Flying machines need parts that are safe, strong, and built to exact size. From airplanes to rockets, each part must work under high stress and pressure.
This is where machining comes in. It helps shape the parts that make flight possible. In the aerospace field, every cut, hole, and surface must be just right. A small mistake can lead to big problems.
Aerospace machining supports major industries like air travel, defense, and space. It plays a quiet but important role in how people and machines reach the sky.
This blog explains the basics of aerospace machining and why it matters so much in today’s world.
What is Aerospace Machining?
Aerospace machining is the process of shaping and finishing parts for aircraft and space systems.
It uses machines like mills, lathes, and drills to cut metal into the right size and shape. These parts must meet strict rules for quality and safety. Even a tiny mistake can lead to failure.
The goal is to make strong, light, and precise parts. These may include airplane wings, engine parts, landing gear, and pieces for rockets or satellites.
Aerospace machining is done in clean, organized shops where the environment is controlled for the best results.
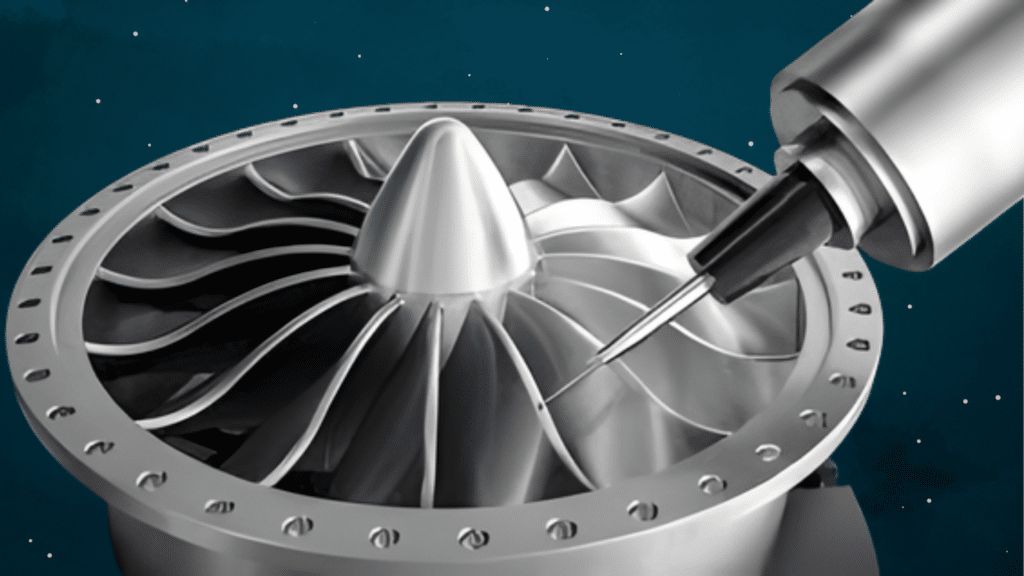
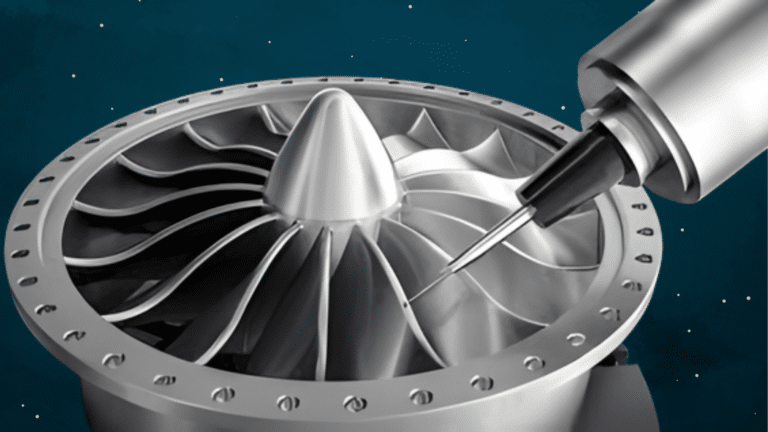
The Role of Precision in Safe Air and Space Travel
Image Source: RapidDirect
In the aerospace industry, there is no room for error. Parts must fit together perfectly. If a piece is too big or too small by even one millimeter, it could cause major problems.
- Planes travel fast and face strong air pressure.
- Spacecraft deal with extreme heat and cold.
- Engines need parts that can handle high speeds and friction.
This is why aerospace machining must follow very tight tolerances. Tolerances are limits set to make sure every part is just the right size and shape.
Common Materials Used in Aerospace Machining
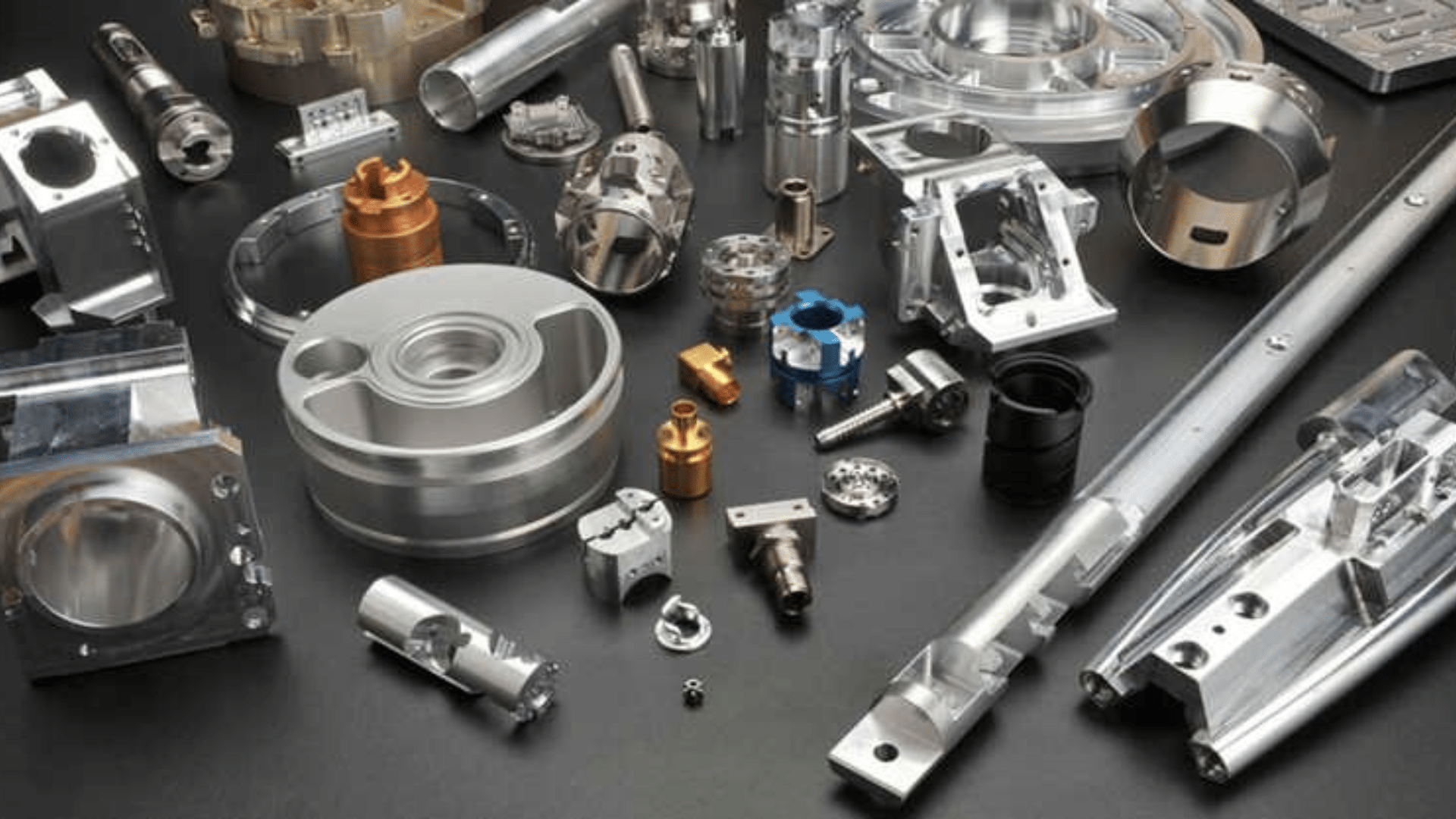

Image Source: RapidDirect
Aerospace parts must be made from materials that are strong but not too heavy. Here are some materials often used:
- Aluminum: Light, strong, and resists rust.
- Titanium: Very strong and handles heat well.
- Stainless Steel: Tough and resists wear.
- Nickel Alloys: Can survive high temperatures.
- Carbon Fiber Composites: Very light and used in modern aircraft.
Each material is chosen based on what the part needs to do. For example, engine parts may need titanium, while cabin parts may use aluminum.
What is CNC Machining?
Image Source: Fastems
CNC stands for “Computer Numerical Control.” It means that machines are guided by computer programs. These programs tell the machines how to cut, drill, or shape the material.
CNC machines are common in aerospace machining because:
- They are very accurate.
- They can repeat the same process many times.
- They can make complex shapes.
- They reduce human error.
With CNC, a part can be made the same way every time, which helps with safety and quality.
Types of Machining in the Aerospace Industry
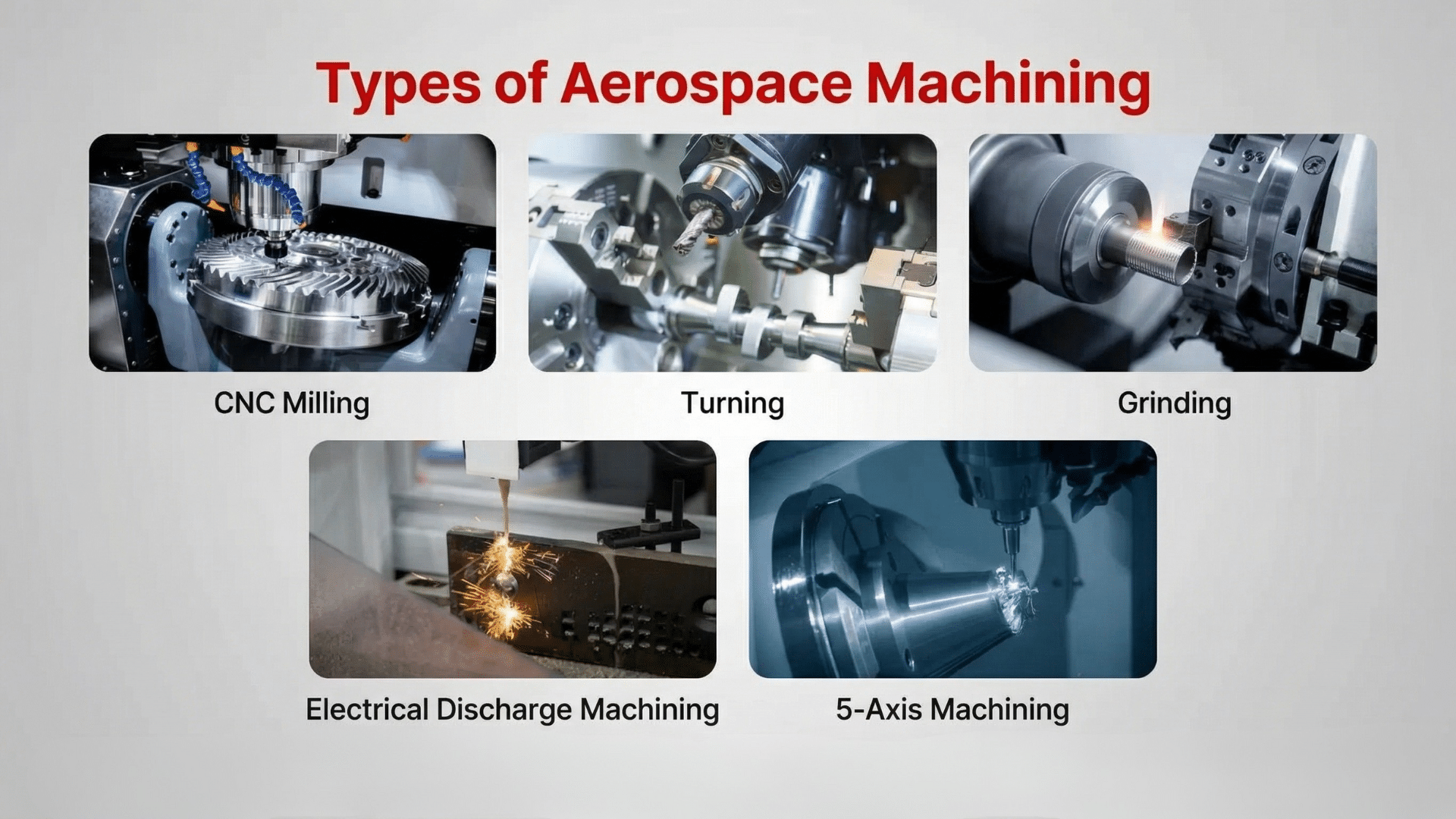
There are many ways to shape parts in aerospace machining. Each method has a special use and works best for certain materials or shapes.
1. Milling
Milling uses a spinning tool to cut material. The tool moves over the surface and removes layers to create shapes.
It’s great for making flat surfaces, holes, or slots. Milling is often used for airplane panels, brackets, and wing parts. It can also shape parts with grooves or patterns.
2. Turning
Turning is used for round parts. The material spins while a cutting tool removes the outer layers. This method is good for making rods, shafts, rings, and discs.
In aerospace, turning helps create parts like landing gear pins or engine shafts that must be perfectly round.
3. Drilling
Drilling makes holes in the material. These holes are often used to fit bolts, screws, or rivets.
In aerospace, drilling is very common because many parts need to be joined together. The holes must be made with care so the pieces fit tightly and stay strong under pressure.
4. Grinding
Grinding uses a wheel to smooth the surface of a part. It gives a fine finish and removes small amounts of material.
This process is useful when a part must be very flat or smooth. Grinding is often used to finish engine parts or surfaces that need tight contact.
5. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
EDM uses small electrical sparks to cut metal. This method does not use physical cutting tools. It works well on hard metals and for making tiny, detailed shapes.
EDM is helpful when regular tools can’t reach tight corners or very thin areas, like in turbine blades or fuel nozzles.
6. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting uses a high-power beam of light to melt or burn through materials. It is fast, clean, and works best on thin metals or complex shapes.
In aerospace machining, laser cutting is used to cut lightweight parts or make small holes with very smooth edges.
7. Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting sprays water mixed with fine grit at high speed to cut material. It can cut through metal, plastic, glass, or composites without adding heat.
This is useful for parts that could be damaged by heat, such as fiber-reinforced panels or plastic-based materials.
Aerospace Machining Services
Aerospace machining involves more than just cutting metal. Many companies offer a wide range of services to support the full process of designing, making, and checking aerospace parts.
| Service Type | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Custom Part Production | Making parts based on blueprints or 3D models for specific aircraft or spacecraft. |
| Prototype Machining | Building test parts to check size, fit, or function before large production. |
| Mass Production | Making many identical parts in large quantities for full aircraft assembly. |
| Precision Machining | Creating parts with very tight tolerances and high accuracy. |
| CNC Programming | Writing computer code to control machines for perfect cuts and shapes. |
| Material Selection Help | Helping choose the right metal or composite based on the part’s purpose. |
| Heat Treatment | Strengthening parts by heating and cooling them to exact levels. |
| Surface Finishing | Polishing or coating parts to protect them or improve how they fit and move. |
| Quality Inspection | Checking each part carefully to make sure it meets safety and size rules. |
| Assembly Services | Putting together machined parts to form larger components. |
Parts Made with Aerospace Machining
A wide range of parts are made using aerospace machining:
- Engine components: turbines, blades, shafts, housings.
- Landing gear: rods, brackets, wheel hubs.
- Fuselage structures: frames, support ribs, panels.
- Wing components: spars, hinges, flaps.
- Cabin interiors: seat frames, mountings, light brackets.
- Spacecraft parts: satellite arms, antenna mounts, fuel components.
Each part must meet high safety and quality rules. Some parts must also survive in space or at high altitudes.
Aerospace Machining vs. Regular Machining
Aerospace machining is more advanced than regular machining because it must meet stricter rules and higher quality demands. Here are the key differences between the two:
| Feature | Aerospace Machining | Regular Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerances | Very tight | More flexible |
| Materials | Titanium, aluminum, alloys | Steel, aluminum, plastics |
| Quality checks | Strict and frequent | Basic or less strict |
| Cost per part | Higher due to tools and time | Lower |
| Use cases | Planes, rockets, satellites | Cars, tools, furniture |
Challenges in Aerospace Machining
This type of machining is not easy. Some common challenges include:
- Tight tolerances: Very little room for error.
- Hard materials: Some metals are tough to cut.
- Complex shapes: Some parts are hard to machine.
- Long job times: Precision work can take hours or days.
- High cost of mistakes: If a part fails, it can be dangerous and expensive.
Skilled workers, strong tools, and good planning are needed to solve these problems.
Final Thoughts
Aerospace machining is more than just cutting metal. It is a detailed, careful process that helps make air and space travel safe.
From engine parts to tiny bolts, everything must be made the right way.
This kind of work takes strong machines, smart software, and skilled people. It also takes a deep focus on safety, quality, and detail.
For anyone interested in aircraft or space systems, learning about aerospace machining is a good place to start.
It shows how careful work on the ground helps people and machines reach the sky, and even beyond.