Ready to learn about one of the most visually striking galaxies visible from Earth tonight? The black eye galaxy stands out among thousands of celestial objects due to its distinctive dark dust lane appearance.
Located relatively close in cosmic terms, this galaxy offers amateur astronomers a rewarding target during spring observing sessions.
Messier 64 has interested astronomers since its initial observation centuries ago with the simple telescopes available then.
This article helps you observe the unique characteristics and offers tips for this remarkable deep-sky object overhead.
What is the Black Eye Galaxy?
It is officially designated Messier 64 or M64, a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Coma Berenices.
This galaxy spans approximately 70,000 light-years across, making it roughly half the size of our Milky Way.
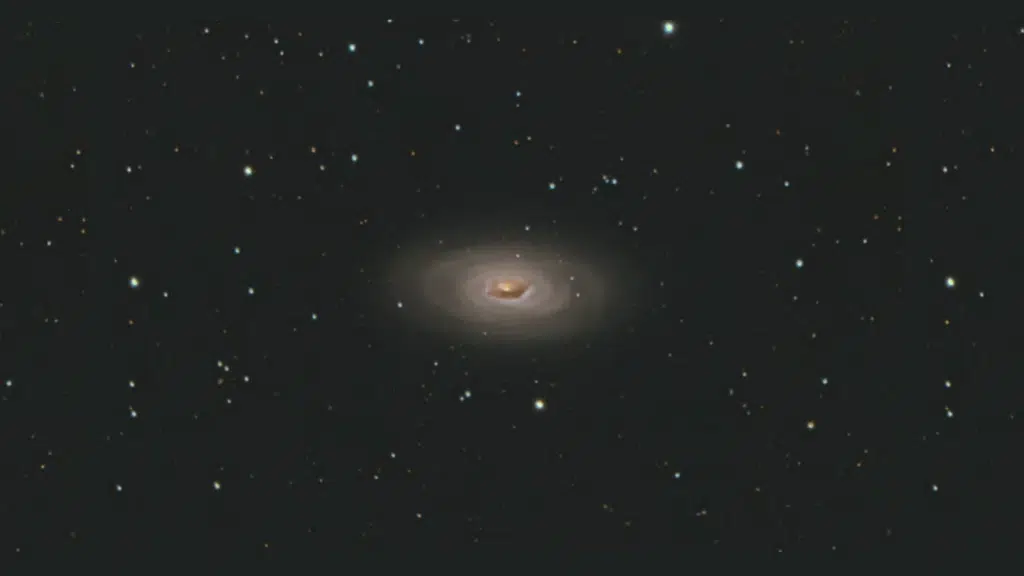
The defining feature is a spectacular dark dust lane on one side of the bright galactic nucleus. This absorption band consists of dense clouds of dust and gas that block light from stars behind it.
Interestingly, the outer regions of the galaxy rotate in the opposite direction from the inner regions, a rare phenomenon.
Scientists believe this counter-rotation resulted from a collision with a smaller galaxy millions of years ago.
Astrophotography of the Messier 64
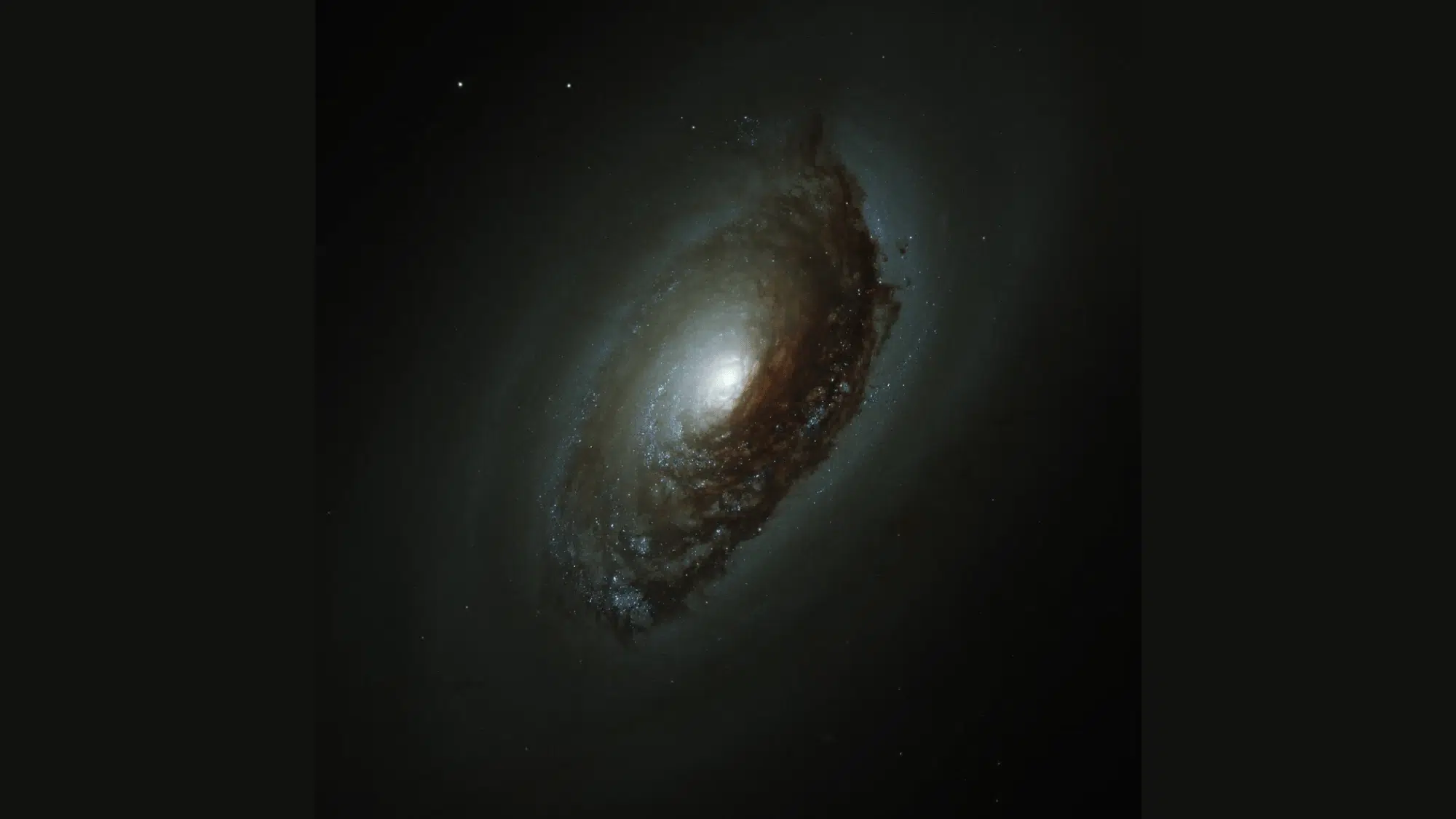

Image Source: Reddit
Capturing the black eye galaxy through astrophotography requires moderate equipment and proper imaging techniques for the best results.
A telescope with an aperture of at least 6 inches, paired with a sensitive camera, reveals the dark dust lane.
Long exposure times ranging from several minutes to hours bring out faint details in the galaxy’s spiral arms.
Combining multiple exposures through image stacking software reduces noise and enhances the contrast of the dust band.
Light pollution filters help urban photographers capture this target despite bright city skies interfering with observations.
How to Find Messier 64
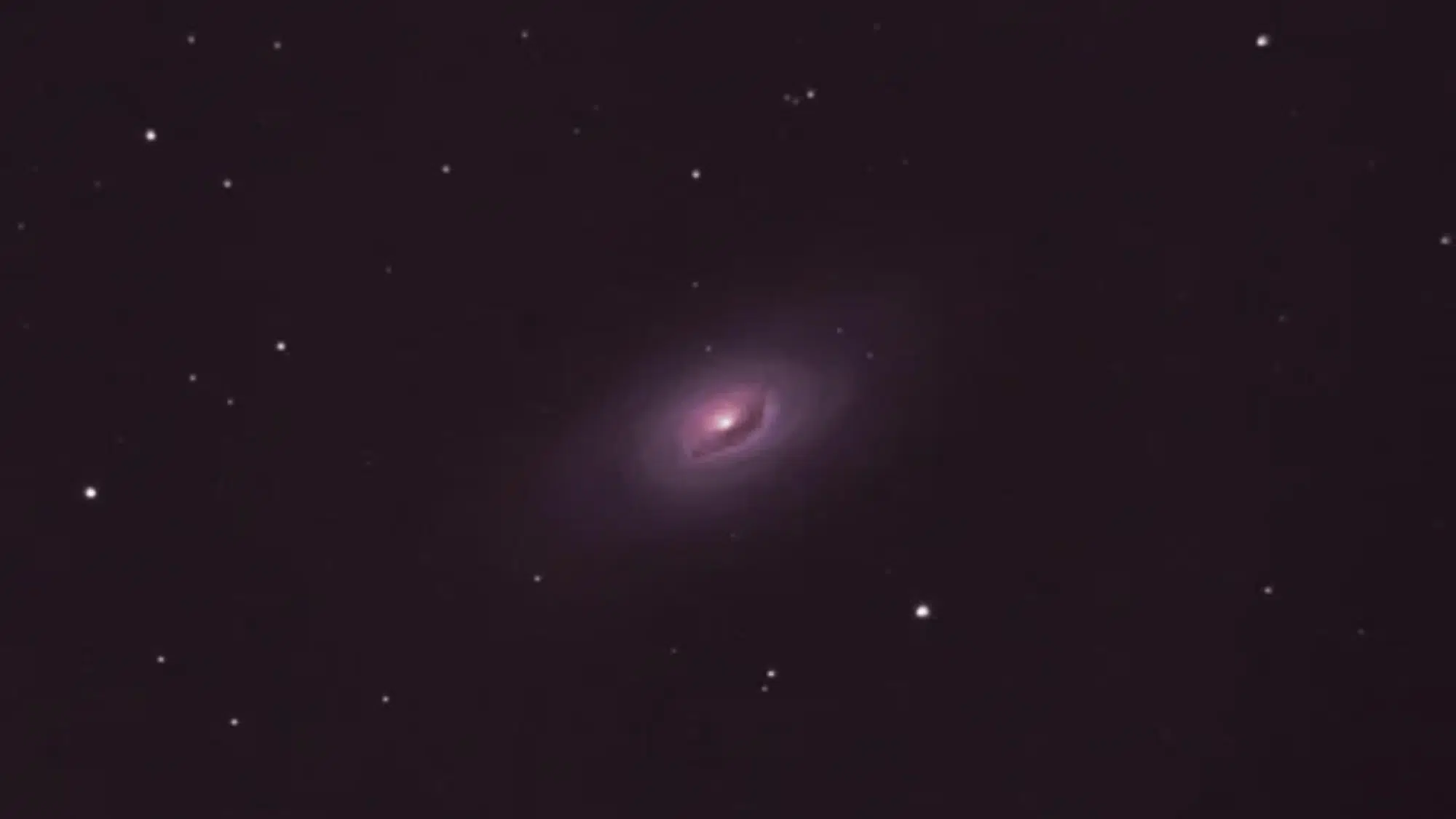

Image Source: Reddit
Locating the black eye galaxy requires understanding its position, brightness, and surrounding reference points for successful observation sessions tonight.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Located in Coma Berenices, northeast of the bright star Arcturus in the Boötes constellation. |
| Object Type | Spiral galaxy (Type Sb) with a prominent dust lane |
| Distance | Approximately 17 million light-years from Earth in a relatively nearby cosmic neighborhood. |
| Magnitude | Visual magnitude of 9.4, making it visible through small telescopes under dark skies. |
| Discovered | Found by Edward Pigott in March 1779, independently founded by Johann Bode weeks later. |
Understanding the Visual Features of the Messier 64
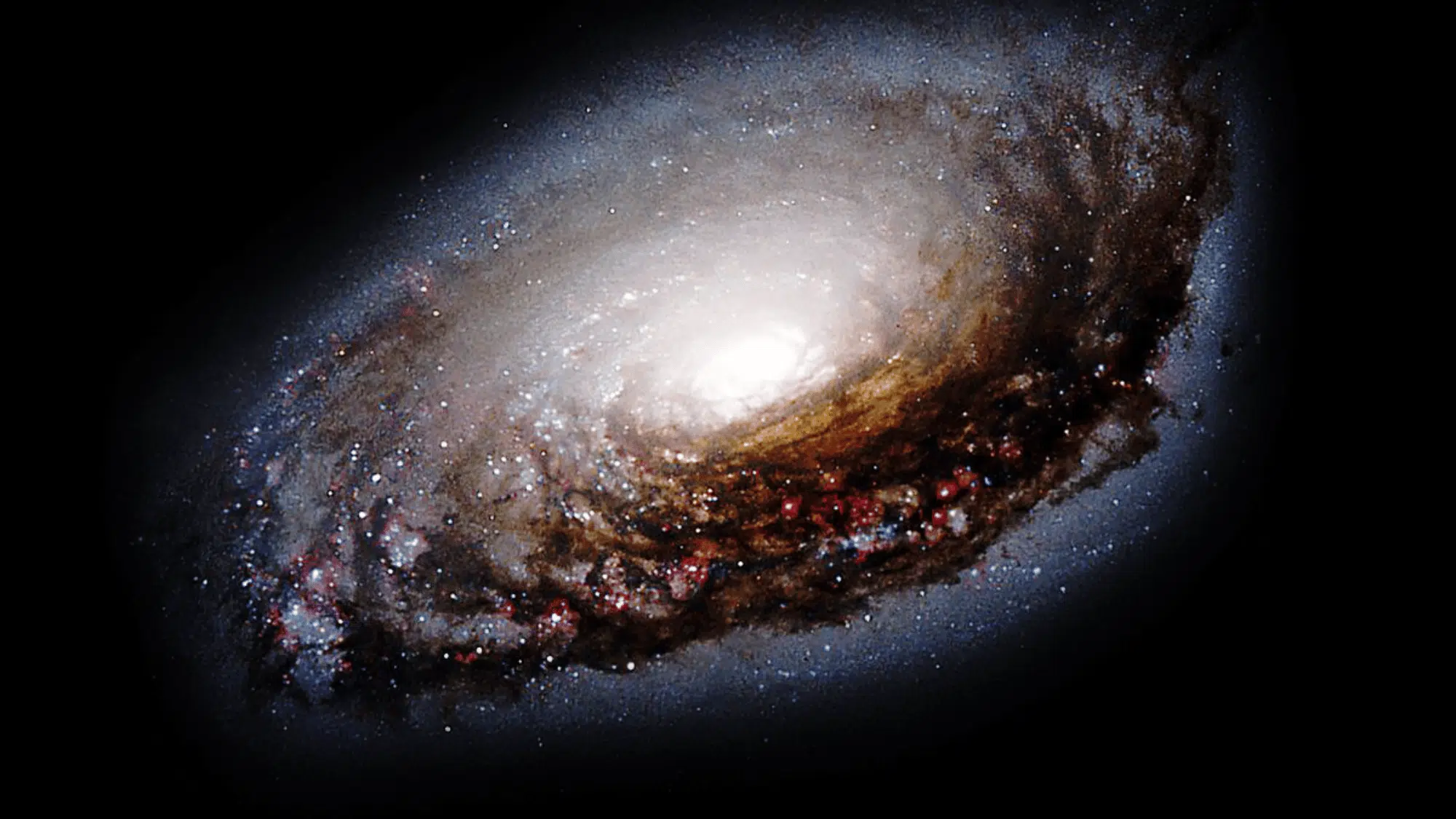

Image Source: Wikipedia Commons
The black eye galaxy displays several distinctive characteristics that make it unique and fascinating for both visual observers and astrophotographers.
- Dark dust lane: A Prominent band of obscuring material creates the distinctive bruised eye appearance visible in images.
- Bright nucleus: Central core shines intensely, providing strong contrast against the dark absorption feature nearby.
- Spiral structure: Arms wind outward from the center, containing billions of stars, though fainter than the nucleus.
- Counter-rotation: Outer regions rotate opposite direction from the inner galaxy, unique among observable spiral galaxies.
- Blue star clusters: Young, hot stars appear in regions where gas compression triggers new star formation.
- Extended halo: Faint outer envelope surrounds the main visible disk, detectable only in long exposure photographs.
Best Time and Conditions to View M64
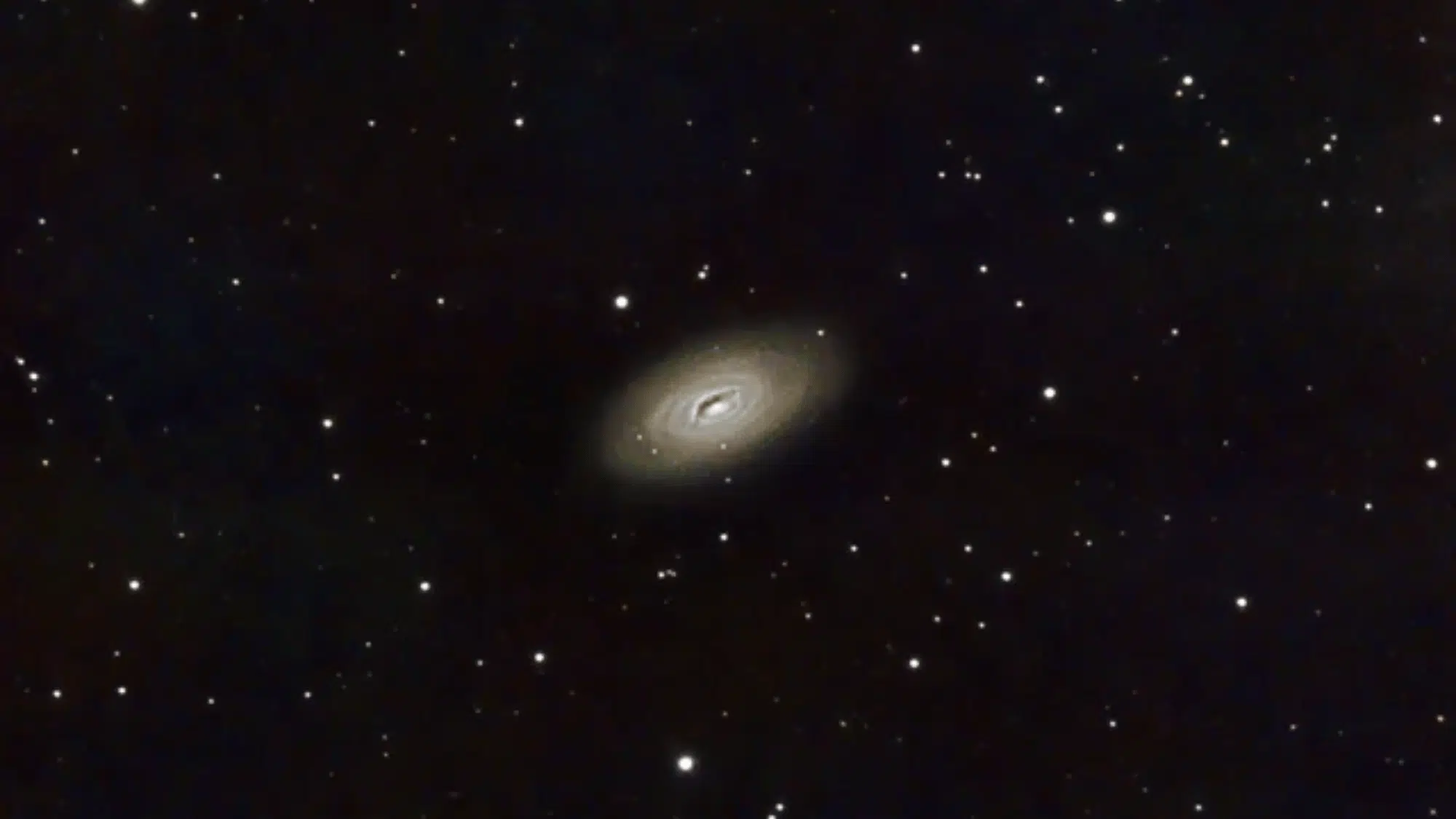

Image Source: Reddit
The M64 becomes visible during specific times and conditions that maximize your chances of successful observation attempts.
Clear, moonless nights provide optimal conditions since M64’s relatively faint magnitude requires dark skies for detection. Here are the ideal viewing parameters for observing this galaxy:
- Season and time: March through May, between 9 PM and midnight when the constellation sits high overhead.
- Moon phase: New moon or thin crescent phases when lunar brightness doesn’t wash out faint details.
- Sky conditions: Clear, transparent skies away from city lights with minimal atmospheric haze or moisture.
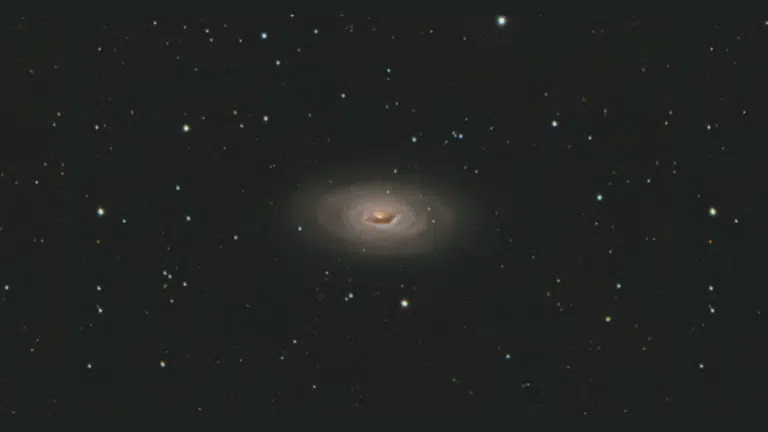
Why Astronomers Call it the Evil Eye Galaxy
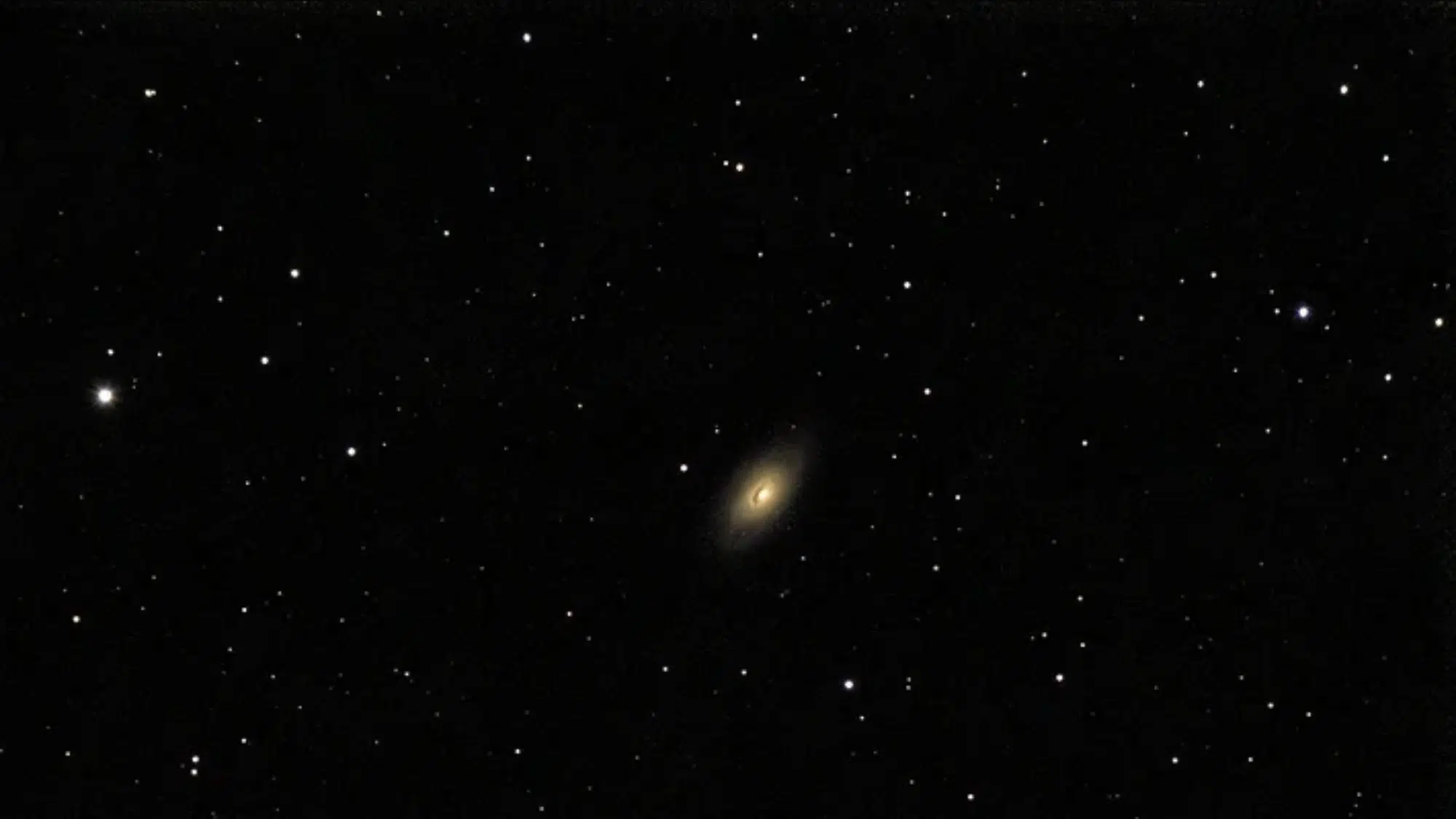

Image Source: Reddit
Some astronomers refer to the black eye galaxy as the “Evil Eye” galaxy due to its menacing appearance in photographs.
The dark dust band combined with the bright nucleus creates an intimidating, watchful expression that resembles a malevolent stare.
This alternative nickname emphasizes the dramatic, somewhat unsettling visual impression the galaxy makes on observers viewing detailed images.
The contrast between light and shadow gives it an almost supernatural quality that captured imaginations throughout history.
While “black eye” remains the more common designation, “evil eye” appears in older astronomical literature and casual references.
Conclusion
The Black Eye Galaxy (Messier 64) stands as a stunning reminder of the universe’s artistry and complexity.
Beyond its striking appearance, it tells a story of cosmic collisions, swirling dust, and the endless cycles of creation that shape galaxies across time.
For amateur astronomers, observing M64 offers more than just a visual treat; it’s a glimpse into the dynamic processes that govern the cosmos.
Every view reveals something new, from its glowing heart to the mysterious shadows that earned it its name.
Captured through a telescope or admired in images, the Black Eye Galaxy continues to inspire awe and curiosity among all who look skyward.