Space travel has allowed people from many countries to take part in human travel beyond Earth. Over time, astronauts have come from different backgrounds, training programs, and generations.
Some began their space travel earlier in life than most, setting age-related records that remain unmatched today.
From government-led missions during the early space race to modern commercial flights, these young astronauts have shown skill, discipline, and determination.
The achievements of the youngest person in space among others highlight how space travel continues to grow through global cooperation.
The Youngest Astronauts in History of Space Travel
Reaching space at a young age is rare. The following astronauts set records by becoming some of the youngest people ever to travel beyond Earth.
1. Gherman Titov (Soviet Union, 1961)

Image Source: Wikipedia
Gherman Titov, from the Soviet Union, became the youngest astronaut in space at age 25. He flew on Vostok 2, just months after Yuri Gagarin’s first flight.
Titov spent more than 25 hours in orbit, testing how the human body handled longer space missions.
His success proved that people could live and work in orbit for extended periods. Titov’s flight remains a milestone in the history of human space exploration.
2. Valentina Tereshkova (Soviet Union, 1963)
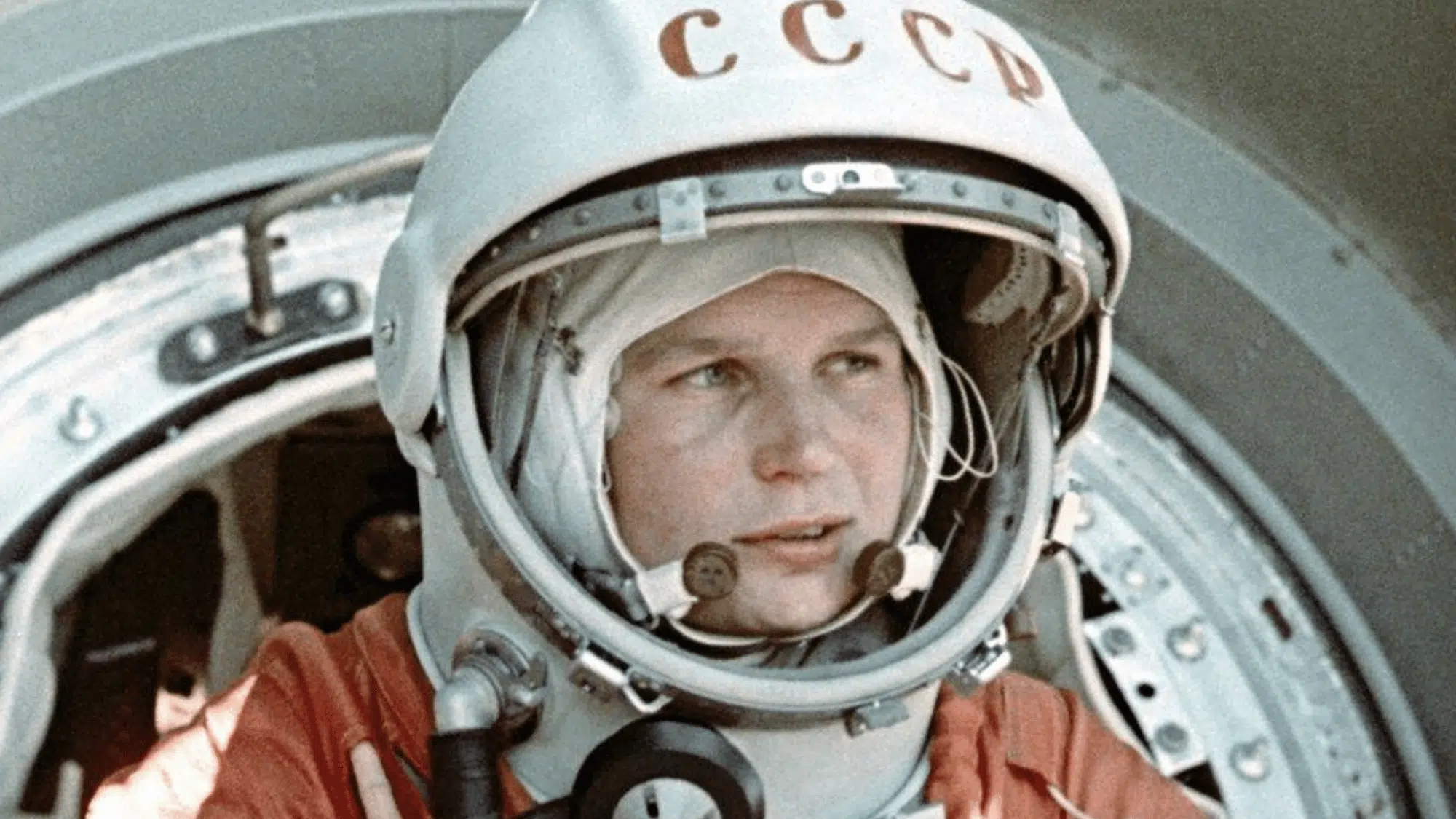

Image Source: BBC
Valentina Tereshkova, also from the Soviet Union, was 26 years old when she became the first woman in space.
She flew on Vostok 6, spending nearly three days in orbit. Her background was as a textile worker and skydiver before her selection as a cosmonaut.
Tereshkova’s mission showed that women could succeed in spaceflight and encouraged more diversity in astronaut programs around the world. She is still remembered as a historic pioneer.
3. Valery Bykovsky (Soviet Union, 1963)

Image Source: WIKIMEDIA COMMONS
Valery Bykovsky, from the Soviet Union, flew on Vostok 5 at the age of 28. His mission lasted almost five days, making it the longest solo spaceflight in history.
Bykovsky’s flight helped scientists study how long a person could remain in orbit without major health problems.
His relatively young age for such a long mission made his accomplishment even more important, setting the stage for future extended flights in space.
4. Boris Yegorov (Soviet Union, 1964)

Boris Yegorov, from the Soviet Union, was 30 years old when he became the first doctor to travel into space on the Voskhod 1 mission.
His job was to study how spaceflight affected the human body. The mission helped scientists understand how people could live and work safely in space.
Yegorov’s role made him one of the youngest and most important medical researchers in early space history.
5. Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez (Cuba, 1980)
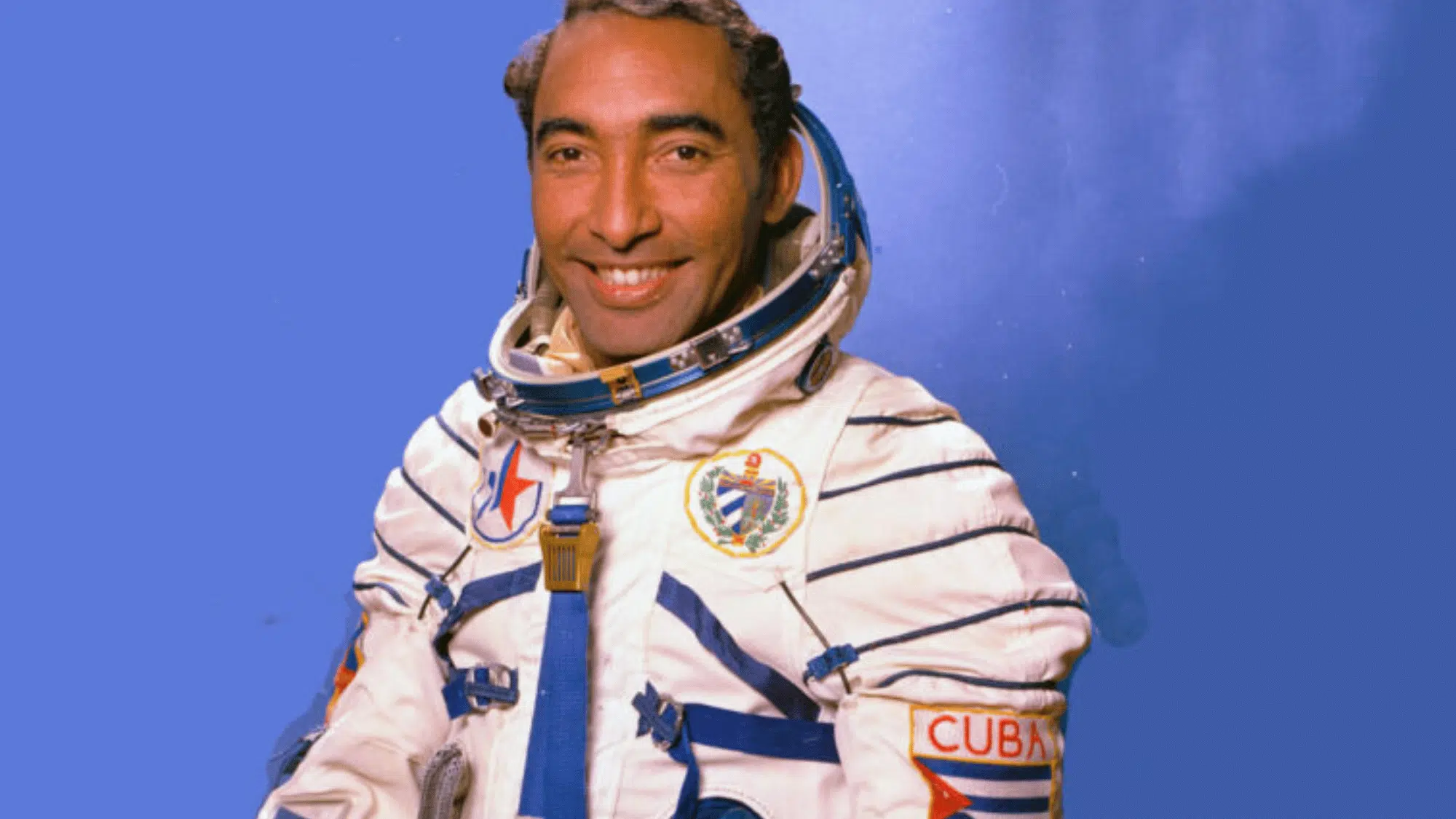

Image Source: Radio Enciclopedia
Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez, from Cuba, was 29 years old when he joined the Soviet Soyuz 38 mission.
He became the first Cuban, the first person from Latin America, and the first Black astronaut in space. His flight lasted about a week and included medical and scientific experiments.
Méndez’s mission was part of the Soviet Intercosmos program, which allowed partner countries to take part in space exploration and expand human spaceflight beyond the superpowers.
6. Dumitru Prunariu (Romania, 1981)
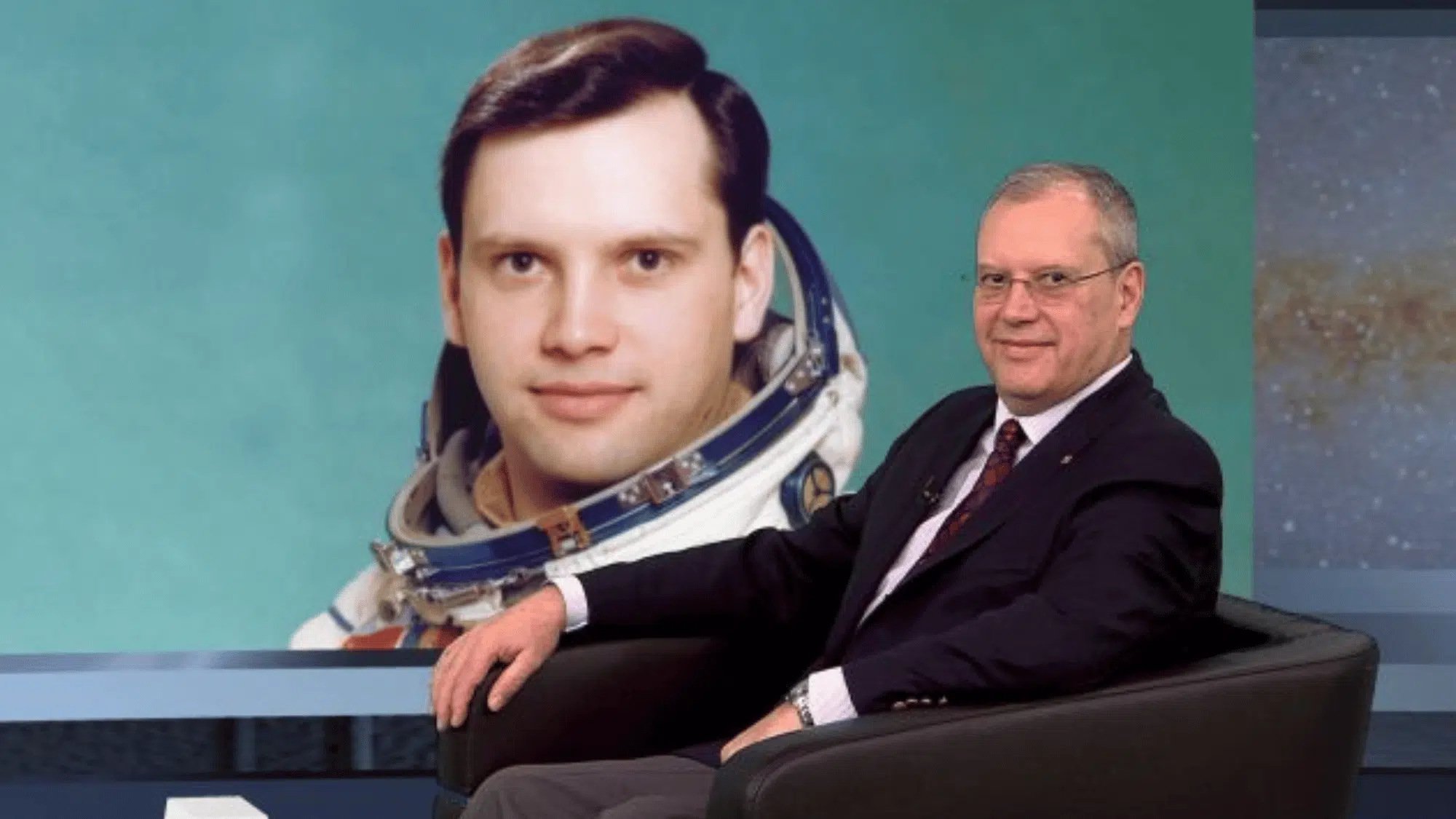

Image Source: Romania de nota 10
Dumitru Prunariu, from Romania, was 28 years old when he flew on the Soyuz 40 mission. He became the first Romanian in space and part of the Soviet Union’s Intercosmos program.
His mission lasted almost eight days and included scientific experiments focused on Earth observation and physics.
At a young age, Prunariu’s flight showed how international cooperation allowed more countries to take part in human space exploration.
7. Sultan bin Salman Al Saud (Saudi Arabia, 1985)
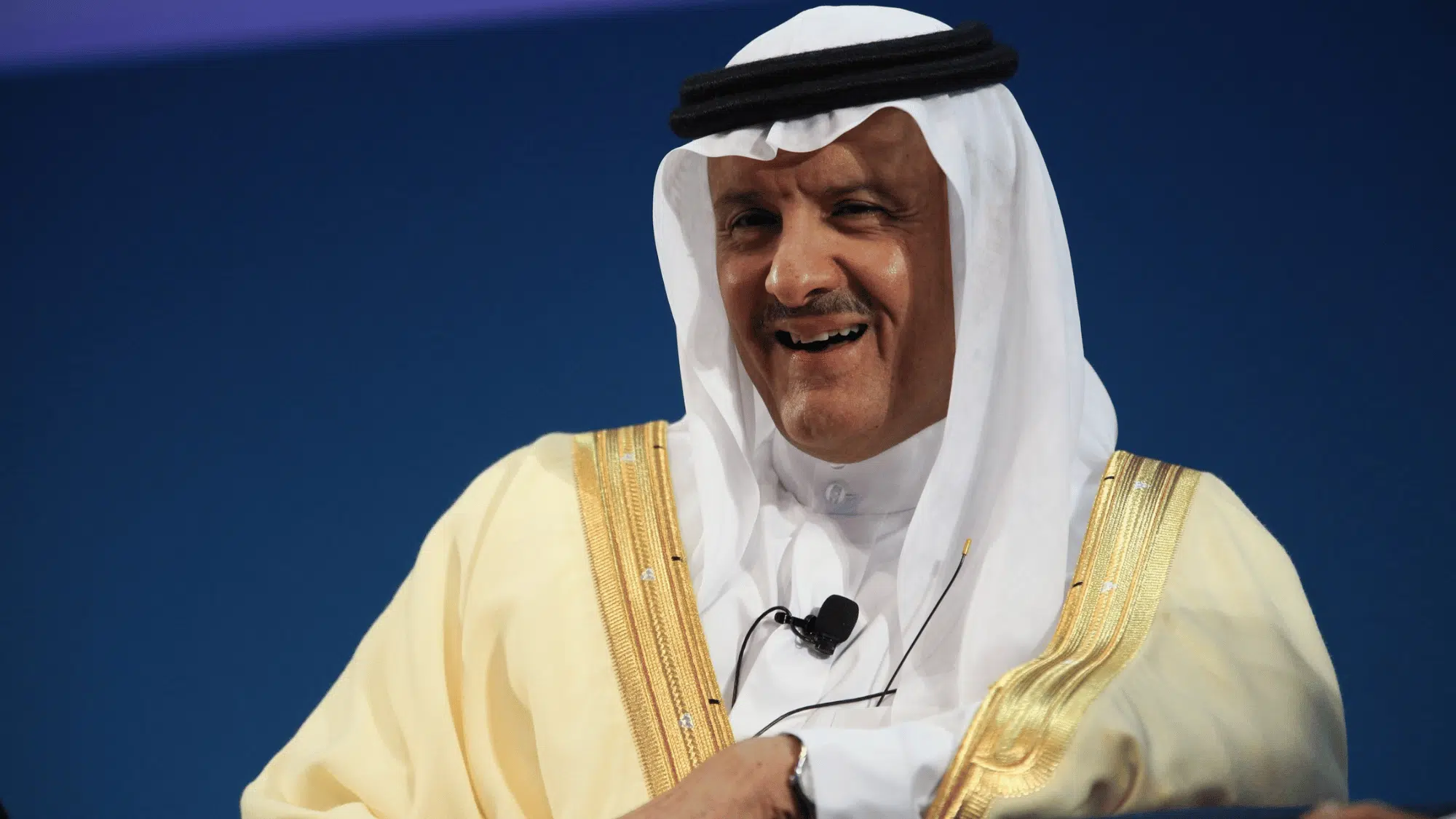

Image Source: Wikipedia
Sultan bin Salman Al Saud, from Saudi Arabia, was 28 years old when he flew aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-51-G.
He was the first Arab, the first Muslim, and one of the youngest astronauts of his time. His week-long mission involved deploying a communications satellite.
His participation marked a step forward for international cooperation in space and showed how space programs were reaching beyond the United States and the Soviet Union.
8. Abdul Ahad Momand (Afghanistan, 1988)
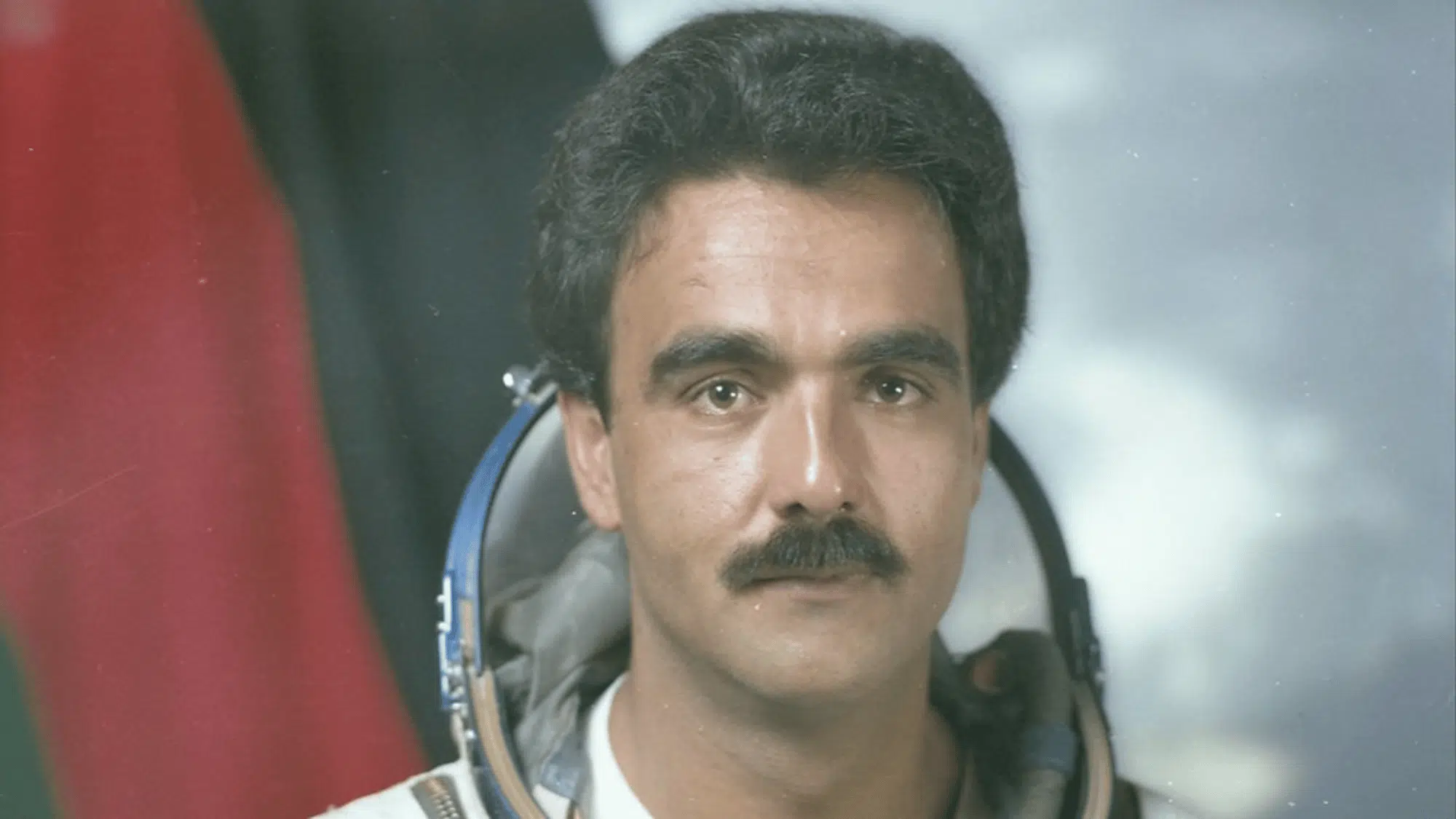

Image Source: BBC
Abdul Ahad Mohmand, from Afghanistan, was 29 years old when he traveled into space on the Soyuz TM-6 mission.
He became the first Afghan and one of the youngest astronauts of his era.
During his nine-day mission aboard the Mir space station, he carried out scientific experiments and represented his country in space for the first time.
His flight was another example of the Soviet Union’s effort to include more nations in space travel.
9. Helen Sharman (United Kingdom,1991)

Image Source: BBC
Helen Sharman, from the United Kingdom, was 27 years old when she flew on Soyuz TM-12.
She became the first British astronaut and the first woman to visit the Mir space station. Her mission lasted about eight days and included experiments in medicine and chemistry.
Sharman’s selection came through a national competition in the UK. At her young age, she became an important example of international participation in space programs.
10. Yuri Malenchenko (Russia, 1994)

Image Source: Wikipedia
Yuri Malenchenko, from Russia, was 32 years old when he commanded the Soyuz TM-19 mission to the Mir space station.
While older than some earlier astronauts, he was still among the younger cosmonauts to lead a mission.
He became the first person to marry in space, holding a satellite video wedding with Ekaterina Dmitrieva while he was on the ISS and she was in Texas, making it the world’s first long-distance wedding.
11. Sally Ride (United States, 1983)

Image Source: NASA
Sally Ride, from the United States, was 32 years old when she flew on the Space Shuttle Challenger, becoming the youngest American astronaut and the first American woman in space.
She worked as a mission specialist on STS-7. Her role included deploying satellites and operating the shuttle’s robotic arm.
Ride’s relatively young age at the time and groundbreaking role as a woman in space made her one of the most important figures in NASA history.
12. Oliver Daemen (Netherlands, 2021)

Image Source: Reuters
Oliver Daemen, from the Netherlands, became the youngest person in space at 18 years old when he joined Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket flight.
His suborbital mission lasted about 10 minutes but made history as part of the new wave of private space travel.
Daemen was not part of a traditional government astronaut program but represented the start of younger people entering space through commercial flights. His record is still the youngest to this day.
Modern Young Astronauts and Space Travelers
After the early space age, younger astronauts continued to make history through modern missions and private space programs.
- Hayley Arceneaux (United States, 2021): At age 29, she became the youngest American in space and the first astronaut with a prosthetic limb on SpaceX’s Inspiration4 mission.
- Christina Koch (United States, 2019): At 34, she set the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman at 328 days and joined the first all-woman spacewalk.
- Thomas Pesquet (France, 2016): At 38, he flew to the ISS as a flight engineer and later became station commander.
- Luca Parmitano (Italy, 2013): At 36, he became the first Italian to command the ISS and is known for handling a dangerous spacewalk emergency.
- Hazzaa Al Mansoori (United Arab Emirates, 2019): At 35, he became the first Emirati astronaut, spending eight days aboard the ISS.
Conclusion
The history of young astronauts shows how space travel has changed over time.
Their missions, regardless of the time period, helped expand scientific knowledge, inspire education, and increase interest in aerospace careers.
It is not just the youngest person in space; all these astronauts also showed that spaceflight is not limited to experience alone but also requires readiness and skill.
Their efforts continue to guide how future missions are planned and how younger generations view exploration beyond Earth.