Have you ever looked up on a clear evening and spotted a peculiar straight line of lights in the sky, moving steadily like a celestial train? You’re not alone.
Thousands of people worldwide have been puzzled by this mesmerizing phenomenon. These aren’t UFOs or shooting stars, but something equally fascinating: Starlink satellites.
This line of lights in the sky has become increasingly common as SpaceX deploys its ambitious satellite internet constellation.
Ready to demystify those mysterious lights? Let’s learn the science and technology behind Starlink’s celestial display
What is Starlink?
Starlink is SpaceX’s ambitious satellite internet constellation designed to provide high-speed broadband access across the globe, especially in remote and underserved areas.
The system consists of thousands of small satellites operating in low Earth orbit (LEO), positioned much closer to Earth than traditional satellites, roughly 340 miles up, compared to 22,000 miles for conventional satellite internet.
These satellites work together as a network, communicating with ground stations and user terminals to deliver internet connectivity.
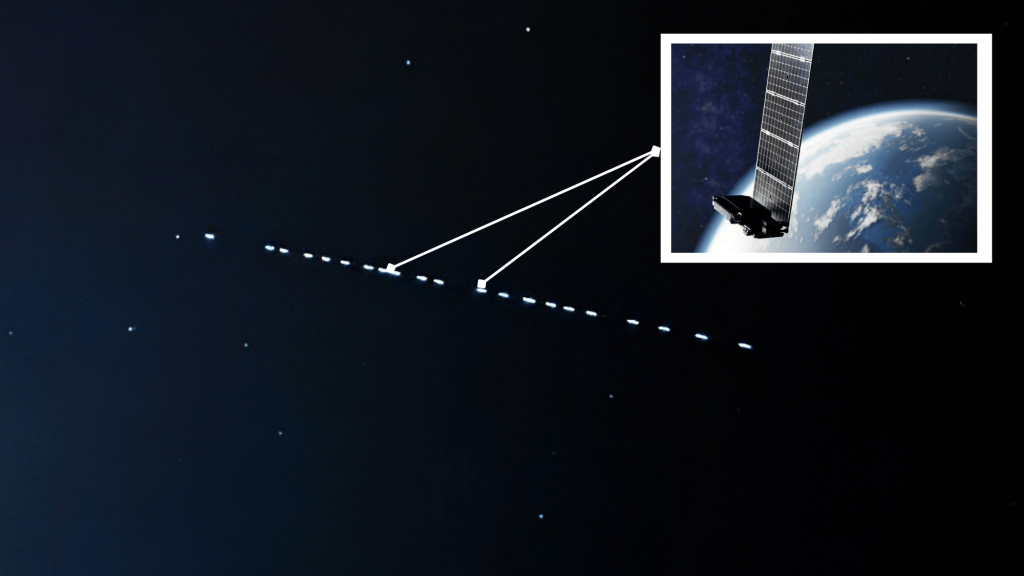
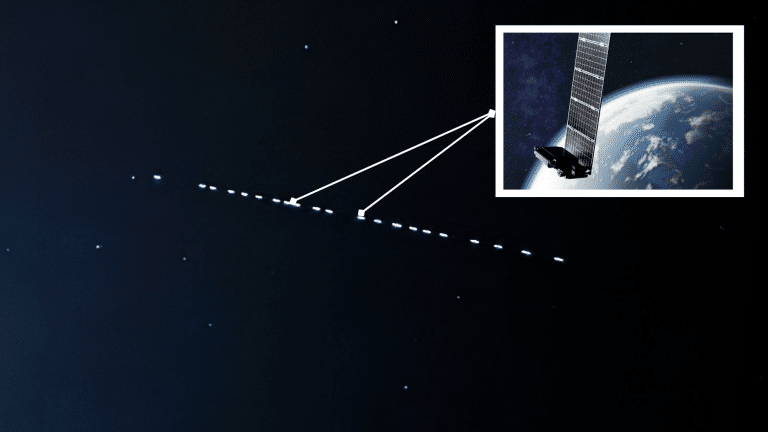
SpaceX launches these satellites in batches of 40-60 at a time, which initially travel together in a visible “train” formation before spreading to their designated positions.
With over 5,000 satellites currently deployed and plans for tens of thousands more, Starlink represents the largest satellite constellation ever created.
Why Do Starlink Satellites Appear as Lines of Lights in the Sky?
The striking line of lights in the sky that attracts observers worldwide occurs due to Starlink’s unique deployment process.
SpaceX launches satellites in batches of 40-60, releasing them into a temporary formation where they travel closely together like a celestial train.
Their solar panels reflect sunlight brilliantly, especially during twilight hours when the ground is dark but satellites remain illuminated above.
This combination of multiple satellites, reflective surfaces, synchronized movement, and optimal lighting conditions creates the spectacular line of lights in the sky.
Key factors that create the line of lights effect:
- Batch deployment: Dozens of satellites released simultaneously stay clustered together
- Solar panel reflection: Flat surfaces catch and reflect sunlight effectively during twilight
- Orbital altitude: Perfect height to remain sunlit while the ground is in darkness
- Uniform spacing: Evenly distributed satellites create a distinctive chain-like appearance
How Starlink Connects the World Through Space Technology
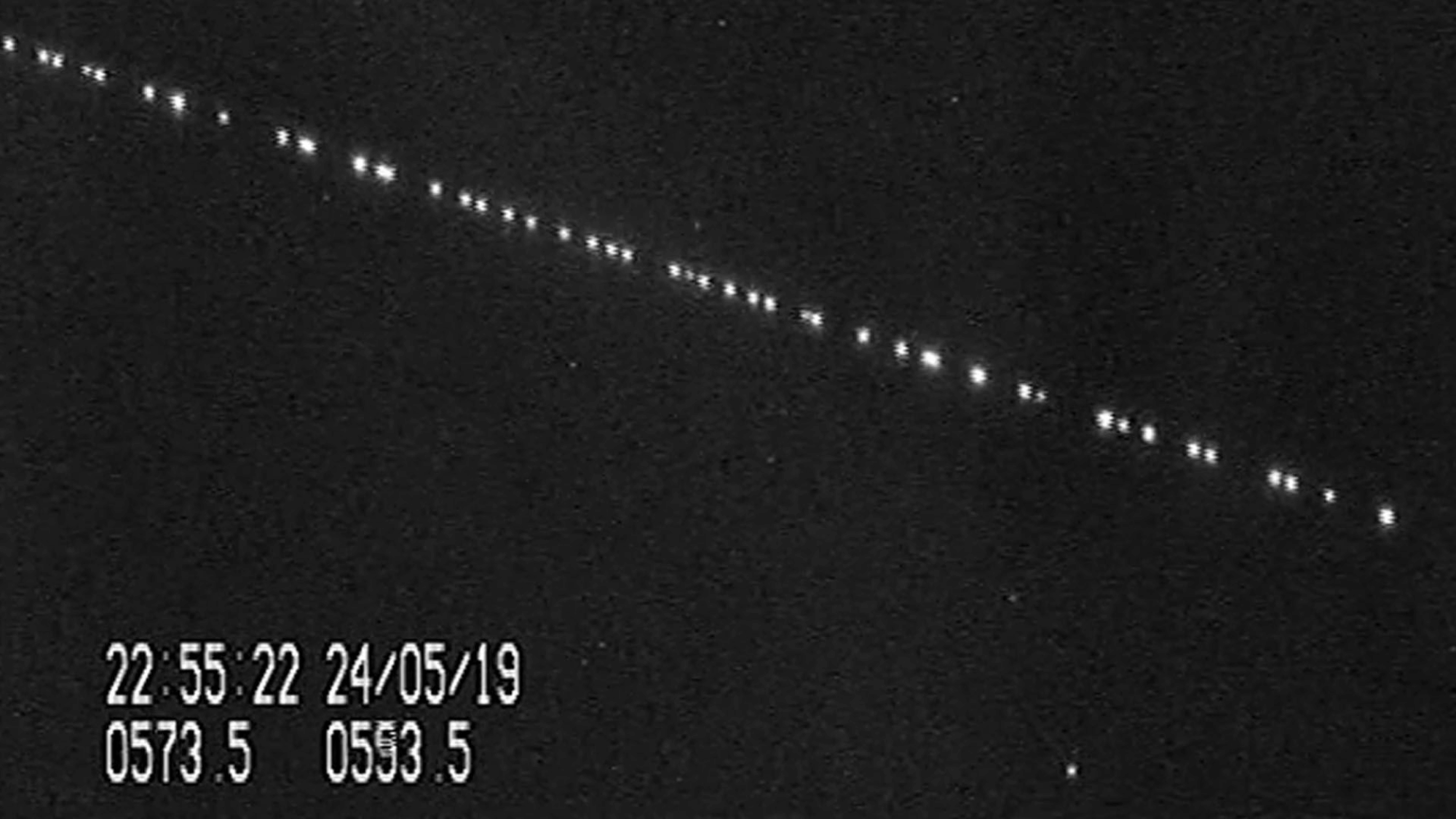

Image Source: Britannica
Understanding how these satellites communicate, connect, and deliver internet helps explain why those trains of lights in the sky represent such a significant technological leap forward.
1. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Positioning
Starlink satellites orbit at approximately 340 miles above Earth, significantly lower than traditional geostationary satellites positioned at 22,000 miles.
This proximity dramatically reduces signal travel time, cutting latency from 600ms to just 20-40ms.
The lower altitude means signals have less distance to travel, resulting in faster, more responsive internet comparable to terrestrial broadband.
However, this positioning requires thousands of satellites working together to maintain continuous global coverage as they rapidly move across the sky.
2. Satellite-to-Satellite Laser Communication
Newer Starlink satellites feature optical inter-satellite links that use lasers to transmit data between satellites at the speed of light through space’s vacuum.
This technology allows data to route through the constellation without constantly relaying to ground stations, proving especially valuable over oceans and remote regions.
The laser links actually transfer data faster than fiber optic cables over long distances since light travels more efficiently through a vacuum than glass.
This creates a space-based mesh network that enhances reliability and reduces dependence on terrestrial infrastructure.
3. Ground Station Connectivity
Starlink operates a global network of ground stations called gateways that connect the satellite constellation to the internet’s backbone infrastructure.
These stations use high-frequency radio waves to communicate with overhead satellites, serving as the bridge between space and Earth’s existing internet systems.
Data travels from users to satellites, potentially through the satellite mesh network, then down to the nearest gateway before connecting to traditional internet infrastructure.
SpaceX continuously expands this gateway network to improve coverage, reduce latency, and increase overall system capacity worldwide.
4. User Terminal (“Dishy”) Technology
The Starlink user terminal is a phased-array antenna that electronically steers its beam to track satellites without any physical movement.
It automatically locates and locks onto passing satellites overhead, seamlessly switching between them to maintain uninterrupted connectivity throughout the day.
The dish features self-heating capabilities to prevent snow accumulation in winter conditions and requires only electrical power and an unobstructed view of the sky.
No professional installation is needed; users simply plug it in, and the system handles satellite acquisition and tracking automatically.
Why Are Starlink Satellites Controversial?
While Starlink delivers internet to underserved areas, its rapid expansion has ignited debate over its impact on astronomy, space safety, and the environment.
- Light Pollution: Starlink satellites reflect sunlight, creating visible streaks across the night sky that interfere with astronomical observations and stargazing.
- Space Traffic Risks: Starlink performs thousands of avoidance maneuvers annually, raising concerns about cascading collisions that could create dangerous debris fields affecting all space operations.
- Environmental Impact: Regular satellite re-entries burn tons of material in the upper atmosphere. Scientists are studying potential consequences for atmospheric chemistry and ozone layers, with long-term environmental effects.
- Astronomical Concerns: Professional telescopes capture bright satellite trails in images, contaminating scientific data. Radio frequency emissions interfere with radio astronomy, potentially obscuring discoveries.
- SpaceX’s Response: SpaceX developed sunshade visors, reducing satellite brightness by 70% and collaborates with astronomers to share orbital data.
When and Where Can You See Starlink Satellites?
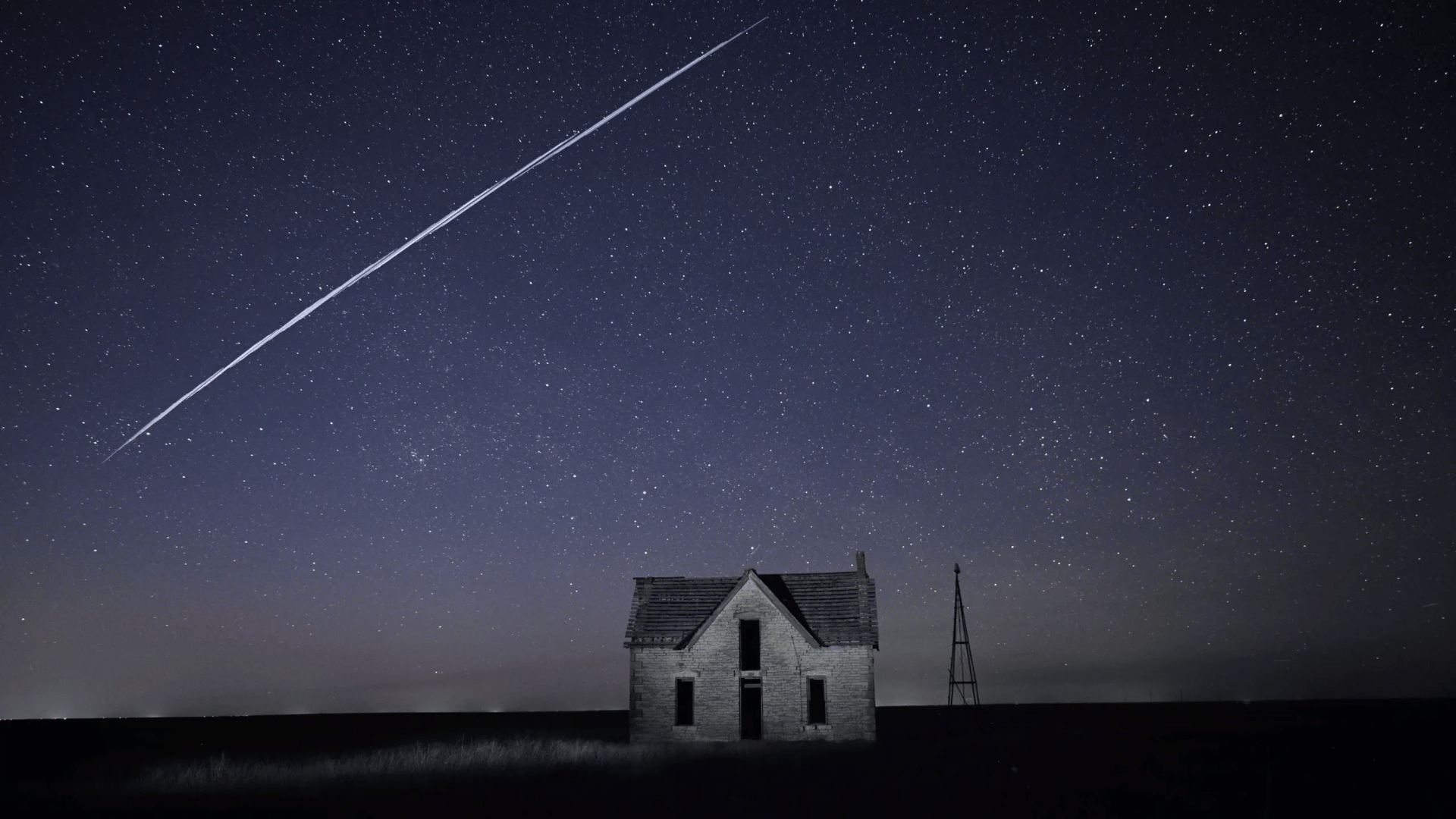

Image Source: WANE 15
You can easily spot Starlink satellites if you know when and where to look, as their visibility depends on timing, light, and sky conditions.
| Aspect | Quick Details |
|---|---|
| Best Time | After sunset or before sunrise. |
| Visibility Duration | Bright for a few days post-launch. |
| Ideal Conditions | Clear, dark skies away from city lights. |
| Where to Look | Visible worldwide in open areas. |
| Appearance | A line of evenly spaced moving dots. |
| Tracking Tools | Find Starlink, Heavens-Above, and Stellarium. |
The Future of Starlink and Satellite Visibility
The future of Starlink focuses on expanding coverage while reducing its impact on the night sky.
SpaceX plans to launch tens of thousands more satellites to improve global internet access, especially in rural and remote areas.
Newer generations of Starlink satellites are being designed with darker coatings, sunshades, and optimized orbits to minimize brightness and preserve astronomical visibility.
SpaceX also aims to amplify laser communication links, improving speed and reducing dependence on ground stations.
As satellite constellations from other companies like Amazon’s Project Kuiper join the skies, managing orbital traffic and light pollution will become crucial.
The challenge ahead is balancing technological progress with responsible space use, ensuring that humanity can stay connected without dimming the beauty of the night sky.
Conclusion
The next time you spot that mesmerizing straight line of lights in the sky. You’ll know you’re witnessing history in motion: SpaceX’s Starlink constellation is connecting our world.
What once seemed like a mysterious phenomenon is actually a glimpse into humanity’s expanding technological frontier.
These luminous trains represent more than just satellites; they symbolize our evolving relationship with space and the ongoing balance between progress and preservation.
Want to experience it yourself? Use the tracking tools we’ve discussed, find a dark spot away from city lights, and look up during twilight hours.