Long before powerful telescopes could explore the skies, people often wondered what filled the dark spaces between the planets.
Our solar system holds many secrets, and one of the most interesting is a region filled with rocky objects floating in space.
If you’ve ever asked yourself where is the asteroid belt located, you’re not alone. Understanding its position helps us learn about our cosmic neighborhood and how everything in space fits together.
Let’s learn about this amazing region and disclose why its position matters so much to scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
What is the Asteroid Belt?
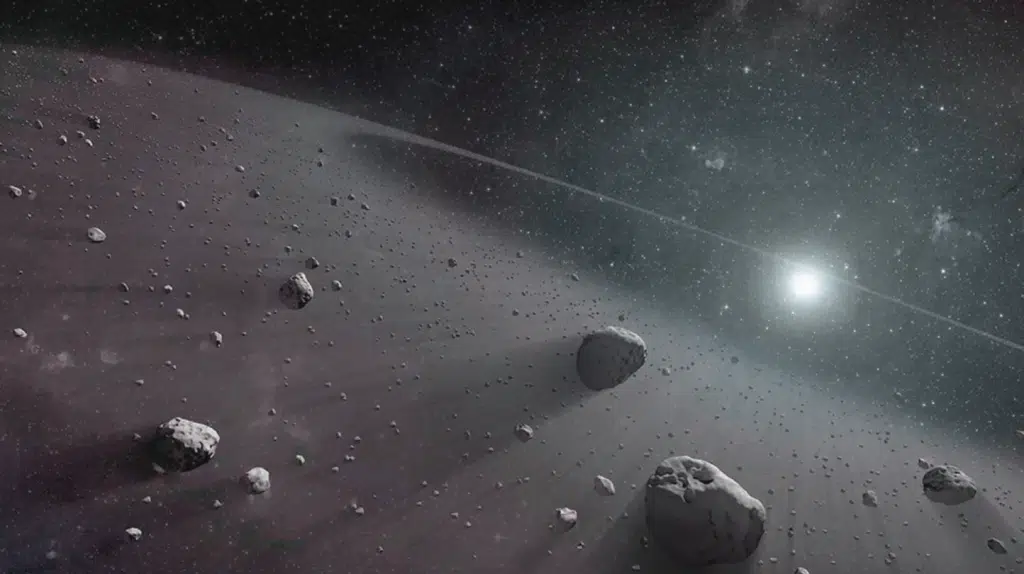
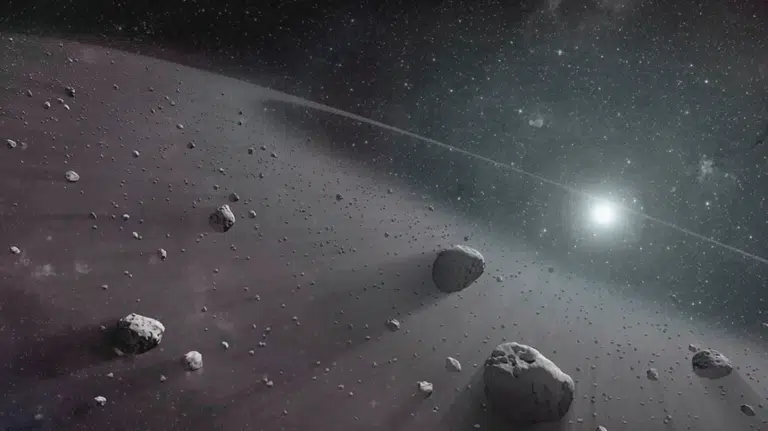
The asteroid belt is a wide region in our solar system filled with rocky objects called asteroids.
They range in size from tiny pebbles to large worlds hundreds of miles across and are made mostly of rock, metal, and dust, leftovers from when the solar system first formed.
Because these space rocks have changed very little over time, studying them helps scientists understand how planets and moons began.
The discovery of the asteroid belt began in 1801, when Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi found the first asteroid, Ceres, orbiting in a region later identified as the asteroid belt.
As more were discovered, astronomers realized they had found an entire region of space, the asteroid belt. Ceres is still the largest object there and is now classified as a dwarf planet.
Exact Location of the Asteroid Belt in the Solar System

Now that we know what it is and how it was discovered, let’s see exactly where the asteroid belt is located.
1. Distance from the Sun
The asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter, forming a natural border between the inner and outer planets.
It begins about 2.1 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun and stretches to around 3.3 AU.
(One AU is the distance from the Earth to the Sun, about 93 million miles.)
So, the asteroid belt sits roughly two to three times farther from the Sun than Earth does. Even though that’s far away, scientists can observe it using telescopes and spacecraft.
2. Movement and Distribution of Asteroids
Millions of asteroids travel around the Sun within this region. They move in stable orbits, all circling the Sun in the same direction as the planets.
Although it may sound crowded, there’s actually a lot of empty space between them, so much that a spacecraft could pass through the belt safely.
Collisions are rare, and most asteroids have been traveling in these same paths for billions of years.
3. The Belt’s Role in the Solar System
The asteroid belt acts like a dividing line between two very different parts of our solar system.
- Inside the belt are the small, rocky planets like Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
- Beyond it lie the massive gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn.
This placement helps scientists understand how gravity and distance shaped the planets’ formation.
It also shows how Jupiter’s strong pull stopped these rocks from joining together to form another planet.
Major Regions within the Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is not just one uniform area of space. It contains different zones and sections, each with its own special characteristics:
| Region / Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Inner Region | Closest to Mars, it contains fewer but denser asteroids. |
| Middle Region | The busiest zone, home to large asteroids like Ceres and Vesta. |
| Outer Region | Extends toward Jupiter and has more distant, darker asteroids. |
| Kirkwood Gaps | Empty zones created by Jupiter’s gravity divide the belt into sections. |
| Asteroid Groups | Clusters like the Hungaria, Cybele, and Hilda families with shared orbits. |
| Compositional Types | Asteroids range from rocky (S-type) to carbon-rich (C-type) materials. |
How the Asteroid Belt Looks in Space

If you could look down on our solar system from above, the asteroid belt would appear as a thin, glowing ring circling the Sun.
Each asteroid moves quietly in its orbit, almost like a slow, graceful dance through space.
Some reflect sunlight and appear shiny because they’re metallic, while others look darker and duller due to their rocky surfaces.
Despite how movies portray it, the asteroid belt is mostly empty and peaceful, with vast distances separating each asteroid.
It’s not a chaotic danger zone; it’s a calm, organized band of space rocks tracing beautiful paths between the two planets.
How Scientists Study the Asteroid Belt’s Location
Scientists have developed many ways to understand the asteroid belt’s position. These methods help them map where asteroids are located in our solar system:
- Ground Telescopes: Scientists use large telescopes on Earth to watch and follow asteroids as they move around the Sun.
- Space Telescopes: Tools like Hubble give clearer pictures of asteroids because they work above the air surrounding our planet.
- Spacecraft Missions: Space agencies send robots through the belt to gather information and take pictures up close of asteroids.
- Computer Models: Researchers build computer programs to guess where asteroids will go and how gravity pulls on them constantly.
- Radar Technology: Special radio signals bounce off asteroids to measure how far away they are and how fast they move.
Myths About the Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is often misunderstood due to movie portrayals and common myths. The table below clears up some of the most frequent misconceptions:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| The asteroid belt is packed with rocks sitting close together. | The belt has vast empty spaces between asteroids, a spaceship could pass through it without hitting anything. |
| Spaceships must constantly dodge asteroids like in movies. | Asteroids are so far apart that seeing one nearby during travel would be rare. |
| The asteroid belt came from a planet that exploded. | The rocks never formed into a planet. Jupiter’s strong gravity prevented them from joining together. |
Conclusion
Now you know exactly where the asteroid belt is located in our solar system. This amazing ring of rocky objects sits between Mars and Jupiter, creating a natural boundary in space.
The asteroid belt’s location helps scientists understand how our solar system formed millions of years ago.
Space exploration continues to reveal new discoveries about this interesting region every day.
Want to learn more exciting facts about our solar system?
Keep reading our blogs for more amazing space topics that will spark your curiosity and expand your knowledge about the universe around us.