Choosing between a refractor and vs reflector telescope can be confusing for people just starting with astronomy.
Both types help stargazers see planets, stars, and other space objects, but they work in different ways.
Refractor telescopes use lenses to gather light, while reflector telescopes use mirrors instead. Each design has benefits and drawbacks that matter for different types of observation.
This blog explains both types in simple terms, allowing anyone to make a smart telescope choice for their stargazing
What is a Refractor Telescope?
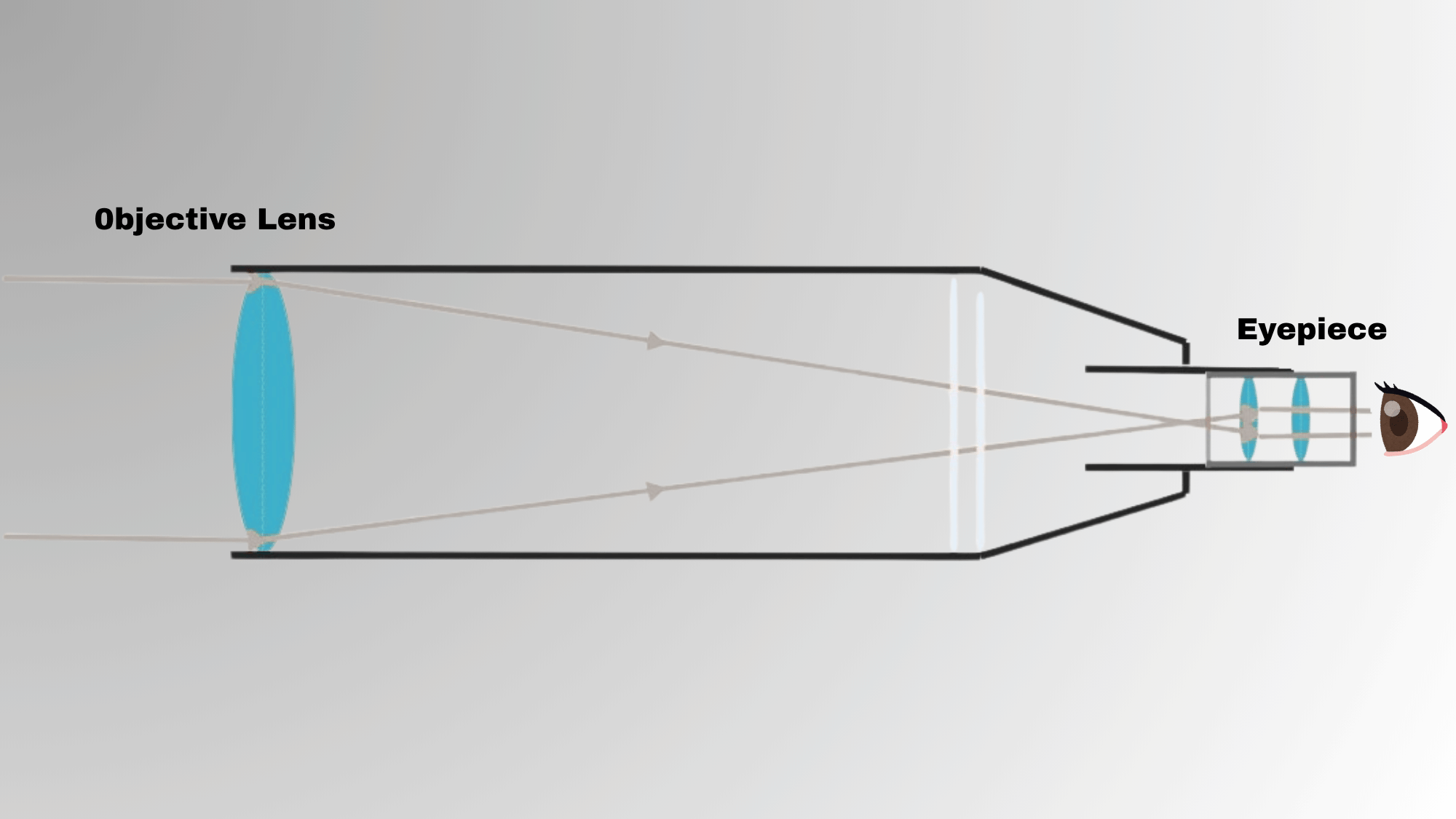
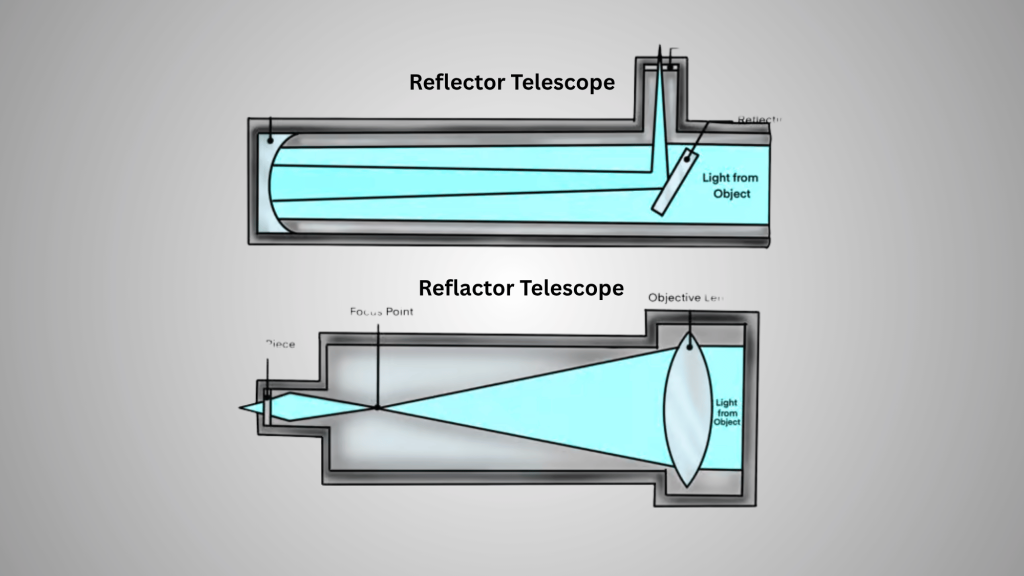
A refractor telescope uses lenses to collect and focus light from space objects. The main lens at the front of the tube gathers light and bends it toward the eyepiece, through which people look. Most refractors contain two lenses:
- The larger one is called the objective lens, which focuses incoming light inside the tube.
- The smaller one is called the eyepiece lens, which focuses the light for viewing.
Refractor telescopes produce very sharp, clear images with excellent contrast that make planets and stars look crisp. They work especially well for viewing bright objects like the moon, planets, and double stars.
When comparing refractor vs reflector telescope options, refractors need less maintenance because the lenses stay protected inside sealed tubes.
Optical Challenges: Chromatic Aberration in Refractors
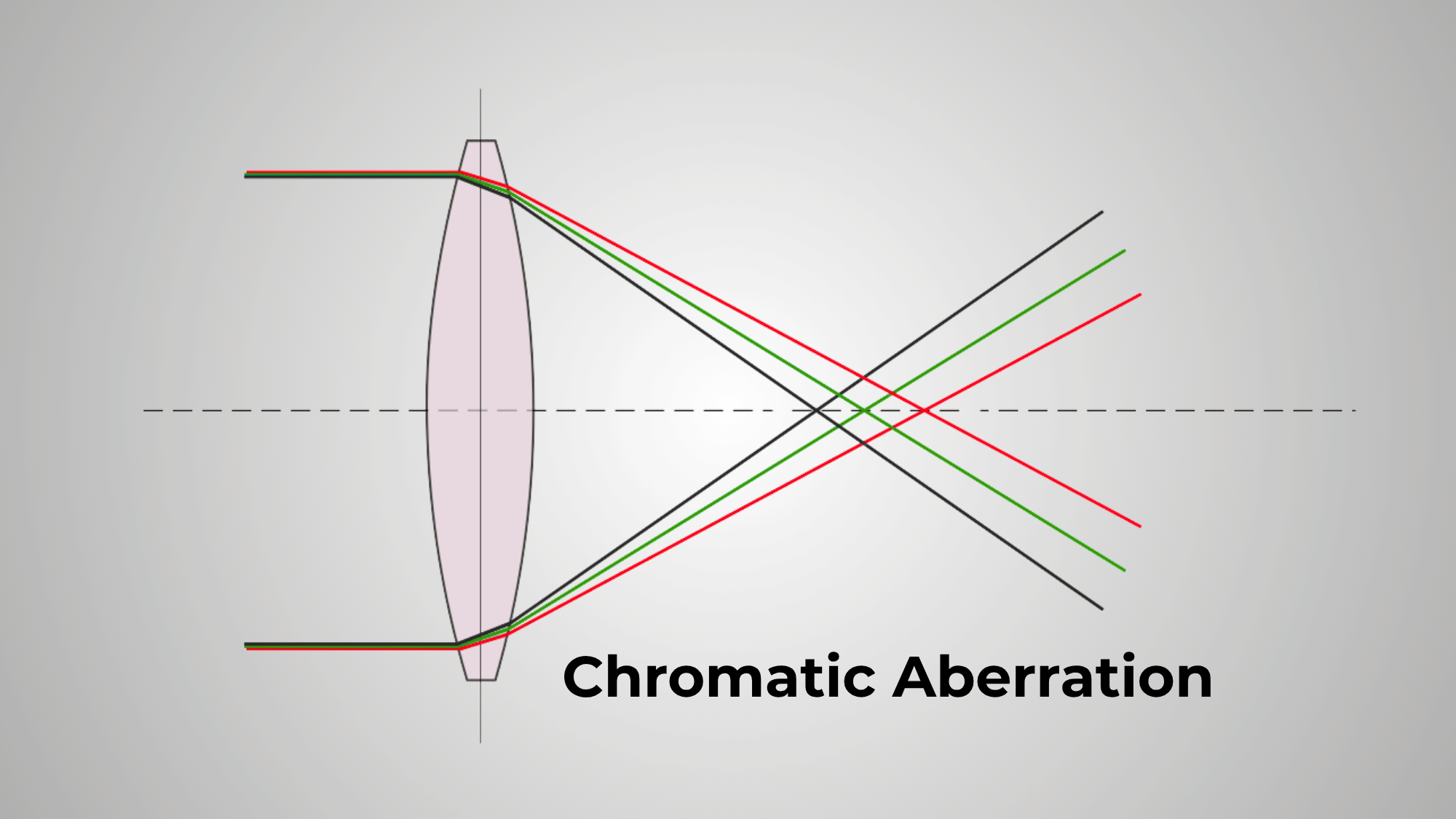
Chromatic aberration is a common optical issue in refractor telescopes where different wavelengths of light fail to focus at the same point, creating colored halos around bright objects like stars and planets.
This occurs because the single lens in achromatic refractors bends blue and red light differently.
Budget refractors often display noticeable purple or green fringing, particularly around the Moon and Venus.
Higher-quality apochromatic (APO) refractors use multiple lens elements with special glass to virtually eliminate this distortion, though at significantly higher cost.
What is a Reflector Telescope?
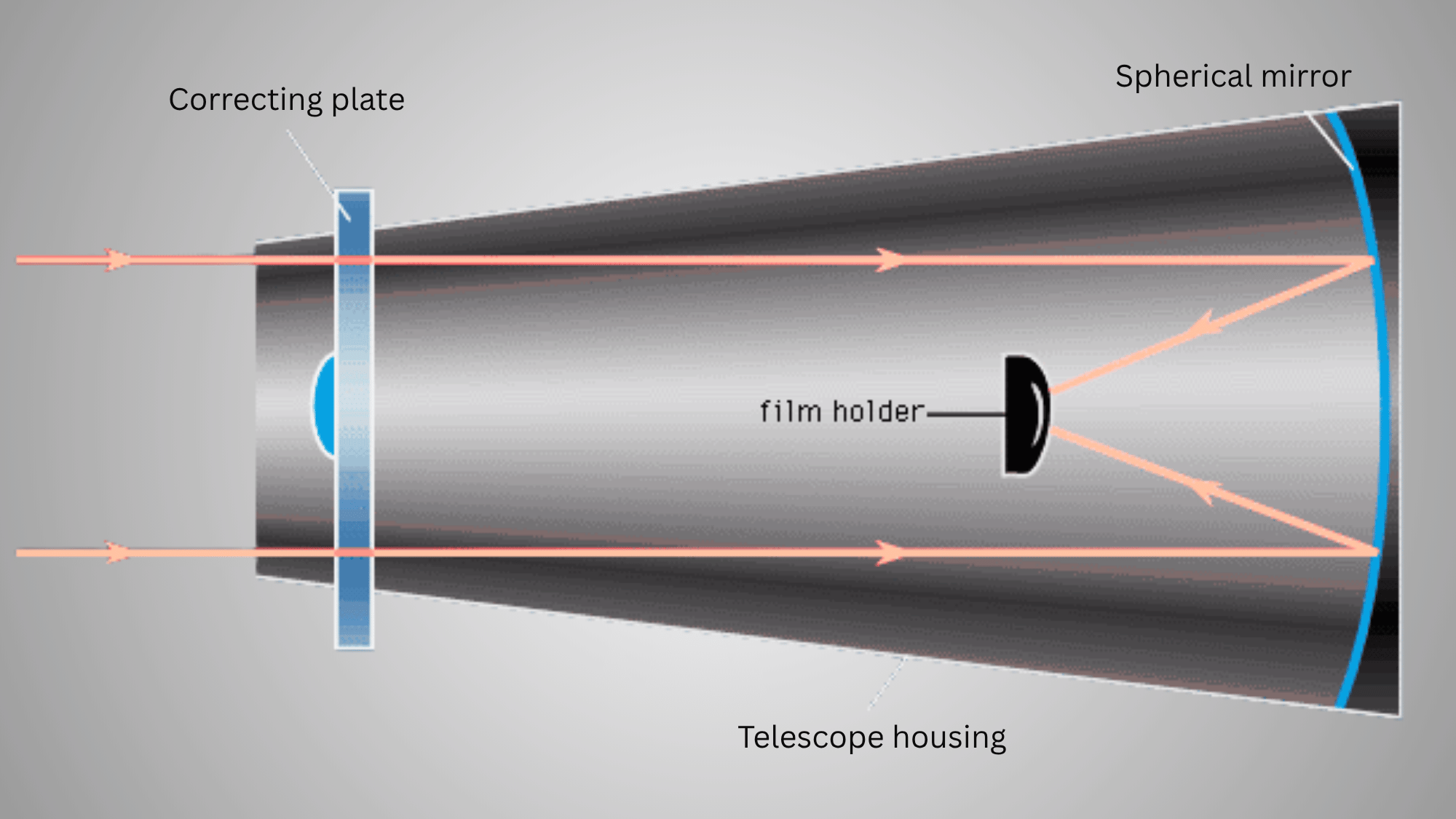
A reflector telescope uses mirrors instead of lenses to collect light and create images of space objects for observers to study. The large primary mirror at the bottom of the tube gathers light and reflects it to a smaller secondary mirror near the top.
This secondary mirror then reflects the light out to the side, where the eyepiece is located for viewing. Its contains multiple designs:
- Newtonian
- Dobsonian
- Richey-Chretién
- Dall-Kirkham and other Cassegrains
These are some designs of Reflector telescopes, which were invented and became popular today because they cost less than refractor telescopes of the same size.
These telescopes work great for viewing faint deep-space objects like nebulae and galaxies that need lots of light-gathering power.
Optical Considerations for Reflector Telescopes
Reflector telescopes utilize curved mirrors instead of lenses, offering exceptional light-gathering capabilities without chromatic aberration.
The primary parabolic mirror collects and focuses light onto a smaller secondary mirror, which redirects the image to the eyepiece.
This secondary mirror creates a central obstruction, typically 20-30% of the aperture diameter, slightly reducing contrast and creating characteristic diffraction spikes around bright stars.
Proper collimation, precise alignment of both mirrors, is critical for sharp images and requires regular adjustment using a collimation tool.
The open-tube design allows air currents to form inside, causing thermal disturbances that blur images until the telescope reaches ambient temperature.
Main Difference Between Refractor vs Reflector Telescopes

Refractor vs reflector telescope differ in design, performance, and purpose. Understanding their main differences helps buyers choose the right telescope.
| Feature | Refractor Telescope | Reflector Telescope |
|---|---|---|
| Light Collection | Uses lenses to bend and focus light | Uses mirrors to reflect and focus light. |
| Image Quality | Sharp, high-contrast images | Good images, but may have some distortion. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, sealed tube design | Higher maintenance, mirrors need cleaning. |
| Cost | More expensive per inch of aperture | Less expensive, better value for size. |
| Best Uses | Planets, moons, double stars, and terrestrial viewing | Deep-space objects, galaxies, nebulae. |
| Setup Time | Ready to use immediately | May need alignment and adjustment. |
| Size Limitations | Expensive to make large apertures | It can be built very large and affordably. |
Essential Accessories for Refractor and Reflector Telescopes
Maximize your telescope’s potential with essential accessories that enhance viewing quality and ensure optimal performance for both refractor and reflector systems.
- Quality Eyepieces: Invest in premium eyepieces with varying focal lengths (5mm-40mm) to achieve optimal magnification for planets, deep-sky objects across both telescope types.
- Barlow Lenses: Double or triple your magnification power cost-effectively by using 2x or 3x Barlow lenses that work universally with standard eyepiece sizes.
- Astronomical Filters: Enhance contrast and reveal hidden details using moon, planetary, and nebula filters that thread directly onto eyepiece barrels for specialized observations.
- Sturdy Mounts: Ensure stable viewing with equatorial or alt-azimuth mounts rated for your telescope’s weight, as longer focal lengths demand greater mounting precision.
- Collimation Tools: Maintain optimal performance with laser collimators or Cheshire eyepieces for reflector alignment, while refractors remain factory-aligned and maintenance-free.
- Maintenance Equipment: Preserve optical quality using lens cleaning supplies, dew shields, protective covers, and red flashlights to protect your investment and enhance observing sessions.
How Refractor and Reflector Telescopes Work
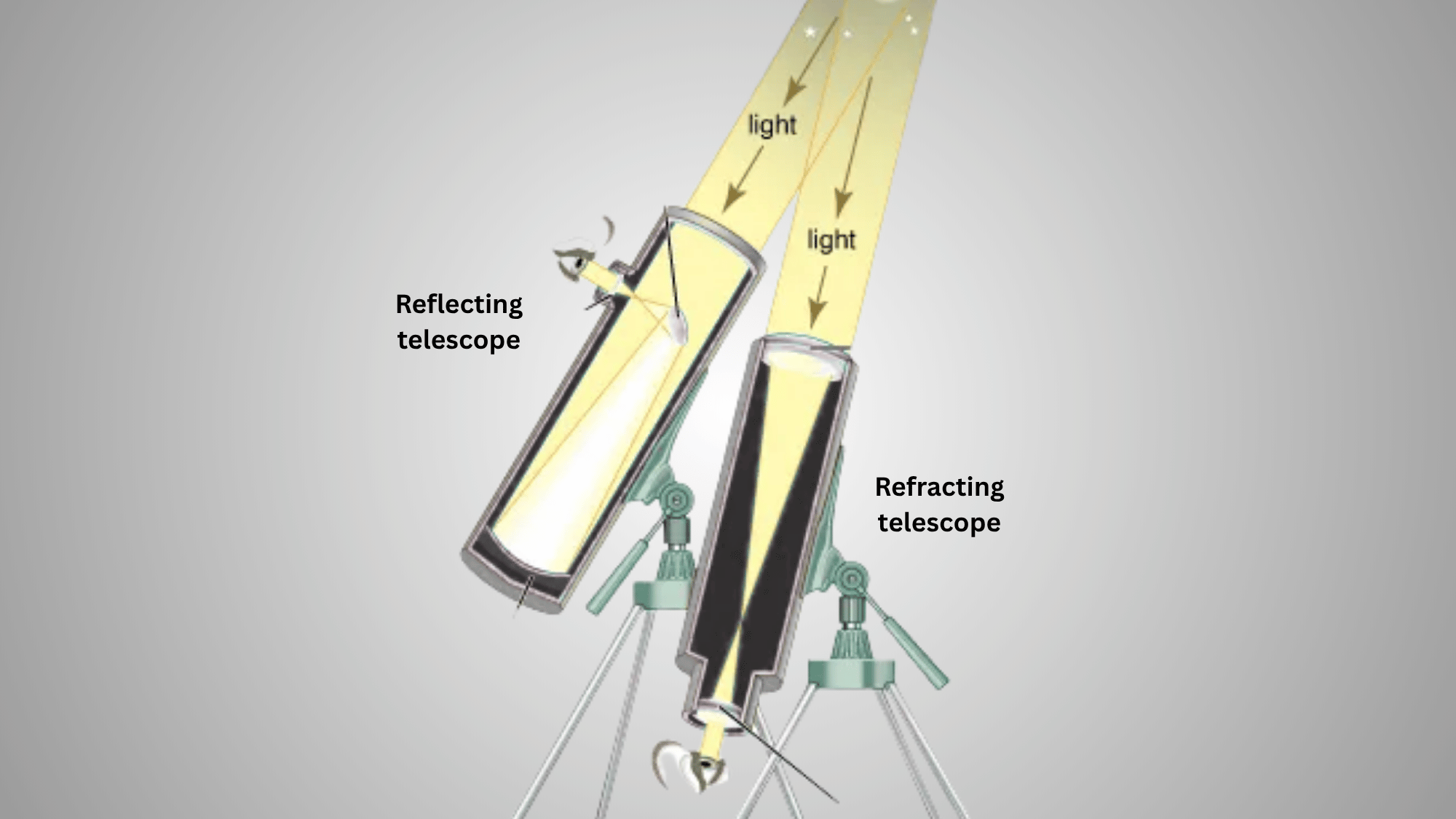
Refractor telescopes use a convex objective lens at the front to gather and bend incoming light, focusing it through a sealed tube to an eyepiece that magnifies the image.
Light travels in a straight path, creating sharp, high-contrast views with minimal maintenance required. The sealed design protects optics from dust and environmental factors.
Reflector telescopes employ curved mirrors instead of lenses. A concave primary mirror at the tube’s base collects light and reflects it forward to a smaller secondary mirror near the opening, which redirects the focused light to a side-mounted eyepiece.
This mirror-based system eliminates chromatic aberration and allows larger apertures at lower costs, though the open tube requires occasional mirror alignment and cleaning for optimal performance.
Application Suitability of Refractor vs Reflector Telescope
Reflector and refractor telescopes serve different astronomy needs based on their design strengths.
Each type excels at specific tasks, from planetary viewing to deep-sky observation. Choosing the right one depends on your goals.
When Refractor Telescopes Work Best
- Planetary and lunar observation benefits from refractors’ sharp, high-contrast images of Saturn’s rings, Jupiter’s bands, and moon craters.
- Their sealed tubes make them great for casual stargazing and viewing landscapes on Earth.
- Compact refractor models suit beginners and travelers who want simple, hassle-free telescope operation.
- Astrophotographers use refractors to capture pinpoint stars across wide fields of view.
When Reflector Telescopes Work Best
- Deep-sky astronomy relies on reflectors’ larger apertures to reveal faint galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters.
- Their superior light-gathering power attracts serious enthusiasts and astrophotographers seeking dim celestial objects.
- Reflectors excel at capturing faint deep-sky details that smaller telescopes cannot show.
- Observers who want to see distant, dim objects in space prefer reflectors over other telescope types.
Comparing Refractor vs Reflector Telescope for Deep-Sky Imaging

Deep-sky astrophotography demands different strengths from refractors and reflectors.
Apochromatic refractors produce stunning images with pinpoint stars across the entire field, free from chromatic aberration and coma.
Their shorter focal lengths capture wide nebulae fields, while sealed optics maintain collimation during long exposures. Large-aperture APO refractors become prohibitively expensive.
Reflector telescopes, particularly Newtonian astrographs, offer exceptional value with larger apertures that gather more light from faint galaxies and nebulae.
They excel at capturing dim deep-sky details but suffer from coma at field edges and require precise collimation before imaging sessions.
Conclusion
Refractor vs reflector telescope ultimately depends on your specific astronomy goals and budget.
Refractors excel at planetary observation and require minimal maintenance, whereas reflectors offer larger apertures at lower costs despite requiring occasional collimation.
Consider your primary targets, available budget, and willingness to perform maintenance.
Both designs can provide years of rewarding celestial experiences when matched to your interests. Ready to find the cosmos? Find your perfect telescope today!