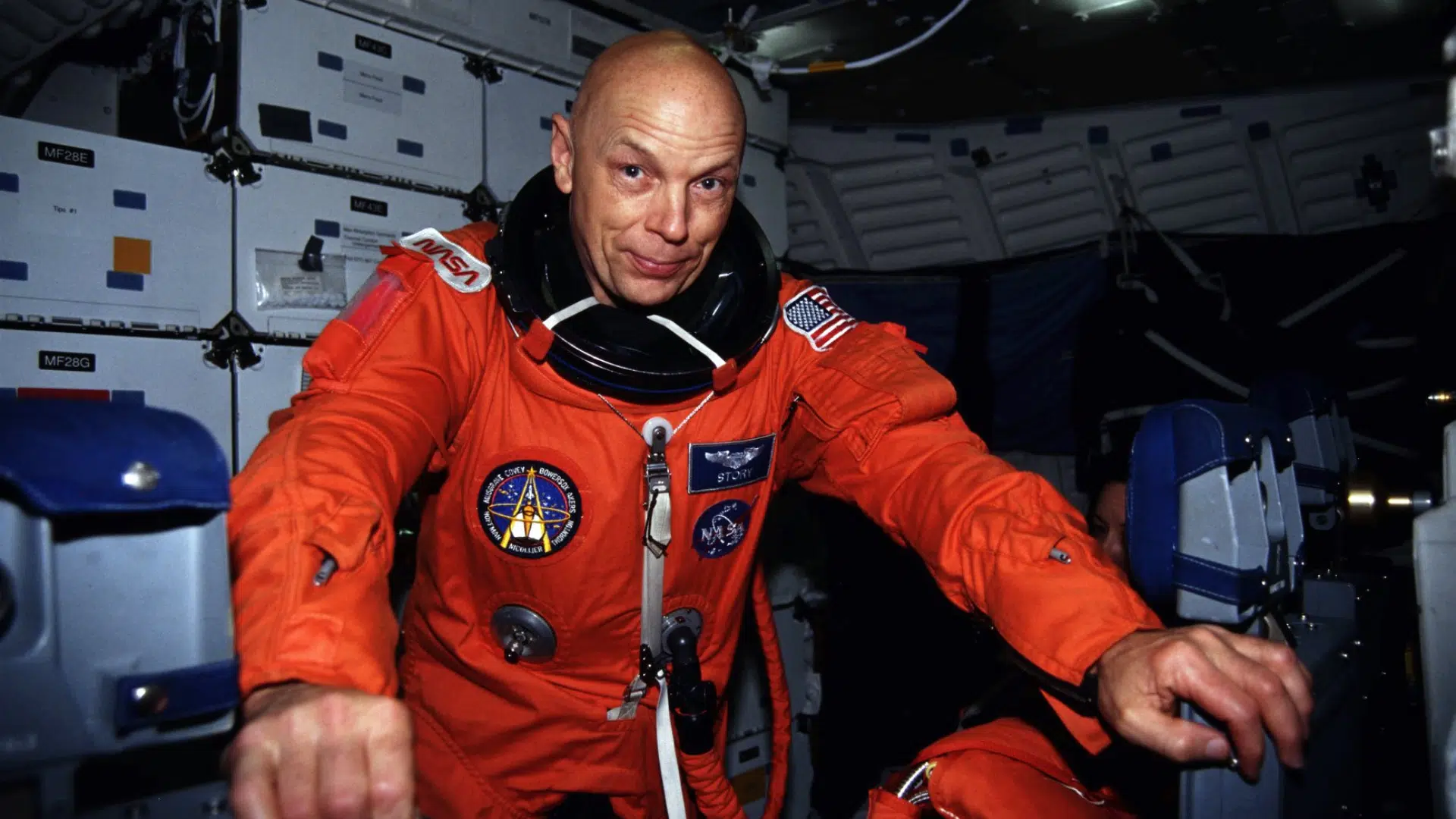

Image Source: Facebook
Before he ever went to space, Musgrave worked behind the scenes to help build and test key space systems. He helped:
- Design better spacesuits
- Improve life support systems
- Develop space tools for working outside the shuttle
- Plan for safe and effective spacewalks
- Support the early design of the Space Shuttle program
He worked with engineers, doctors, and fellow astronauts to solve problems and prepare for future missions. His medical background also helped NASA understand how space affects the human body, which became important in later shuttle flights.
Space Missions: How Many Times Did He Fly?
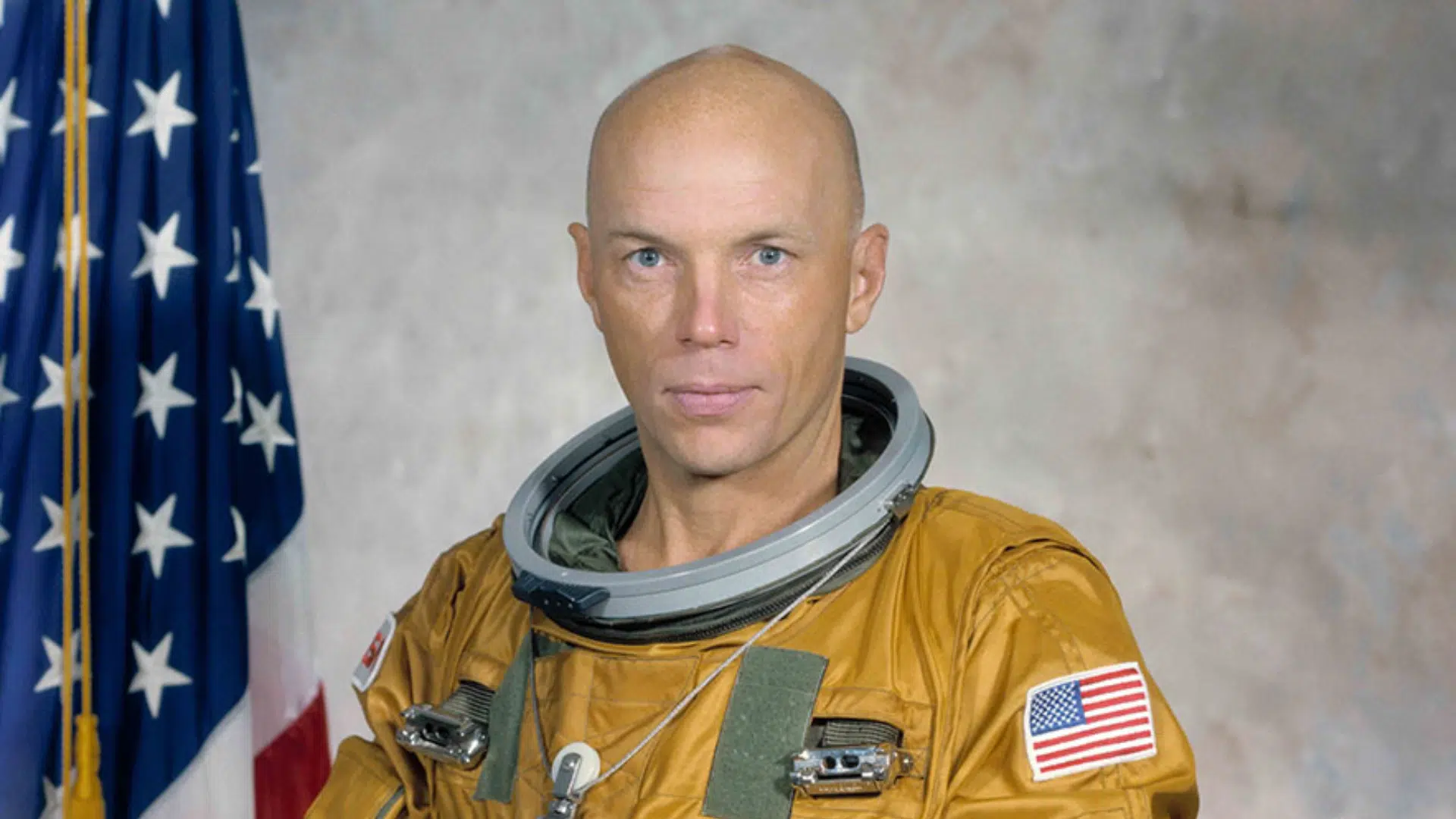

Image Source: Wikipedia
Story Musgrave flew in space six times, which is still a record for one astronaut. He flew on the following space shuttle missions:
STS-6 (1983) – Challenger
This was the first flight of the Challenger shuttle. Musgrave and fellow astronaut Don Peterson performed the first spacewalk of the shuttle program. This mission proved astronauts could safely work outside the shuttle.
STS-51-F (1985) – Challenger
This mission was a science flight. It carried Spacelab, a special space science lab. Musgrave worked on different science experiments while in orbit.
STS-33 (1989) – Discovery
This mission was run by the Department of Defense. Musgrave was the flight engineer. The mission was short but important.
STS-44 (1991) – Atlantis
Again, this was a Department of Defense mission. Musgrave was a key crew member. He helped with satellite deployment and system testing.
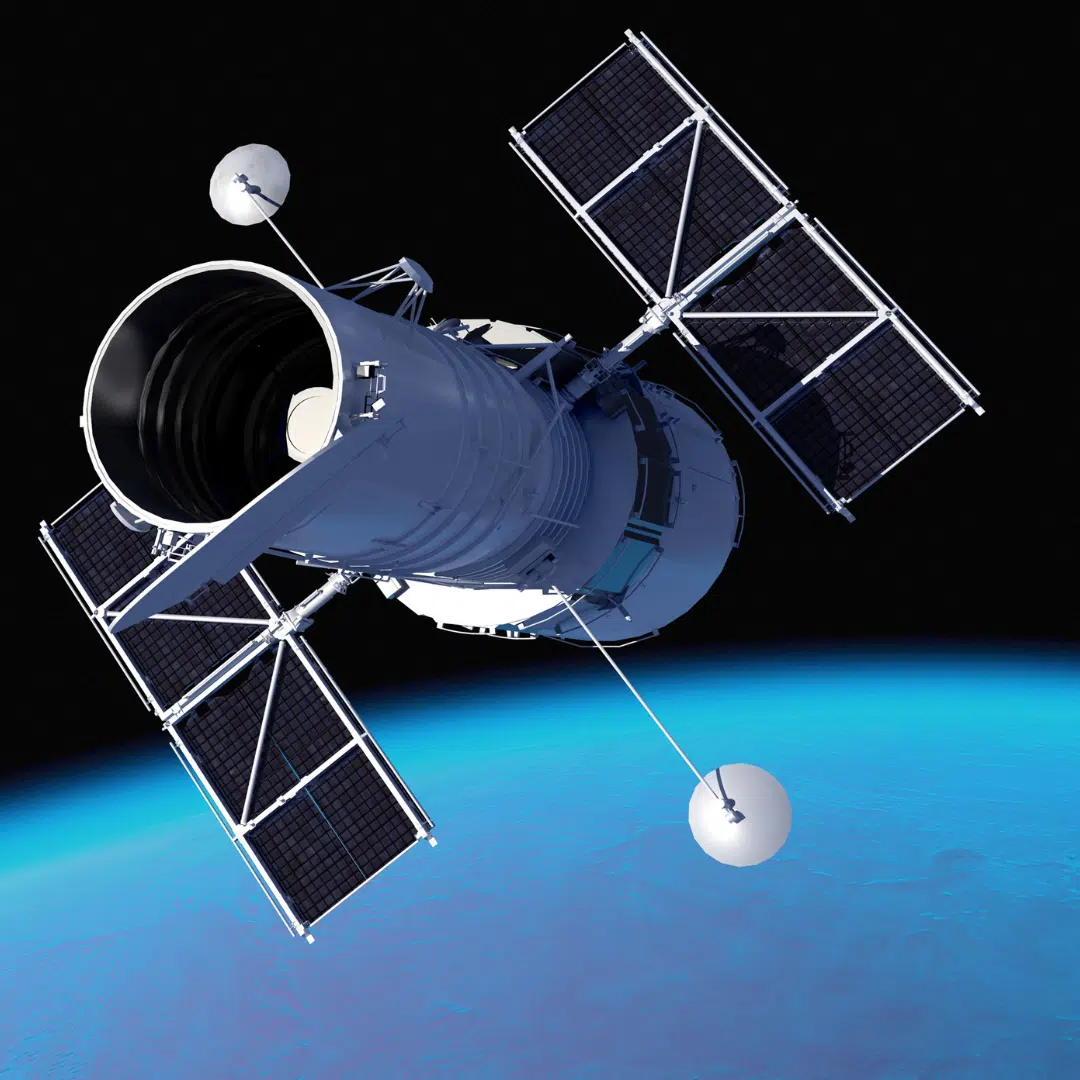
STS-61 (1993) – Endeavour
This was one of his most famous missions. Musgrave helped fix the Hubble Space Telescope. The telescope had problems after launch, and this repair mission saved it. Musgrave did three spacewalks on this flight.
STS-80 (1996) – Columbia
This was his final spaceflight. It was also the longest shuttle flight at the time, lasting nearly 18 days. The mission studied Earth and tested equipment.
Musgrave’s Key Roles During Shuttle Missions
Musgrave was not just a passenger. He played important roles on every mission:
- Spacewalker: He tested suits, fixed tools, and helped with space repairs.
- Engineer: He helped monitor shuttle systems and fix problems.
- Medical doctor: He kept an eye on crew health and collected data.
- Scientist: He ran experiments and helped collect research for labs on Earth.
- Trainer: He helped teach other astronauts how to use new tools and suits.
Because he had so many skills, Musgrave could do many jobs during space missions. His vast knowledge made him a valuable team member on every flight.
How Story Musgrave Helped Improve NASA
Beyond his space missions, Story Musgrave helped NASA improve how it worked as an organization. He worked closely with engineers, trainers, and planners to make future missions safer and more effective.
He helped design better spacesuits and tools, making spacewalks safer and easier for astronauts. He supported more realistic astronaut training, pushing for methods that matched what crews would face during missions.
He also gave feedback on shuttle systems and designs, helping engineers think through small but important changes.
More importantly, he encouraged a culture of critical thinking at NASA. He believed astronauts should not just follow plans but also ask questions, solve problems, and improve the systems around them.
Life After NASA
Musgrave retired from NASA in 1997, after 30 years of service. But he didn’t slow down. He stayed very active.
He gave talks across the country, sharing his story with schools, colleges, and groups. He worked with tech and space companies, helping design new tools and systems. He also became a businessman, working in design, medicine, and education.
Musgrave believed that life is about constantly learning. After NASA, he kept studying, working, and teaching.
Awards and Honors
Over his long career, Musgrave received many awards, including:
- NASA Distinguished Service Medal
- NASA Space Flight Medal (six times)
- NASA Exceptional Service Medal
- Induction into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame
These awards show how much he gave to NASA, science, and space travel.
Final Thoughts on His Legacy
Story Musgrave’s life shows what can happen when someone keeps learning and never gives up. He worked hard, asked questions, and used his many skills to help others.
From walking in space to fixing the Hubble Telescope, he played a key role in NASA’s history. His deep thinking and teamwork made space travel safer and smarter.
Even after leaving NASA, he kept sharing his knowledge and ideas. His story is not just about space; it’s about using your mind and staying curious.
Want to learn more about astronauts like Musgrave? Keep reading our blog for more inspiring space stories.